Abstract
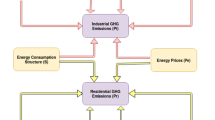
Pollution and energy crisis are actual issues in Europe, including the EU Central and Eastern European states. In this context, the objective of this paper is to assess the impact of economic growth and electricity prices for non-household consumers on pollution. The empirical findings reveal the U pattern for energy industry and inverted U pattern for manufacturing in the period 2007–2021 in the EU countries from Central and Eastern Europe. Renewable energy consumption reduces the CO2 and GHG emissions in energy industry. FDI and electricity prices determine the reduction in GHG and CO2 emissions in both sectors. These results are the basis for policy recommendations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are publicly available and authors provided their source into the manuscript.
References
Acevedo-Ramos JA, Valencia CF, Valencia CD (2023) The Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis for Colombia: impact of economic development on greenhouse gas emissions and ecological footprint. Sustain 15(4):3738
Acheampong AO, Adams S, Boateng E (2019) Do globalization and renewable energy contribute to carbon emissions mitigation in Sub-Saharan Africa? Sci Total Environ 677:436–446
Adams S, Acheampong AO (2019) Reducing carbon emissions: the role of renewable energy and democracy. J Clean Prod 240:118245
Adebayo TS (2020) Revisiting the EKC hypothesis in an emerging market: an application of ARDL-based bounds and wavelet coherence approaches. SN Applied Sciences 2(12):1–15
Adesina KS, Mwamba JWM (2019) Does economic freedom matter for CO2 emissions? Lessons from Africa. J Dev Areas 53(3):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1353/jda.2019.0044
Alotaibi A, Alajlan N (2021) Using quantile regression to analyze the relationship between socioeconomic indicators and carbon dioxide emissions in G20 countries. Sustainability 13(13):7011. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13137011
Alvarado R, Murshed M, Cifuentes-Faura J, Işık C, Hossain MR, Tillaguango B (2023) Nexuses between rent of natural resources, economic complexity, and technological innovation: the roles of GDP, human capital and civil liberties. Resources Policy 85:103637
Amin N, Shabbir MS, Song H, Farrukh MU, Iqbal S, Abbass K (2023) A step towards environmental mitigation: do green technological innovation and institutional quality make a difference? Technol Forecast Soc Change 190:122413
Ansari, M.A., Haider, S. and Khan, N.A. (2020) Does trade openness affects global carbon dioxide emissions: evidence from the top CO2 emitters, Manag Environ Qual, Vol. 31 No. 1, pp. 32-53. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-12-2018-0205
Arellano M, Bond S (1991) Some tests of specification for panel data: Monte Carlo evidence and an application to employment equations. Rev Econ Stud 58(2):277–297
Bader Y, Ganguli S (2019) Analysis of the association between economic growth, environmental quality and health standards in the Gulf Cooperation Council during 1980-2012. Manag Environ Qual 30(5):1050–1071. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEQ-03-2018-0061
Belaïd F, Al-Sarihi A, Al-Mestneer R (2023) Balancing climate mitigation and energy security goals amid converging global energy crises: the role of green investments. Renew Energ 205:534–542
Bjørnskov C (2020) Economic freedom and the CO2 Kuznets Curve. Available at SSRN 3508271. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3508271
Chen L (2022) How CO2 emissions respond to changes in government size and level of digitalization? Evidence from the BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:457–467
Chen Y, Zhao J, Lai Z, Wang Z, **a H (2019) Exploring the effects of economic growth, and renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on China’s CO2 emissions: evidence from a regional panel analysis. Renew Energ 140:341–353
Cheon S, Kim J, Kim J (2017) An analysis on the influence of economic freedom index, renewable energy generation ratio, energy consumption and GDP on CO2 emission. J Korean Soc Miner Energy Resour Eng 54(3):242–252
Chung CY, Yang J, Yang X, He J (2022) Long-term effects of ambient air pollution on lung cancer and COPD mortalities in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Environ Impact Assess Rev 97:106865
Cifuentes-Faura J (2021) Environmental policies to combat climate change in europe and possible solutions: European green deal and circular economy. Int J Sustain Policy Pract 17(2):27–36
Cifuentes-Faura J (2022a) European Union policies and their role in combating climate change over the years. Air Qual Atmos Health 15(8):1333–1340
Cifuentes-Faura J (2022b) Circular economy and sustainability as a basis for economic recovery post-COVID-19. Circ Econ Sustain 2(1):1–7
Degand E (2011) China and India: economic development and environmental issues. In: EIAS newsletter (March/April). European Institute for Asian Studies, Brussels
Diaz N, Ninomiya K, Noble J, Dornfeld D (2012) Environmental impact characterization of milling and implications for potential energy savings in industry. Procedia CIRP 1:518–523
Do T, Dinh H (2020) Short-and long-term effects of GDP, energy consumption, FDI, and trade openness on CO2 emissions. Accounting 6(3):365–372
