Abstract
This research aims to examine the validity of the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis in 37 Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries over the period from 1960 to 2019. Panel Quantile Regressions (QR) show that for the lower quartile, economic growth does not impact emissions; for the central quartile a U-shaped curve emerges; while for the upper quartile, an N-shaped curve is found. In addition, cointegrating regressions highlight that economic growth, fossil fuel consumption, and population exert a detrimental effect on the environment, while renewable energy consumption reduces carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. These results are confirmed by panel causality tests since a feedback mechanism is found between CO2 emissions and the remaining series. Furthermore, single-country estimates provide evidence of great variability in the sample.

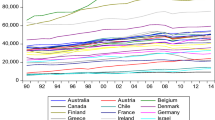
Source: authors’ elaborations in STATA
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
I confirm that all relevant data are included in the article and information file.
References
Abbasi KR, Shahbaz M, Zhang J, Irfan M, Alvarado R (2022) Analyze the environmental sustainability factors of China: The role of fossil fuel energy and renewable energy. Renew Energy 187:390–402
Abbasi KR, Awan A, Bandyopadhyay A, Rej S, Banday TP (2023) Investigating the inverted N-shape EKC in the presence of renewable and nuclear energy in a global sample. Clean Technol Environ Policy 25(4):1179–1194**e
Adebayo TS (2022) Renewable energy consumption and environmental sustainability in Canada: does political stability make a difference? Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(40):61307–61322
Adedoyin FF, Ozturk I, Agboola MO, Agboola PO, Bekun FV (2021) The implications of renewable and non-renewable energy generating in Sub-Saharan Africa: The role of economic policy uncertainties. Energy Policy 150:112115
Afzal M (2006) Causality between exports, world income and economic growth in Pakistan. Int Econ J 20(1):63–77
Ahmad N, Du L, Lu J, Wang J, Li H-Z, Hashmi MZ (2017) Modelling the CO2 emissions and economic growth in Croatia: is there any environmental Kuznets curve? Energy 123:164–172
Ahmed A, Uddin GS, Sohag K (2016) Biomass energy, technological progress and the environmental Kuznets curve: Evidence from selected European countries. Biomass Bioenerg 90:202–208
Ahmed Z, Zafar MW, Ali S (2020) Linking urbanization, human capital, and the ecological footprint in G7 countries: an empirical analysis. Sustain Cities Soc 55:102064
Alam MM, Murad MW, Noman AHM, Ozturk I (2016) Relationships among carbon emissions, economic growth, energy consumption and population growth: Testing Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis for Brazil, China, India and Indonesia. Ecol Ind 70:466–479
Albulescu CT, Artene AE, Luminosu CT, Tămășilă M (2020) CO 2 emissions, renewable energy, and environmental regulations in the EU countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(27):33615–33635
AlKhars MA, Alwahaishi S, Fallatah MR, Kayal A (2022) A literature review of the Environmental Kuznets Curve in GCC for 2010–2020. Environ Sustain Indic 14:100181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indic.2022.100181
Allard A, Takman J, Uddin GS, Ahmed A (2018) The N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve: an empirical evaluation using a panel quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(6):5848–5861
Al-Mulali U, Saboori B, Ozturk I (2015a) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Vietnam. Energy Policy 76:123–131
Al-Mulali U, Tang CF, Ozturk I (2015b) Does financial development reduce environmental degradation? Evidence from a panel study of 129 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(19):14891–14900
Al-Mulali U, Weng-Wai C, Sheau-Ting L, Mohammed AH (2015c) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecol Ind 48:315–323
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I, Solarin SA (2016) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in seven regions: The role of renewable energy. Ecol Ind 67:267–282
Alsaleh M, Abdulwakil MM, Abdul-Rahim AS (2021) Land-use change impacts from sustainable hydropower production in EU28 region: An empirical analysis. Sustainability 13(9):4599
Alshehry AS, Belloumi M (2015) Energy consumption, carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: The case of Saudi Arabia. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 41:237–247
Álvarez-Herránz A, Balsalobre D, Cantos JM, Shahbaz M (2017) Energy innovations-GHG emissions nexus: fresh empirical evidence from OECD countries. Energy Policy 101:90–100
Ansari MA, Ahmad MR, Siddique S, Mansoor K (2020) An environment Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: Evidence from GCC countries. Carbon Manag 11(4):355–368
Anser MK, Shabbir MS, Tabash MI, Shah SHA, Ahmad M, Peng MY-P, Lopez LB (2021) Do renewable energy sources improve clean environmental-economic growth? Empirical investigation from South Asian economies. Energy Explor Exploit. https://doi.org/10.1177/01445987211002278
