Abstract
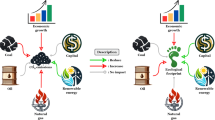
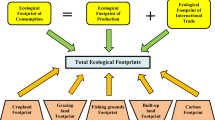
The global warming phenomenon has been an issue of considerable discussion and debate among academics and decision-makers over the past few decades. Therefore, a deeper comprehension of the relationships between environmental deterioration and its causes is necessary in nations that rely on fossil fuels. This study examines the relationship between per capita carbon dioxide emissions and total natural resources, nonrenewable energy, industrialization, and ecological footprint from 2001 to 2020 in the case of major fossil fuel–consuming countries. The most recent panel Granger causality and panel-corrected standard error (PCSE) simulation models are used in this study. The findings indicate that natural resources, ecological footprint, and registered companies impede environmental quality. Similarly, the same results were noted by employing the generalized least square method. A feedback effect was noted between carbon dioxide emission and ecological footprint, while unidirectional causality between coal consumption and carbon emission. In light of these findings, it is advised that instead of pursuing policies that encourage the use of coal and petroleum, new energy policies enhance the share of nonfossil fuels in the energy mix for controlling rapid industrialization, extraction of natural resources, and environmental and economic issues.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset used during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbasi KR, Shahbaz M, Zhang J, Irfan M, Alvarado R (2022) Analyze the environmental sustainability factors of China: the role of fossil fuel energy and renewable energy. Renew Energy 187:390–402
Adebayo TS (2022) Environmental consequences of fossil fuel in Spain amidst renewable energy consumption: a new insights from the wavelet-based Granger causality approach. Int J Sust Dev World 29(7):579–592
Ahmed Z, Asghar MM, Malik MN, Nawaz K (2020) Moving towards a sustainable environment: the dynamic linkage between natural resources, human capital, urbanization, economic growth, and ecological footprint in China. Resour Policy 67:101677
Ahmed F, Ali I, Kousar S, Ahmed S (2022) The environmental impact of industrialization and foreign direct investment: empirical evidence from Asia-Pacific region. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:29778–29792
Ajmi AN, Inglesi-Lotz R (2021) Revisiting the Kuznets curve hypothesis for Tunisia: carbon dioxide vs. ecological footprint. Energy Sources Part B 16(5):406–419
Ali I, Sun H, Tariq G, Ali H, Baz K, Mahmood H, Khan I, Yao J (2022) Asymmetric impact of coal and gas on carbon dioxide emission in six Asian countries: using asymmetric and non-linear approach. J Clean Prod 367:132934
Ansari MA (2022) Re-visiting the environmental Kuznets curve for ASEAN: a comparison between ecological footprint and carbon dioxide emissions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 168:112867
Anwar A, Siddique M, Dogan E, Sharif A (2021) The moderating role of renewable and non-renewable energy in environment-income nexus for ASEAN countries: evidence from Method of Moments Quantile Regression. Renew Energy 164:956–967
Arslan HM, Khan I, Latif MI, Komal B, Chen S (2022) Understanding the dynamics of natural resources rents, environmental sustainability, and sustainable economic growth: new insights from China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(39):58746–58761
Badeeb RA, Lean HH, Shahbaz M (2020) Are too many natural resources to blame for the shape of the environmental Kuznets curve in resource-based economies? Resour Policy 68:101694
Baz K, Xu D, Ampofo GMK, Ali I, Khan I, Cheng J, Ali H (2019) Energy consumption and economic growth nexus: new evidence from Pakistan using asymmetric analysis. Energy 189:116254
Baz K, Xu D, Ali H, Ali I, Khan I, Khan MM, Cheng J (2020) Asymmetric impact of energy consumption and economic growth on ecological footprint: using asymmetric and nonlinear approach. Sci Total Environ 718:137364
Baz K, Cheng J, Xu D, Abbas K, Ali I, Ali H, Fang C (2021) Asymmetric impact of fossil fuel and renewable energy consumption on economic growth: a nonlinear technique. Energy 226:120357
Caglar AE, Yavuz E, Mert M, Kilic E (2022) The ecological footprint facing asymmetric natural resources challenges: evidence from the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:10521–10534
Chakamera C, Alagidede P (2018) Electricity crisis and the effect of CO2 emissions on infrastructure-growth nexus in Sub Saharan Africa. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 94:945–958
Cho JH, Sohn SY (2018) A novel decomposition analysis of green patent applications for the evaluation of R&D efforts to reduce CO2 emissions from fossil fuel energy consumption. J Clean Prod 193:290–299
Chu LK (2022) Determinants of ecological footprint in OCED countries: do environmental-related technologies reduce environmental degradation? Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(16):23779–23793
Dagar V, Khan MK, Alvarado R, Rehman A, Irfan M, Adekoya OB, Fahad S (2022) Impact of renewable energy consumption, financial development and natural resources on environmental degradation in OECD countries with dynamic panel data. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(12):18202–18212
Dzator M, Acheampong AO, Dzator J (2021) Does transport infrastructure development contribute to carbon emissions? Evidence from develo** countries. Environ Sustain Econ, Elsevier, pp 19–33
Elfaki KE, Khan Z, Kirikkaleli D, Khan N (2022) On the nexus between industrialization and carbon emissions: evidence from ASEAN+ 3 economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:31476–31485
Hdom HA, Fuinhas JA (2020) Energy production and trade openness: assessing economic growth, CO2 emissions and the applicability of the cointegration analysis. Energ Strat Rev 30:100488
Ibrahim RL, Huang Y, Mohammed A, Adebayo TS (2023) Natural resources-sustainable environment conflicts amidst COP26 resolutions: investigating the role of renewable energy, technology innovations, green finance, and structural change. Int J Sustain Dev World Ecol 30(4):445–457
