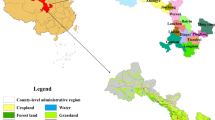
Abstract
Against the backdrop of China’s “double carbon” objective, the exploration of low-carbon land consolidation has become a prominent area of focus for enhancing the development of ecological civilization. In this study, three typical projects at different time points (2016, 2019, and 2022) in Wudi County were selected to measure the carbon effect of land consolidation from four perspectives: artificial and industrial materials, mechanical shift consumption, land use structure, and farmland ecosystem. Based on the calculation of carbon effect of land consolidation by using carbon emission coefficient method, the changes of land use structure and carbon storage of farmland ecosystem before and after land consolidation were corrected by using GIS tools and net ecosystem productivity (NEP) model based on remote sensing technology, and the carbon emission intensity of each land consolidation project was finally obtained. The study summarized the influencing factors of carbon emissions through the above analysis and uses the fuzzy interpretation structure (FISM) model to provide the hierarchy of influencing factors of carbon emissions, thus proposing a low-carbon promotion path for land consolidation. The findings of this study can serve as a useful reference for low-carbon land consolidation efforts. The results showed that (1) the first, second, and third projects emitted 6140.06 t, 1243.78 t, and 17,604.62 t of carbon, respectively. Among them, the largest contributors to these emissions were labor and industrial materials, followed by mechanical shift; land use structure and farmland ecosystem were the main sources of carbon sinks and have a positive impact on the carbon cycle. (2) The carbon emission intensity of project one, project two, and project three after standardization is 0.26, 0.49, and 0.25, respectively, which are all at a high level. (3) According to the FISM model categorized 15 low-carbon upgrading paths, it was recommended that the government take a leading role in Wudi County by develo** a scientific and rational construction plan. Additionally, efforts were made to actively protect farmland and forest land from destruction, reduce energy and material consumption, increase carbon storage in the farmland ecosystem, and promote low carbonization of land consolidation to the fullest extent possible.
Graphical Abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Abubakari Z, van der Molen P, Bennett RM, Kuusaana ED (2016) Land consolidation, customary lands, and Ghana’s Northern Savannah Ecological Zone: an evaluation of the possibilities and pitfalls. Land Use Policy 54:386–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2016.02.033
Adhikari K, Hartemink AE (2017) Soil organic carbon increases under intensive agriculture in the Central Sands, Wisconsin, USA. Geoderma Reg 10:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geodrs.2017.07.003n
Baumann M, Gasparri I, Piquer-Rodríguez M et al (2017) Carbon emissions from agricultural expansion and intensification in the Chaco. Glob Chang Biol 23:1902–1916. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13521
Cay T, Uyan M (2013) Evaluation of reallocation criteria in land consolidation studies using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Land Use Policy 30(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2012.04.023
Cheng Y (2020) Research on carbon effect calculation and decision optimization of land remediation projects. Jiangxi University of Finance and Economics. https://doi.org/10.27175/dcnki.gjxcu.2020.001450
Chong D, Wang N, Su S, Li L (2023) Global warming impact assessment of asphalt pavement by integrating temporal aspects: a dynamic life cycle assessment perspective. Transp Res Part D: Transp Environ 117:103663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2023.103663
Chuai X, Huang X, Wang W et al (2015) Land use, total carbon emissions change and low carbon land management in Coastal Jiangsu, China. J Clean Prod 103(15):77–86.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.03.046
Cui XL, Wei XQ, Liu W et al (2018) Spatial and temporal analysis of carbon sources and sinks through land use/cover changes in the Bei**g-Tian**-Hebei urban agglomeration region. Phys Chem Earth 110:61–70.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2018.10.001
Dong Y, Liu S, Wang J et al (2017) Assessment of risk and carbon sequestration function of land consolidation based on landscape pattern. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 33(7):246–253. https://doi.org/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.07.032
Ertunç E (2023) The effect of land consolidation projects on carbon footprint. Land 12(2):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/land.12020507
Forster EJ, Healey JR, Dymond C et al (2021) Commercial afforestation can deliver effective climate change mitigation under multiple decarbonisation pathways. Nat Commun 12(1):3831. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24084-x