Anwar A, Sinha A, Sharif A, Siddique M, Irshad S, Anwar W, Malik S (2021) The nexus between urbanization, renewable energy consumption, financial development, and CO2 emissions: evidence from selected Asian countries. Environ Dev Sustain 24:6556–6576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01716-2
Awan AM, Azam M, Saeed IU, Bakhtyar B (2020) Does globalization and financial sector development affect environmental quality? A panel data investigation for the Middle East and North African countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(36):45405–45418
Ayad H, Sari-Hassoun SE, Usman M, Ahmad P (2023) The impact of economic uncertainty, economic growth and energy consumption on environmental degradation in MENA countries: Fresh insights from multiple thresholds NARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(1):1806–1824
Aydin M, Koc P, Sahpaz KI (2023) Investigating the EKC hypothesis with nanotechnology, renewable energy consumption, economic growth and ecological footprint in G7 countries: panel data analyses with structural breaks. Energy Sources Part B 18(1):2163724
Azam M, Rehman ZU, Ibrahim Y (2022) Causal nexus in industrialization, urbanization, trade openness, and carbon emissions: Empirical evidence from OPEC economies. Environ Dev Sustain 24:13990–14010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-02019-2
Bahramara S, Golpîra H (2018) Robust optimization of micro-grids operation problem in the presence of electric vehicles. Sustain Cities Soc 37:388–395
Beck KA, Joshi P (2015) An analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve for carbon dioxide emissions: evidence for OECD and non-OECD countries. Eur J Sustain Dev 4(3):33–33
Begum RA, Sohag K, Abdullah SMS, Jaafar M (2015) CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic and population growth in Malaysia. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 41:594–601
Bekhet HA, Othman NS (2018) The role of renewable energy to validate dynamic interaction between CO2 emissions and GDP toward sustainable development in Malaysia. Energy Econ 72:47–61
Bektaş V, Ursavaş N (2023) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis with globalization for OECD countries: the role of convergence clubs. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(16):47090–47105
Bekun FV, Gyamfi BA, Onifade ST, Agboola MO (2021) Beyond the environmental Kuznets Curve in E7 economies: accounting for the combined impacts of institutional quality and renewables. J Clean Prod 314:127924
Bekun FV (2022) Mitigating emissions in India: accounting for the role of real income, renewable energy consumption and investment in energy. Int J Energy Econ Policy 12(1):188–192. https://doi.org/10.32479/ijeep.12652
Bello MO, Solarin SA, Yen YY (2018) The impact of electricity consumption on CO2 emission, carbon footprint, water footprint and ecological footprint: the role of hydropower in an emerging economy. J Environ Manag 219:218–230
Bhattacharya M, Paramati SR, Ozturk I, Bhattacharya S (2016) The effect of renewable energy consumption on economic growth: Evidence from top 38 countries. Appl Energy 162:733–741
Bildirici ME, Gökmenoğlu SM (2017) Environmental pollution, hydropower energy consumption and economic growth: Evidence from G7 countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 75:68–85
Bilgili F, Koçak E, Bulut Ü (2016) The dynamic impact of renewable energy consumption on CO2 emissions: a revisited Environmental Kuznets Curve approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 54:838–845
Boubellouta B, Kusch-Brandt S (2022) Driving factors of e-waste recycling rate in 30 European countries: new evidence using a panel quantile regression of the EKC hypothesis coupled with the STIRPAT model. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02356-w
Boukhelkhal A (2022) Energy use, economic growth and CO2 emissions in Africa: does the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis exist? New evidence from heterogeneous panel under cross-sectional dependence. Environ Dev Sustain 24(11):13083–13110
Bradford DF, Fender RA, Shore SH, Wagner M (2005) The environmental Kuznets curve: exploring a fresh specification. Contributions in Economic Analysis & Policy 4(1):1–28
Caglar AE, Zafar MW, Bekun FV, Mert M (2022) Determinants of CO2 emissions in the BRICS economies: The role of partnerships investment in energy and economic complexity. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 51:101907
Çelik B, Barak D, Koçak E (2023) An empirical investigation of waste management and ecological footprints in OECD countries. In: Muthu SS (eds) Environmental assessment of recycled waste. Environmental Footprints and eco-design of products and processes. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-8323-8_4
Chandran V, Tang CF (2013) The impacts of transport energy consumption, foreign direct investment and income on CO2 emissions in ASEAN-5 economies. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 24:445–453
Cheikh NB, Zaied YB, Chevallier J (2021) On the nonlinear relationship between energy use and CO2 emissions within an EKC framework: Evidence from panel smooth transition regression in the MENA region. Res Int Bus Financ 55:101331