Dogan E, Inglesi-Lotz R (2020) The impact of economic structure to the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis: evidence from European countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:12717–12724
Dogan E, Seker F (2016) Determinants of CO2 emissions in the European Union: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy. Renew Energ 94:429–439
Dong K, Dong X, Jiang Q (2020) How renewable energy consumption lower global CO2 emissions? Evidence from countries with different income levels. World Econ 43(6):1665–1698
Farooq S, Ozturk I, Majeed MT, Akram R (2022) Globalization and CO2 emissions in the presence of EKC: a global panel data analysis. Gondw Res 106:367–378
Haug AA, Ucal M (2019) The role of trade and FDI for CO2 emissions in Turkey: non-linear relationships. Energy Econ 81:297–307
Hu H, ** countries. Appl Energy 211:1229–1244
Huang Y, Haseeb M, Usman M, Ozturk I (2022) Dynamic association between ICT, renewable energy, economic complexity and ecological footprint: is there any difference between E-7 (develo**) and G-7 (developed) countries? Technol Soc 68:101853
Ibrahim RL, Ajide KB (2021) Nonrenewable and renewable energy consumption, trade openness, and environmental quality in G-7 countries: the conditional role of technological progress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(33):45212–45229
Itoo HH, Ali N (2023) Analyzing the causal nexus between CO2 emissions and its determinants in India: evidences from ARDL and EKC approach. Manag Environ Qual 34(1):192–213
Jahanger A, Hossain MR, Usman M, Onwe JC (2023) Recent scenario and nexus between natural resource dependence, energy use and pollution cycles in BRICS region: does the mediating role of human capital exist? Resour Policy 81:103382
Jain M (2017) Does sustainable “economic development path” pair with “climatic mortification”: testimony from bric and other develo** nations. Amity Glob Bus Rev 12(1):91–99
Jain M, Kaur S (2022) Carbon emissions, inequalities and economic freedom: an empirical investigation in selected South Asian economies. Int J Soc Econ 49(6):882–913
Jamil K, Liu D, Gul RF, Hussain Z, Mohsin M, Qin G, Khan FU (2022) Do remittance and renewable energy affect CO2 emissions? An empirical evidence from selected G-20 countries. Energy & Environment 33(5):916–932
Jiang L, Lin C, Lin P (2014) The determinants of pollution levels: firm-level evidence from Chinese manufacturing. J Comp Econ 42(1):118–142
Jiang R, Liu B (2023) How to achieve carbon neutrality while maintaining economic vitality: An exploration from the perspective of technological innovation and trade openness. Sci Total Environ 868:161490.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161490
Joshi P, Beck K (2018) Democracy and carbon dioxide emissions: assessing the interactions of political and economic freedom and the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Res Soc Sci 39:46–54
Kahia M, Ben Jebli M, Belloumi M (2019) Analysis of the impact of renewable energy consumption and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions in 12 MENA countries. Clean Technol Environ Policy 21:871–885
Kais S, Sami H (2016) An econometric study of the impact of economic growth and energy use on carbon emissions: panel data evidence from fifty-eight countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 59:1101–1110
Katircioglu S, Katircioglu S (2018) Testing the role of fiscal policy in the environmental degradation: the case of Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:5616–5630
Kim AB (2023) 2023 Index of economic freedom. The Heritage Foundation. Available at: https://www.heritage.org/index/about
Kim YS (2015) Electricity consumption and economic development: are countries converging to a common trend? Energy Econ 49:192–202
Laplante B, Smits K (1998) Estimating industrial pollution in Latvia. ECSSD Rural Development and Environment Sector, Working Paper, 4
Lawson LA (2020) GHG emissions and fossil energy use as consequences of efforts of improving human well-being in Africa. J Environ Manage 273:111136
Lazăr D, Minea A, Purcel AA (2019) Pollution and economic growth: evidence from Central and Eastern European countries. Energy Econ 81:1121–1131
Leitão NC, Lorente DB (2020) The linkage between economic growth, renewable energy, tourism, CO2 emissions, and international trade: the evidence for the European Union. Energies 13(18):4838
Liddle B (2018) Consumption-based accounting and the trade-carbon emissions nexus. Energy Econ 69:71–78
Lorente DB, Mohammed KS, Cifuentes-Faura J, Shahzad U (2023) Dynamic connectedness among climate change index, green financial assets and renewable energy markets: novel evidence from sustainable development perspective. Renew Energ 204:94–105
Makhdum MSA, Usman M, Kousar R, Cifuentes-Faura J, Radulescu M, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2022) How do institutional quality, natural resources, renewable energy, and financial development reduce ecological footprint without hindering economic growth trajectory? Evidence from China. Sustain 14(21):13910
Massagony A, Budiono (2022) Is the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis valid on CO2 emissions in Indonesia? Int J Environ Stud 80(1):20–31
McWilliams B, Sgaravatti G, Tagliapietra S and Zachmann G (2022) A grand bargain to steer through the European Union’s energy crisis (Vol. 22, No. 14, pp. 2022-2009). Bruegel.