Jamil M, He N, Zhao W, **ang H, Gupta MK, Iqbal A (2022) Khan AM (2022) Assessment of energy consumption, carbon emissions and cost metrics under hybrid MQL-Dry ice blasting system: a novel cleaner production technology for manufacturing sectors. J Clean Prod 360:132111
Jie H, Khan I, Alharthi M, Zafar MW, Saeed A (2023) Sustainable energy policy, socio-economic development, and ecological footprint: the economic significance of natural resources, population growth, and industrial development. Util Policy 81:101490
Khan A, Chenggang Y, Hussain J, Bano S, Nawaz A (2020) Natural resources, tourism development, and energy-growth-CO2 emission nexus: a simultaneity modeling analysis of BRI countries. Resour Policy 68:101751
Khan I, Hou F, Zakari A, Irfan M, Ahmad M (2022a) Links among energy intensity, non-linear financial development, and environmental sustainability: new evidence from Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. J Clean Prod 330:129747
Khan I, Lei H, Shah AA, Khan I, Baz K, Koondhar MA, Hatab AA (2022b) Environmental quality and the asymmetrical nonlinear consequences of energy consumption, trade openness and economic development: prospects for environmental management and carbon neutrality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(10):14654–14664
Khan I, Zakari A, Zhang J, Dagar V, Singh S (2022c) A study of trilemma energy balance, clean energy transitions, and economic expansion in the midst of environmental sustainability: new insights from three trilemma leadership. Energy 248:123619
Kurniawan R, Sugiawan Y, Managi S (2021) Economic growth–environment nexus: an analysis based on natural capital component of inclusive wealth. Ecol Ind 120:106982
Lin B, Jia Z (2020) Economic, energy and environmental impact of coal-to-electricity policy in China: a dynamic recursive CGE study. Sci Total Environ 698:134241
Liu H, Alharthi M, Atil A, Zafar MW, Khan I (2022) A non-linear analysis of the impacts of natural resources and education on environmental quality: green energy and its role in the future. Resour Policy 79:102940
McDonald GW, Patterson MG (2004) Ecological footprints and interdependencies of New Zealand regions. Ecol Econ 50(1–2):49–67
Mujtaba A, Jena PK (2021) Analyzing asymmetric impact of economic growth, energy use, FDI inflows, and oil prices on CO 2 emissions through NARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:30873–30886
Mujtaba A, Jena PK, Mukhopadhyay D (2020) Determinants of CO 2 emissions in upper middle-income group countries: an empirical investigation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:37745–37759
Murshed M, Saboori B, Madaleno M, Wang H, Doğan B (2022) Exploring the nexuses between nuclear energy, renewable energy, and carbon dioxide emissions: the role of economic complexity in the G7 countries. Renew Energy 190:664–674
Network GF (2018) Global footprint network advancing the science of sustainability. News: 2017
Onofrei M, Gavriluţă A-F, Bostan I, Filip BF, Popescu CL, Jitaru G (2020) Impacts of the allocation of governmental resources for improving the environment. An empirical analysis on develo** european countries. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(8):2783
Ozcan B, Tzeremes P, Dogan E (2019) Re-estimating the interconnectedness between the demand of energy consumption, income, and sustainability indices. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:26500–26516
Pesaran MH (2021) General diagnostic tests for cross-sectional dependence in panels. Empir Econ 60:13–50
Rees W, Wackernagel M (2008) Urban ecological footprints: why cities cannot be sustainable—and why they are a key to sustainability. Urban Ecology. Springer, pp 537–555
Shahbaz M, Solarin SA, Mahmood H, Arouri M (2013) Does financial development reduce CO2 emissions in Malaysian economy? A time series analysis. Econ Model 35:145–152
Shahbaz M, Sharma R, Sinha A, Jiao Z (2021) Analyzing nonlinear impact of economic growth drivers on CO2 emissions: designing an SDG framework for India. Energy Policy 148:111965
Tobechukwu NM, Azubuike IM (2020) Panel data estimators in the presence of serial and spatial correlation with panel heteroscedasticity: a simulation study. Q J Econom Res 6(1):1–11
Toumi S, Toumi H (2019) Asymmetric causality among renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth in KSA: evidence from a non-linear ARDL model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(16):16145–16156
Wackernagel M, Rees W (1998) Our ecological footprint: reducing human impact on the earth, vol 9. New Society Publishers
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 69(6):709–748
Zafar MW, Zaidi SAH, Khan NR, Mirza FM, Hou F, Kirmani SAA (2019) The impact of natural resources, human capital, and foreign direct investment on the ecological footprint: the case of the United States. Resour Policy 63:101428
Zahoor Z, Latif MI, Khan I, Hou F (2022) Abundance of natural resources and environmental sustainability: the roles of manufacturing value-added, urbanization, and permanent cropland. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(54):82365–82378
Zakari A, Li G, Khan I, **dal A, Tawiah V, Alvarado R (2022a) Are abundant energy resources and Chinese business a solution to environmental prosperity in Africa? Energy Policy 163:112829
Zakari A, Tawiah V, Khan I, Alvarado R, Li G (2022b) Ensuring sustainable consumption and production pattern in Africa: evidence from green energy perspectives. Energy Policy 169:113183
Funding
The Key Project of Philosophy and Social Science Research in Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province (Grant 2021SJZDA139).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HA: conceptualization, methodology. IA: conceptualization. KB: writing — original draft. HA: writing — review and editing. IA: writing — review and editing. IA: supervision, project administration and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ali, H., Ali, I. & Baz, K. Do industrialization and nonrenewable energy affect environmental quality? Evidence from top fossil fuel–consuming countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 109800–109809 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30038-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30038-1