Chen J, Wang P, Cui L, Huang S, Song M (2018) Decomposition and decoupling analysis of CO2 emissions in OECD. Appl Energy 231:937–950
Chen Y, Wang Z, Zhong Z (2019a) CO2 emissions, economic growth, renewable and non-renewable energy production and foreign trade in China. Renew Energy 131:208–216
Chen Y, Zhao J, Lai Z, Wang Z, **a H (2019b) Exploring the effects of economic growth, and renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on China’s CO2 emissions: Evidence from a regional panel analysis. Renew Energy 140:341–353
Chen H, Tackie EA, Ahakwa I, Musah M, Salakpi A, Alfred M, Atingabili S (2022a) Does energy consumption, economic growth, urbanization, and population growth influence carbon emissions in the BRICS? Evidence from panel models robust to cross-sectional dependence and slope heterogeneity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(25):37598–37616
Chen X, Ma W, Valdmanis V (2022b) Can labor productivity growth reduce carbon emission? Evidence from OECD countries and China. Manag Environ Qual: An Int J 33(3):644–656
Choi I (2001) Unit root tests for panel data. J Int Money Financ 20(2):249–272
Churchill SA, Inekwe J, Ivanovski K, Smyth R (2018) The environmental Kuznets curve in the OECD: 1870–2014. Energy Econ 75:389–399
Cole MA, Rayner AJ, Bates JM (1997) The environmental Kuznets curve: an empirical analysis. Environ Dev Econ 2(4):401–416
Croutzet A, Dabbous A (2021) Do FinTech trigger renewable energy use? Evidence from OECD countries. Renew Energy 179:1608–1617
Culas RJ (2012) REDD and forest transition: Tunneling through the environmental Kuznets curve. Ecol Econ 79:44–51
de Souza Mendonca AK, Barni GdAC, Moro MF, Bornia AC, Kupek E, Fernandes L (2020) Hierarchical modeling of the 50 largest economies to verify the impact of GDP, population and renewable energy generation in CO2 emissions. Sustain Prod Consum 22:58–67
Destek MA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Investigation of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: the role of energy and financial development. Sci Total Environ 650:2483–2489
Destek MA, Sinha A (2020) Renewable, non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and ecological footprint: evidence from organisation for economic Co-operation and development countries. J Clean Prod 242:118537
Dietz T, Rosa EA (1997) Effects of population and affluence on CO2 emissions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 94(1):175–179
Dijkgraaf E, Vollebergh HR (2005) A test for parameter homogeneity in CO2Panel EKC estimations. Environ Resource Econ 32(2):229–239
Dinda S (2004) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol Econ 49(4):431–455
Dogan E, Inglesi-Lotz R (2020) The impact of economic structure to the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis: evidence from European countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(11):12717–12724
Dong K, Sun R, Hochman G (2017a) Do natural gas and renewable energy consumption lead to less CO2 emission? Empirical evidence from a panel of BRICS countries. Energy 141:1466–1478
Dong K, Sun R, Hochman G, Zeng X, Li H, Jiang H (2017b) Impact of natural gas consumption on CO2 emissions: panel data evidence from China’s provinces. J Clean Prod 162:400–410
Dong K, Hochman G, Zhang Y, Sun R, Li H, Liao H (2018) CO2 emissions, economic and population growth, and renewable energy: Empirical evidence across regions. Energy Econ 75:180–192
Driscoll JC, Kraay AC (1998) Consistent covariance matrix estimation with spatially dependent panel data. Rev Econ Stat 80(4):549–560
Esteve V, Tamarit C (2012) Threshold cointegration and nonlinear adjustment between CO2 and income: the environmental Kuznets curve in Spain, 1857–2007. Energy Econ 34(6):2148–2156
Fakher HA, Inglesi-Lotz R (2022) Revisiting environmental Kuznets curve: an investigation of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption role. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(87583):87601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21776-9
Farooq S, Ozturk I, Majeed MT, Akram R (2022) Globalization and CO2 emissions in the presence of EKC: A global panel data analysis. Gondwana Res 106:367–378
Ferhi A, Helali K (2023) The impact of renewable energy on the environment and socio-economic welfare: empirical evidence from OECD countries. J Knowl Econ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-023-01320-x
Fisher RA (1992) Statistical methods for research workers. Statistical methods for research workers. In: Kotz S, Johnson NL (eds) Breakthroughs in statistics. Springer Series in Statistics, Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4380-9_6
Gnangoin TY, Kassi DF, Edjoukou AJ-R, Kongrong O, Yuqing D (2022) Renewable energy, non-renewable energy, economic growth and CO2 emissions in the newly emerging market economies: The moderating role of human capital. Front Environ Sci 10:1017721
Golpîra H (2020) Smart energy-aware manufacturing plant scheduling under uncertainty: A risk-based multi-objective robust optimization approach. Energy 209:118385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.118385