Milin IA, Mungiu Pupazan MC, Rehman A, Chirtoc IE, Ecobici N (2022) Examining the relationship between rural and urban populations’ access to electricity and economic growth: a new evidence. Sustain 14(13):8125
Naseem S, Guang Ji T (2021) A system-GMM approach to examine the renewable energy consumption, agriculture and economic growth’s impact on CO2 emission in the SAARC region. GeoJournal 86(5):2021–2033
Nasir MA, Huynh TLD, Tram HTX (2019) Role of financial development, economic growth & foreign direct investment in driving climate change: a case of emerging ASEAN. J Environ Manage 242:131–141
Nathaniel SP, Iheonu CO (2019) Carbon dioxide abatement in Africa: the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption. Sci Total Environ 679:337–345
Naudé W (2011) Climate change and industrial policy. Sustain 3(7):1003–1021
Naz S, Sultan R, Zaman K, Aldakhil AM, Nassani AA, Abro MMQ (2019) Moderating and mediating role of renewable energy consumption, FDI inflows, and economic growth on carbon dioxide emissions: evidence from robust least square estimator. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(3):2806–2819
Ozcan B (2013) The nexus between carbon emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in Middle East countries: a panel data analysis. Energy Policy 62:1138–1147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2013.07.016
Pata UK, Aydin M (2020) Testing the EKC hypothesis for the top six hydropower energy-consuming countries: Evidence from Fourier Bootstrap ARDL procedure. J Clean Prod 264:121699
Pesaran MH (2015) Testing weak cross-sectional dependence in large panels. Econom Rev 34(6–10):1089–1117
Pesaran MH, Yamagata T (2008) Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. J Econom 142(1):50–93
Qadeer A, Anis M, Ajmal Z, Kirsten KL, Usman M, Khosa RR et al (2022) Sustainable development goals under threat? Multidimensional impact of COVID-19 on our planet and society outweigh short term global pollution reduction. Sustain Cities Soc 83:103962
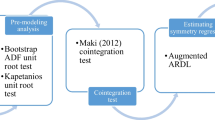
Rafindadi AA, Usman O (2019) Globalization, energy use, and environmental degradation in South Africa: startling empirical evidence from the Maki-cointegration test. J Environ Manage 244:265–275
Rafindadi AA, Muye IM, Kaita RA (2018) The effects of FDI and energy consumption on environmental pollution in predominantly resource-based economies of the GCC. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 25:126–137
Rafique MZ, Li Y, Larik AR, Monaheng MP (2020) The effects of FDI, technological innovation, and financial development on CO2 emissions: evidence from the BRICS countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(19):23899–23913
Sadiq M, Wen F, Bashir MF, Amin A (2022) Does nuclear energy consumption contribute to human development? Modeling the effects of public debt and trade globalization in an OECD heterogeneous panel. J Clean Prod 375:133965
Sajeev A, Kaur S (2020) Environmental sustainability, trade and economic growth in India: implications for public policy. Int Trade, Politics and Development 4(2):141–160
Saqib N, Ozturk I, Usman M, Sharif A, Razzaq A (2022) Pollution haven or halo? How European countries leverage FDI, energy, and human capital to alleviate their ecological footprint. Gondw Res 116:136–148
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2018) Empirical study of the environmental Kuznets curve and environmental sustainability curve hypothesis for Australia, China, Ghana and USA. J Clean Prod 201:98–110
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Ali A, Bhattacharya M (2017) The impact of globalization on CO2 emissions in China. Singap Econ Rev 62(04):929–957
Shahbaz M, Nasir MA, Roubaud D (2018) Environmental degradation in France: the effects of FDI, financial development, and energy innovations. Energy Econ 74:843–857
Shahnazi R, Shabani ZD (2021) The effects of renewable energy, spatial spillover of CO2 emissions and economic freedom on CO2 emissions in the EU. Renew Energ 169:293–307
Sharma GD, Shahbaz M, Singh S, Chopra R, Cifuentes-Faura J (2023) Investigating the nexus between green economy, sustainability, bitcoin and oil prices: contextual evidence from the United States. Resour Policy 80:103168
Simionescu M, Cifuentes-Faura J (2023) Sustainability policies to reduce pollution in energy supply and waste sectors in the V4 countries. Util Policy 82:101551
Simionescu M, Rădulescu M, Cifuentes-Faura J (2023b) Renewable energy consumption-growth nexus in European countries: a sectoral approach. Eval Rev 47(2):287–319
Simionescu M, Radulescu M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Cifuentes-Faura J (2023a) Pollution, political instabilities and electricity price in the CEE countries during the war time. J Environ Manage 343:118206
Sinha A, Sengupta T, Alvarado R (2020) Interplay between technological innovation and environmental quality: formulating the SDG policies for next 11 economies. J Clean Prod 242:118549