Goh C, Junginger M, Potter L et al (2018) Identifying key factors for mobilising under-utilised low carbon land resources: a case study on Kalimantan. Land Use Policy 70:198–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.10.016
Gong J, Hu Z, Chen W et al (2017) Urban expansion dynamics and modes in metropolitan Guangzhou, China. Land Use Policy 72:100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.12.025
Guo B, ** X, Yang X et al (2015) Determining the effects of land consolidation on the multifunctionlity of the cropland production system in China using a SPA-fuzzy assessment model. Eur J Agron 63:12–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2014.11.002
Hao QT, Huang MX, Bao G (2011) Study on carbon emission calculation methods overview and its comparison. Chin J Environ Manag 4:51–55.https://doi.org/10.16868/j.cnki.1674-6252.2011.04.011
Huang XJ, Zhang XY, Lu XH et al (2021) Land development and utilization for carbon neutralization. J Nat Resour 36(12):2995–3006. https://doi.org/10.31497/zrzyxb.20211201
Huang X, ** X, Zhang X et al (2017) Emergy analysis of the impact of land remediation projects on farmland ecosystems. J China Agric Univ 22(04):47–58. https://doi.org/10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2017.04.06
Inceyol Y, Cay T (2022) Comparison of traditional method and genetic algorithm optimization in the land reallocation stage of land consolidation. Land Use Policy 115:105989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.105989
Janus J, Markuszewska I (2019) Forty years later: assessment of the long-lasting effectiveness of land consolidation projects. Land Use Policy 83:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.01.024A
Janus J, Ertunç E (2023) Impact of land consolidation on agricultural decarbonization: estimation of changes in carbon dioxide emissions due to farm transport. Sci Total Environ 873:162391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162391
Kaenchan P, Guinée J, Gheewala SH (2018) Assessment of ecosystem productivity damage due to land use. Sci Total Environ 621:1320–1329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.096
Kang T, Wang H, He Z, Liu Z, Ren Y, Zhao P (2023) The effects of urban land use on energy-related CO2 emissions in China. Sci Total Environ 870:161873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161873
Kim Y-N, Krasilnikova N, Choi Y-S, Yeo G-T (2023) Structural analysis of factors for revitalizing lena river logistics using ISM method. Asian J Shipp Logist 39(2):46–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajsl.2023.02.001
Koc I, Cay T, Babaoglu I (2022) A novel metaheuristic algorithm by efficient crossover operator for land readjustment. Expert Syst Appl 188:116082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.116082
Li H, ** X, Han B, Xu W, Zhou Y (2022a) The theoretical research and practical path of comprehensive land consolidation under the goal of ‘double carbon’. Geogr Res 41(12):3164–3182. https://doi.org/10.11821/dlyj020220208
Li M, Peng J, Lu Z, Zhu P et al (2023) Research progress on carbon sources and sinks of farmland ecosystems. Resour Environ Sustain 11:100099.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resenv.2022.100099
Li X, Hui N, Yang Y et al (2021) Short-term effects of land consolidation of dryland-to-paddy conversion on soil CO2 flux. J Environ Manage 292:112691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112691
Li Z, Sun ZY, Chen YB et al (2020) The net GHG emissions of the China Three Gorges Reservoir: I. Pre-impoundment GHG inventories and carbon balance. J Clean Prod 256:120653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120635
Lin Z, Wang P, Liu Q et al (2022) The spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of carbon storage in arable land and identification of carbon sink areas in the Huaihai Economic Zone from 2005 to 2020. J Agric Eng 38(19):259–268. https://doi.org/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.19.028
Liu XP, Ou JP, Chen YM et al (2019b) Scenario simulation of urban energy-related CO2 emissions by coupling the socio economic factors and spatial structures. Appl Energy 238:1163–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.01.173
Liu Y, Li J, Yang Y (2017) Strategic adjustment of land use policy under the economic transformation. Land Use Policy 74:5–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.07.005
Liu Y, Yang L, Li X et al (2022) Research on the path of China’s transformation and development under the goal of carbon neutrality. J Bei**g Univ Technol 24(04):27–36. https://doi.org/10.15918/j.jbitss1009-3370.2022.1604
Mainul Bari ABM, Siraj MT, Paul SK, Khan SA (2022) A hybrid multi-criteria decision-making approach for analysing operational hazards in heavy fuel oil-based power plants. Decis Anal J 3:100069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dajour.2022.100069
National Development and Reform Commission. Guidelines for compiling provincial greenhouse gas inventories[R/OL].(2011-05)[2022-03-22]. http://www.360doc.com/document/22/0506/16/79374256_ 1030046376.shtml.