Golpîra H, Javanmardan A (2021) Decentralized Decision System for Closed-Loop Supply Chain: A Bi-Level Multi-Objective Risk-Based Robust Optimization Approach. Comput Chem Eng 154:107472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2021.107472
Golpîra H, Khan SAR (2019) A multi-objective risk-based robust optimization approach to energy management in smart residential buildings under combined demand and supply uncertainty. Energy 170:1113–1129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.12.185
Golpîra H, Khan SAR, Zhang Y (2018) Robust smart energy efficient production planning for a general job-shop manufacturing system under combined demand and supply uncertainty in the presence of grid-connected microgrid. J Clean Prod 202:649–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.151
Golpîra H, Bahramara S, Tirkolaee EB (2021a) Sustainable production-consumption of the microgrids: an optimal approach for industrial area. In: Chiappetta Jabbour CJ, Khan SAR (eds) Sustainable production and consumption systems. Industrial Ecology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4760-4_2
Golpîra H, Khan SAR, Safaeipour S (2021b) A review of logistics internet-of-things: current trends and scope for future research. J Ind Inf Integr 22:100194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jii.2020.100194
Golpîra H, Sadeghi H, Bahramara S (2021c) Electricity supply chain coordination: newsvendor model for optimal contract design. J Clean Prod 278:123368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123368
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1995) Economic growth and the environment. Q J Econ 110(2):353–377
Guang-Wen Z, Murshed M, Siddik AB, Alam MS, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Mahmood H (2023) Achieving the objectives of the 2030 sustainable development goals agenda: Causalities between economic growth, environmental sustainability, financial development, and renewable energy consumption. Sustain Dev 31(2):680–697
Gyamfi BA, Agozie DQ, Bekun FV, Köksal C (2023) Beyond the environmental Kuznets Curve in South Asian economies: accounting for the combined effect of information and communication technology, human development and urbanization. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03281-2
Harris R, Sollis R (2003) Applied time series modelling and forecasting: Wiley. https://eprints.gla.ac.uk/33105/
Hashmi R, Alam K (2019) Dynamic relationship among environmental regulation, innovation, CO2 emissions, population, and economic growth in OECD countries: A panel investigation. J Clean Prod 231:1100–1109
Hausman JA (1978) Specification tests in econometrics. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society 46(6):1251–1271. https://doi.org/10.2307/1913827
He J, Richard P (2010) Environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 in Canada. Ecol Econ 69(5):1083–1093
Hu M, Li R, You W, Liu Y, Lee C-C (2020) Spatiotemporal evolution of decoupling and driving forces of CO2 emissions on economic growth along the Belt and Road. J Clean Prod 277:123272
Huang WM, Lee GW, Wu CC (2008) GHG emissions, GDP growth and the Kyoto protocol: a revisit of environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis 36(1):239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2007.08.035
Hussain M, Usman M, Khan JA, Tarar ZH, Sarwar MA (2020) Reinvestigation of environmental Kuznets curve with ecological footprints: empirical analysis of economic growth and population density. J Public Aff 2(1). https://doi.org/10.1002/pa.2276
Im KS, Pesaran MH, Shin Y (2003) Testing for unit roots in heterogeneous panels. J Econom 115(1):53–74
Işık C, Ongan S, Özdemir D (2019) Testing the EKC hypothesis for ten US states: an application of heterogeneous panel estimation method. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(11):10846–10853
Isik C, Ongan S, Ozdemir D, Ahmad M, Irfan M, Alvarado R, Ongan A (2021) The increases and decreases of the environment Kuznets curve (EKC) for 8 OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(22):28535–28543
Islam M, Alam M, Ahmed F, Al-Amin AQ (2023) Economic growth and environmental pollution nexus in Bangladesh: revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis. Int J Environ Stud 80:68–92
Jahanger A, Chishti MZ, Onwe JC, Awan A (2022) How far renewable energy and globalization are useful to mitigate the environment in Mexico? Application of QARDL and spectral causality analysis. Renew Energy 201:514–525
Jahanger A, Hossain MR, Onwe JC, Ogwu SO, Awan A, Balsalobre-Lorente D (2023) Analyzing the N-shaped EKC among top nuclear energy generating nations: a novel dynamic common correlated effects approach. Gondwana Res 116:73–88
Jebli MB, Youssef SB, Ozturk I (2016) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and trade in OECD countries. Ecol Ind 60:824–831
** T (2022) The evolutionary renewable energy and mitigation impact in OECD countries. Renew Energy 189:570–586
Kao C (1999) Spurious regression and residual-based tests for cointegration in panel data. J Econom 90(1):1–44