Sørensen B (2011) Life-cycle analysis of energy systems: from methodology to applications. Royal Society of Chemistry
Stefanski R (2013) Structural transformation and pollution. In: Paper presented at the University of Surrey Economics Seminar. March 8
Talbi B, Jebli MB, Bashir MF, Shahzad U (2022) Does economic progress and electricity price induce electricity demand: a new appraisal in context of Tunisia. J Public Aff 22(1):e2379
Tan-Soo JS, Zhang XB, Qin P, **e L (2019) Using electricity prices to curb industrial pollution. J Environ Manage 248:109252
Uche E, Das N, Bera P, Cifuentes-Faura J (2023) Understanding the imperativeness of environmental-related technological innovations in the FDI–environmental performance nexus. Renew Energ 206:285–294
Usman M, Radulescu M (2022) Examining the role of nuclear and renewable energy in reducing carbon footprint: does the role of technological innovation really create some difference? Sci Total Environ 841:156662
Usman M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Jahanger A, Ahmad P (2023) Are Mercosur economies going green or going away? An empirical investigation of the association between technological innovations, energy use, natural resources and GHG emissions. Gondw Res 113:53–70
Usman M, Jahanger A, Makhdum MSA, Radulescu M, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Jianu E (2022) An empirical investigation of ecological footprint using nuclear energy, industrialization, fossil fuels and foreign direct investment. Energies 15(17):6442
Usman M, Makhdum MSA, Kousar R (2021) Does financial inclusion, renewable and non-renewable energy utilization accelerate ecological footprints and economic growth? Fresh evidence from 15 highest emitting countries. Sustain Cities Soc 65:102590
Van Tran N, Van Tran Q, Do LTT, Dinh LH, Do HTT (2019) Trade off between environment, energy consumption and human development: do levels of economic development matter? Energy 173:483–493
Wang J, Usman M, Saqib N, Shahbaz M, Hossain MR (2023c) Asymmetric environmental performance under economic complexity, globalization and energy consumption: Evidence from the World’s largest economically complex economy. Energy 279:128050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.128050
Wang M, Hossain MR, Mohammed KS, Cifuentes-Faura J, Cai X (2023b) Heterogenous effects of circular economy, green energy and globalization on CO2 emissions: policy based analysis for sustainable development. Renew Energ 211:789–801
Wang R, Usman M, Radulescu M, Cifuentes-Faura J, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2023a) Achieving ecological sustainability through technological innovations, financial development, foreign direct investment, and energy consumption in develo** European countries. Gondw Res 119:138–152
Wang Z, Gao L, Wei Z, Majeed A, Alam I (2022) How FDI and technology innovation mitigate CO2 emissions in high-tech industries: evidence from province-level data of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(3):4641–4653
Wood J, Herzog I (2014) Economic freedom and air quality. Fraser Institute, Vancouver, Canada, April
Wu J, Abban OJ, Boadi AD, Charles O (2022) The effects of energy price, spatial spillover of CO2 emissions, and economic freedom on CO2 emissions in Europe: a spatial econometrics approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(42):63782–63798
**uhui J, Raza MY (2022) Delving into Pakistan’s industrial economy and carbon mitigation: an effort toward sustainable development goals. Energ Strat Rev 41:100839
Zhang R, Yang L, Yao Y, Zheng C (2013) Gray relational analysis of industrial structure and carbon emission intensity: based on Guangzhou data. In: Proceedings of the 2013 international conference on business computing and global information, pp 1186–9
Zhang M, Mu H, Ning Y, Song Y (2009) Decomposition of energy-related CO2 emission over 1991–2006 in China. Ecol Econ 68(7):2122–2128
Zhang Z, Fu H, **e S, Cifuentes-Faura J, Nasilloyevich UB (2023) Role of green finance and regional environmental efficiency in China. Renew Energ 214:407–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2023.05.076
Zhou X, Zhang J, Li J (2013) Industrial structural transformation and carbon dioxide emissions in China. Energy Policy 57:43–51
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Mihaela Simionescu: data collection; formal analysis; material preparation; Magdalena Radulescu: investigation, discussion of results, conclusions; Javier Cifuentes-Faura: investigation; writing the original draft. All authors approved the manuscript to be submitted for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
All authors approved the manuscript to be submitted for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Simionescu, M., Radulescu, M. & Cifuentes-Faura, J. Pollution and electricity price in the EU Central and Eastern European countries: a sectoral approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 95917–95930 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29109-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29109-0