Niroula GS, Thapa GB (2005) Impacts and causes of land fragmentation, and lessons learned from land consolidation in South Asia. Land Use Policy 22(4):358–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2004.10.001n
Obrist D, Pearson C, Webster J et al (2016) A synthesis of terrestrial mercury in the western United States: spatial distribution defined by land cover and plant productivity. Sci Total Environ 568:522–535. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.104
Post WM, Kwon KC (2000) Soil carbon sequestration and land-use change: processes and potential. Glob Chang Biol 6:317–327. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2000.00308.x
Potma Gonçalves DR, Carlos de MoraesSá J, Mishra U et al (2018) Soil carbon inventory to quantify the impact of land use change to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions and ecosystem services. Environ Pollut 243:940–952.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.07.068
Shan W, ** X, Yang X et al (2020a) A framework for assessing carbon effect of land consolidation with life cycle assessment: a case study in China. J Environ Manage 266:110557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110557
Sheng Y, Liu X, Zhang S et al (2020) Study on carbon benefit of land consolidation project in Shache County, **njiang. Northeast Agric Sci 45(01):119–123. https://doi.org/10.16423/j.cnki.1003-8701.2020.01.025
Wang J, Zhong L, Bai Z et al (2018) The impact of agricultural land consolidation on carbon storage and food production capacity. J Agric Eng 34(24):256–265. https://doi.org/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.24.031
Wang X, Lu Y, Chen C, Yi X, Cui H (2023) Total-factor energy efficiency of ten major global energy-consuming countries. J Environ Sci 137:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2023.02.031
Wang Y, Zhang H, Zhang C, Liu C (2021) Is ecological protection and restoration of full-array ecosystems conducive to the carbon balance? A case study of Hubei Province, China. Technol Forecast Soc Change 166:120578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120578
Wei CC, Ren SM, Yang PL et al (2021) Effects of irrigation methods and salinity on CO2 emissions from farmland soil during growth and fallow periods. Sci Total Environ 752:141639. https://doi.org/10.1016/lj.scitotenv.2020.141639
Wise M, Dooley J, Luckow P et al (2014) Agriculture, land use, energy and carbon emission impacts of global biofuel mandates to mid-century. Appl Energy 114(2):763–773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.08.042
Wu Y, Zhou Y, Guo Y, Wang L et al (2017a) The energy emission computing of land consolidation from the dual perspectives clustering method. Cluster Computing 20:979–987. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-017-0875-7
Wu Z, Yang K, Xue H, Zuo J, Li S (2022) Major barriers to information sharing in reverse logistics of construction and demolition waste. J Clean Prod 350:131331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131331
Yang W, Li X, Li W, Zhang Y, Zhang H, Ran Y (2022) Carbon effect calculation and upgrading strategy of agricultural land consolidation project in urban edge of Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Front Chem 10:1022644. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2022.1022644
Yi D, Ou M, Guo et al (2022) Research progress and trend of land use carbon emissions and low carbon optimization. Resour Sci 44(08):1545–1559. https://doi.org/10.18402/resci.2022.08.02
Zang Y, Yang Y, Liu YT et al (2021) Toward serving land consolidation on the table of sustainability: an overview of the research landscape and future directions. Land Use Policy 109:105669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105696
Zhang J, Bao T, Zhenghai LI et al (2016) Analysis of organic carbon sink increment and management in Uxin Banner, Inner Mongolia, China. Acta Ecol Sin 36(9):2552–2559. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201408051561