Kartal MT, Ali U, Nurgazina Z (2022) Asymmetric effect of electricity consumption on CO2 emissions in the USA: analysis of end-user electricity consumption by nonlinear quantile approaches. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(55):83824–83838
Khan A, Safdar S (2023) Symmetric and asymmetric analysis of trade and environment in Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(5):11399–11416
Khan SAR, Zhang Y, Anees M, Golpîra H, Lahmar A, Qianli D (2018) Green supply chain management, economic growth and environment: A GMM based evidence. J Clean Prod 185:588–599
Khan SAR, Sharif A, Golpîra H, Kumar A (2019a) A green ideology in Asian emerging economies: From environmental policy and sustainable development. Sustain Dev 27(6):1063–1075
Khan SAR, Yu Z, Golpîra H, Sharif H (2019b) The nexus between corporate social responsibility and corporate performance: an empirical evidence. LogForum 5(12):291–303. https://doi.org/10.17270/J.LOG.2019.328
Khan SAR, Yu Z, Sharif A, Golpîra H (2020) Determinants of economic growth and environmental sustainability in South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation: evidence from panel ARDL. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:45675–45687
Khan I, Hou F, Le HP (2021a) The impact of natural resources, energy consumption, and population growth on environmental quality: Fresh evidence from the United States of America. Sci Total Environ 754:142222
Khan SAR, Yu Z, Golpira H, Sharif A, Mardani A (2021b) A state-of-the-art review and meta-analysis on sustainable supply chain management: Future research directions. J Clean Prod 278:123357
Khan H, Khan I, BiBi R (2022a) The role of innovations and renewable energy consumption in reducing environmental degradation in OECD countries: an investigation for Innovation Claudia Curve. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(29):43800–43813
Khan I, Lei H, Shah AA, Khan I, Baz K, Koondhar MA, Hatab AA (2022b) Environmental quality and the asymmetrical nonlinear consequences of energy consumption, trade openness and economic development: prospects for environmental management and carbon neutrality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(10):14654–14664
Kilinc-Ata N, Likhachev VL (2022) Validation of the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis and role of carbon emission policies in the case of Russian Federation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:63407–63422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20316-9
Koc S, Bulus GC (2020) Testing validity of the EKC hypothesis in South Korea: role of renewable energy and trade openness. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(23):29043–29054
Koengkan M, Fuinhas JA, Santiago R (2020) The relationship between CO2 emissions, renewable and non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth, and urbanisation in the Southern Common Market. J Environ Econ Policy 9(4):383–401
Kongkuah M (2023) Impact of economic variables on CO2 emissions in belt and road and OECD countries. Environ Monit Assess 195:835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-023-11440-1
Kongkuah M, Yao H, Yilanci V (2021) The relationship between energy consumption, economic growth, and CO2 emissions in China: the role of urbanisation and international trade. Environ Dev Sustain 1–25
Kuznets S (2019) Economic growth and income inequality: Routledge
Lau E, Tan C-C, Tang C-F (2016) Dynamic linkages among hydroelectricity consumption, economic growth, and carbon dioxide emission in Malaysia. Energy Sources Part B 11(11):1042–1049
Leal PH, Marques AC (2020) Rediscovering the EKC hypothesis for the 20 highest CO2 emitters among OECD countries by level of globalization. Int Econ 164:36–47
Lee C-C, Chiu Y-B, Sun C-H (2009) Does one size fit all? A reexamination of the environmental Kuznets curve using the dynamic panel data approach. Rev Agric Econ 31(4):751–778
Lee C-C, Chiu Y-B, Sun C-H (2010) The environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for water pollution: do regions matter? Energy Policy 38(1):12–23
Lee CC, Olasehinde‐Williams G (2022) Does economic complexity influence environmental performance? Empirical evidence from OECD countries. Int J Finance Econ. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijfe.2689
Leitão A (2010) Corruption and the environmental Kuznets curve: empirical evidence for sulfur. Ecol Econ 69(11):2191–2201
Leitão NC, Dos Santos Parente CC, Balsalobre-Lorente D, Cantos Cantos JM (2023) Revisiting the effects of energy, population, foreign direct investment, and economic growth in Visegrad countries under the EKC scheme. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(6):15102–15114
Levin A, Lin C-F, Chu C-SJ (2002) Unit root tests in panel data: asymptotic and finite-sample properties. J Econom 108(1):1–24
Li R, Lee H (2022) The role of energy prices and economic growth in renewable energy capacity expansion–Evidence from OECD Europe. Renew Energy 189:435–443
Li J, Chen Y, Li Z, Huang X (2019) Low-carbon economic development in Central Asia based on LMDI decomposition and comparative decoupling analyses. J Arid Land 11:513–524
Li F, Wu Y-C, Wang M-C, Wong W-K, **ng Z (2021) Empirical study on CO2 emissions, financial development and economic growth of the BRICS countries. Energies 14(21):7341
Lin B, Raza MY (2019) Analysis of energy related CO2 emissions in Pakistan. J Clean Prod 219:981–993
Liu W (2020) EKC test study on the relationship between carbon dioxide emission and regional economic growth. Carbon Manag 11(4):415–425
Lorente DB, Álvarez-Herranz A (2016) Economic growth and energy regulation in the environmental Kuznets curve. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(16):16478–16494
Maddala GS, Wu S (1999) A comparative study of unit root tests with panel data and a new simple test. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 61(S1):631–652
Magazzino C (2016) The relationship between real GDP, CO2 emissions, and energy use in the GCC countries: A time series approach. Cogent Econ Finance 4(1):1152729
Magazzino C (2017) The relationship among economic growth, CO2 emissions, and energy use in the APEC countries: a panel VAR approach. Environ Syst Decis 37(3):353–366
Magazzino C, Cerulli G (2019) The determinants of CO2 emissions in MENA countries: a responsiveness scores approach. Int J Sust Dev World 26(6):522–534
Magazzino C, Falcone PM (2022) Assessing the relationship among waste generation, wealth, and GHG emissions in Switzerland: Some policy proposals for the optimization of the municipal solid waste in a circular economy perspective. J Clean Prod 351:131555
Magazzino C, Mele M, Morelli G, Schneider N (2021a) The nexus between information technology and environmental pollution: Application of a new machine learning algorithm to OECD countries. Util Policy 72:101256
Magazzino C, Mutascu M, Sarkodie SA, Adedoyin FF, Owusu PA (2021b) Heterogeneous effects of temperature and emissions on economic productivity across climate regimes. Sci Total Environ 775:145893
Magazzino C, Mele M (2022) A new machine learning algorithm to explore the CO2 emissions-energy use-economic growth trilemma. Ann Oper Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04787-0
Magazzino C (2023) Ecological footprint, electricity consumption, and economic growth in China: geopolitical risk and natural resources governance. Empir Econ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00181-023-02460-4
Magazzino C, Gallegati M, Giri F (2023a) The Environmental Kuznets Curve in a long-term perspective: Parametric vs semi-parametric models. Environ Impact Assess Rev 98:106973
Magazzino C, Mele M, Drago C, Kuşkaya S, Pozzi C, Monarca U (2023b) The trilemma among CO2 emissions, energy use, and economic growth in Russia. Sci Rep 13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-37251-5
Mahalik MK, Padhan H, Patel G, Mishra S, Chyrmang R (2023) The role of gender life expectancy in environmental degradation: new insights for the BRICS economies. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03097-0
Mahmood H, Furqan M, Hassan MS, Rej S (2023) The Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) Hypothesis in China: A Review. Sustainability 15(7):6110
Majeed MT, Mazhar M, Samreen I, Tauqir A (2022) Economic complexities and environmental degradation: Evidence from OECD countries. Environ Dev Sustain 24(4):5846–5866
Martınez-Zarzoso I, Bengochea-Morancho A (2004) Pooled mean group estimation of an environmental Kuznets curve for CO2. Econ Lett 82(1):121–126
Maruotti A, Alaimo Di Loro P (2023) CO2 emissions and growth: a bivariate bidimensional mean‐variance random effects model. Environmetrics 34(5). https://doi.org/10.1002/env.2793
Mele M, Magazzino C, Schneider N, Gurrieri AR, Golpira H (2022) Innovation, income, and waste disposal operations in Korea: evidence from a spectral granger causality analysis and artificial neural networks experiments. Econ Politica 39(2):427–459
Menegaki AN, Tsagarakis KP (2015) Rich enough to go renewable, but too early to leave fossil energy? Renew Sustain Energy Rev 41:1465–1477
Mikayilov JI, Galeotti M, Hasanov FJ (2018) The impact of economic growth on CO2 emissions in Azerbaijan. J Clean Prod 197:1558–1572
Minlah MK, Zhang X (2021) Testing for the existence of the Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) for CO 2 emissions in Ghana: evidence from the bootstrap rolling window Granger causality test. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(2):2119–2131
Mitić P, Fedajev A, Radulescu M, Rehman A (2023) The relationship between CO2 emissions, economic growth, available energy, and employment in SEE countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(6):16140–16155
Mosikari TJ, Eita JH (2020) CO2 emissions, urban population, energy consumption and economic growth in selected African countries: A Panel Smooth Transition Regression (PSTR). OPEC Energy Rev 44(3):319–333
Muhammad B (2019) Energy consumption, CO2 emissions and economic growth in developed, emerging and Middle East and North Africa countries. Energy 179:232–245
Mujtaba G, Shahzad SJH (2021) Air pollutants, economic growth and public health: implications for sustainable development in OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(10):12686–12698