Zhang J, Chen H, Liu D et al (2022a) Study on the spatial and temporal differentiation and influencing factors of land use carbon emissions based on county scale. J Northwest Univ 52(01):21–31. https://doi.org/10.16152/j.cnki.xdxbzr.2022-01-003
Zhang M, Lai L, Huang X et al (2013) Carbon emission intensity of regional land use change in China. Resour Sci 35(04):792–799
Zhang P, Li Y, Yin H et al (2022b) Spatio-temporal variation and dynamic simulation of ecosystem carbon storage in the north-south transitional zone of China. J Nat Resour 37(5):1183–1197. https://doi.org/10.31497/zrzyxb.20220506
Zhang Z, Hu B, Zhang S et al (2019) Carbon effect analysis and calculation of temporary land reclamation-Taking Guangxi as an example. J Agric Resour Environ 36(06):744–756. https://doi.org/10.13254/j.jare.2019.0170
Zhang Z, Lao Y, Wei J et al (2021) Calculation method and application of carbon emission quota of land consolidation based on PAS2050 specification. Notice Soil Water Conserv 41(06):190–200. https://doi.org/10.13961/j.cnki.stbctb.2021.06.026
Zhao RQ, Huang XJ, Zhong TY et al (2013) Carbon effect evaluation and low-carbon optimization of regional land use. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 29(17):220–229. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2013.17.029
Zhao J, **e D (2023) Analysis of building energy efficiency and carbon emission reduction in the context of “dual carbon”. Shanghai Energy Conservation 09:1275–1278. https://doi.org/10.13770/j.cnki.issn2095-705x.2023.09.007
Zheng R, Liu L, Ma Y et al (2016) Influencing factors and hierarchical analysis of ecological regulation and adoption of tea farmers based on Logistic-ISM model. Tea Science 40(05):696–706. https://doi.org/10.13305/j.cnki.jts.2020.05.015
Zhong L, Wang J, Zhang X, Ying L (2020) Effects of agricultural land consolidation on ecosystem services: trade-offs and synergies. J Clean Prod 264:121412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121412
Zhou B, Liao Z, Chen S et al (2022) Net primary productivity of forest ecosystems in the southwest karst region from the perspective of carbon neutralization. Forests.https://doi.org/10.3390/f13091367
Zhou Y, Guo L, Liu Y (2018) Land consolidation boosting poverty alleviation in China: theory and practice. Land Use Policy 82:339–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.12.024
Zhou Y, Guo L, Liu Y (2019) Land consolidation boosting poverty alleviation in China: theory and practice. Land Use Policy 82:339–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.12.024
Zhou Y, Li Y, Xu C (2020) Land consolidation and rural revitalization in China: mechanisms and paths. Land Use Policy 91:104379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2019.104379
Acknowledgements
The authors would extend appreciation to all the anonymous reviewers and editors for their constructive comments that improved the study.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Qingdao Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project (No. QDSKL2201184).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TC: data curation, methodology, conceptualization ideas. YY: writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
The authors confirm consent to publication and authorship of the study. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the manuscript.
Consent for publication
The authors confirm consent to publication and authorship of the study. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, ., Cao, T. Measurement of carbon effect in land consolidation projects and evaluation of low-carbon promotion paths: a case study of Wudi County, Shandong Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 113068–113087 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30208-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30208-1