Murshed M, Apergis N, Alam MS, Khan U, Mahmud S (2022) The impacts of renewable energy, financial inclusivity, globalization, economic growth, and urbanization on carbon productivity: Evidence from net moderation and mediation effects of energy efficiency gains. Renew Energy 196:824–838
Naimoglu M (2023) The effect of energy prices, energy losses, and renewable energy use on CO2 emissions in energy-importing develo** economies in the presence of an environmental Kuznets curve. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(20):58755–58772
Nan S, Huang J, Wu J, Li C (2022) Does globalization change the renewable energy consumption and CO2 emissions nexus for OECD countries? New evidence based on the nonlinear PSTR model. Energ Strat Rev 44:100995
Naseem S, Mohsin M, Zia-UR-Rehman M, Baig SA, Sarfraz M (2022) The influence of energy consumption and economic growth on environmental degradation in BRICS countries: an application of the ARDL model and decoupling index. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(9):13042–13055
Ng C-F, Choong C-K, Lau L-S (2020) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: asymmetry analysis and robust estimation under cross-section dependence. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:18685–18698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08351-w
Ng C-F, Yii K-J, Lau L-S, Go Y-H (2022) Unemployment rate, clean energy, and ecological footprint in OECD countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:42863–42872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17966-6
OECD (2010) Cities and climate change. OECD Publishing, Paris
Omri A, Daly S, Rault C, Chaibi A (2015) Financial development, environmental quality, trade and economic growth: What causes what in MENA countries. Energy Econ 48:242–252
Onifade ST, Alola AA, Erdoğan S, Acet H (2021) Environmental aspect of energy transition and urbanization in the OPEC member states. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(14):17158–17169
Orubu CO, Omotor DG (2011) Environmental quality and economic growth: Searching for environmental Kuznets curves for air and water pollutants in Africa. Energy Policy 39(7):4178–4188
Ozcan B, Ulucak R (2021) An empirical investigation of nuclear energy consumption and carbon dioxide (CO2) emission in India: Bridging IPAT and EKC hypotheses. Nucl Eng Technol 53(6):2056–2065
Özokcu S, Özdemir Ö (2017) Economic growth, energy, and environmental Kuznets curve. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 72:639–647
Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U (2015) Investigating the validity of the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Cambodia. Ecol Ind 57:324–330
Ozturk I, Farooq S, Majeed MT, Skare M (2023) An empirical investigation of financial development and ecological footprint in South Asia: Bridging the EKC and pollution haven hypotheses. Geosci Front 101588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101588
Padhan H, Sahu SK, Dash U (2022) Economic globalization and environmental quality: a study of OECD economies. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02479-0
Park S, Lee Y (2011) Regional model of EKC for air pollution: Evidence from the Republic of Korea. Energy Policy 39(10):5840–5849
Pata UK, Samour A (2022) Do renewable and nuclear energy enhance environmental quality in France? A new EKC approach with the load capacity factor. Prog Nucl Energy 149:104249
Pedroni P (1999) Critical values for cointegration tests in heterogeneous panels with multiple regressors. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 61(S1):653–670
Pesaran MH (2006) Estimation and inference in large heterogeneous panels with a multifactor error structure. Econometrica 74(4):967–1012
Pesaran MH, Smith R (1995) Estimating long-run relationships from dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Econom 68(1):79–113
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RP (1999) Pooled mean group estimation of dynamic heterogeneous panels. J Am Stat Assoc 94(446):621–634
Poudel BN, Paudel KP, Bhattarai K (2009) Searching for an environmental Kuznets curve in carbon dioxide pollutant in Latin American countries. J Agric Appl Econ 41(1379-2016–112740):13–27
Radmehr R, Henneberry SR, Shayanmehr S (2021) Renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and economic growth nexus: a simultaneity spatial modeling analysis of EU countries. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 57:13–27
Rahman MM, Saidi K, Mbarek MB (2020) Economic growth in South Asia: the role of CO2 emissions, population density and trade openness. Heliyon 6(5):e03903
Raihan A, Tuspekova A (2022) Toward a sustainable environment: Nexus between economic growth, renewable energy use, forested area, and carbon emissions in Malaysia. Resour Conserv Recycl Adv 15:200096
Rehman FU, Islam MM, Raza SA (2023) Does disaggregate energy consumption matter to export sophistication and diversification in OECD countries? A robust panel model analysis. Renew Energy 206:274–284
Roca J, Alcántara V (2001) Energy intensity, CO2 emissions and the environmental Kuznets curve. The Spanish case. Energy Policy 29(7):553–556
Saboori B, Sulaiman J, Mohd S (2012) Economic growth and CO2 emissions in Malaysia: a cointegration analysis of the environmental Kuznets curve. Energy Policy 51:184–191
Salari M, Javid RJ, Noghanibehambari H (2021) The nexus between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth in the US. Econ Anal Policy 69:182–194
Saqib N, Sharif A, Razzaq A, Usman M (2023) Integration of renewable energy and technological innovation in realizing environmental sustainability: the role of human capital in EKC framework. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30(6):16372–16385
Selvanathan S, Jayasinghe MS, Selvanathan EA, Abbas SA, Iftekhar MS (2022) Energy consumption, agriculture, forestation and CO2 emission nexus: an application to OECD countries. Appl Econ 55(37):4359–4376. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2022.2128296
Sen D, Tunç KM, Günay ME (2021) Forecasting electricity consumption of OECD countries: A global machine learning modeling approach. Util Policy 70:101222
Shafiei S, Salim RA (2014) Non-renewable and renewable energy consumption and CO2 emissions in OECD countries: a comparative analysis. Energy Policy 66:547–556
Shahbaz M, Lean HH, Shabbir MS (2012) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Pakistan: cointegration and Granger causality. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16(5):2947–2953
Shahbaz M, Mutascu M, Azim P (2013) Environmental Kuznets curve in Romania and the role of energy consumption. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 18:165–173
Sharif A, Raza SA, Ozturk I, Afshan S (2019) The dynamic relationship of renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption with carbon emission: a global study with the application of heterogeneous panel estimations. Renew Energy 133:685–691
Sharif A, Baris-Tuzemen O, Uzuner G, Ozturk I, Sinha A (2020) Revisiting the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption on Turkey’s ecological footprint: Evidence from Quantile ARDL approach. Sustain Cities Soc 57:102138
Sulemana I, James HS, Rikoon JS (2017) Environmental Kuznets Curves for air pollution in African and developed countries: exploring turning point incomes and the role of democracy. J Environ Econ Policy 6(2):134–152
Sun H, Samuel CA, Amissah JCK, Taghizadeh-Hesary F, Mensah IA (2020) Non-linear nexus between CO2 emissions and economic growth: a comparison of OECD and B&R countries. Energy 212:118637
Teal F, Eberhardt M (2010) Productivity analysis in global manufacturing production. https://ora.ox.ac.uk/objects/uuid:f9d91b40-d8b7-402d-95eb-75a9cbdcd000
Tenaw D, Beyene AD (2021) Environmental sustainability and economic development in sub-Saharan Africa: A modified EKC hypothesis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 143:110897
Tiwari AK, Shahbaz M, Hye QMA (2013) The environmental Kuznets curve and the role of coal consumption in India: cointegration and causality analysis in an open economy. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 18:519–527
Uddin MGS, Bidisha SH, Ozturk I (2016) Carbon emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth relationship in Sri Lanka. Energy Sources Part B 11(3):282–287
Ummalla M, Goyari P (2021) The impact of clean energy consumption on economic growth and CO2 emissions in BRICS countries: Does the environmental Kuznets curve exist? J Public Aff 21(1):e2126
Uzair Ali M, Gong Z, Ali MU, Asmi F, Muhammad R (2022) CO2 emission, economic development, fossil fuel consumption and population density in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh: a panel investigation. Int J Financ Econ 27(1):18–31
Wan Q, Miao X, Afshan S (2022) Dynamic effects of natural resource abundance, green financing, and government environmental concerns toward the sustainable environment in China. Resour Policy 79:102954
Wang S, Zhou D, Zhou P, Wang Q (2011) CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in China: A panel data analysis. Energy Policy 39(9):4870–4875
Wang Q, Dong Z, Li R, Wang L (2022) Renewable energy and economic growth: new insight from country risks. Energy 238:122018
Wang SX, Fu YB, Zhang ZG (2015) Population growth and the environmental Kuznets curve 36:146–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chieco.2015.08.012
**e Q, Adebayo TS, Irfan M, Altuntaş M (2022) Race to environmental sustainability: can renewable energy consumption and technological innovation sustain the strides for China? Renew Energy 197:320–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.07.138
Yilanci V, Pata UK (2020) Investigating the EKC hypothesis for China: the role of economic complexity on ecological footprint. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:32683–32694
You W-H, Zhu H-M, Yu K, Peng C (2015) Democracy, financial openness, and global carbon dioxide emissions: heterogeneity across existing emission levels. World Dev 66:189–207
Zhang Y, Wang Q, Tian T, Yang Y (2022) Volatility in natural resources, economic performance, and public administration quality: Evidence from COVID-19. Resour Policy 76:102584
Zhao J, Jiang Q, Dong X, Dong K (2020) Would environmental regulation improve the greenhouse gas benefits of natural gas use? A Chinese case study. Energy Econ 87:104712
Zhu H, Duan L, Guo Y, Yu K (2016) The effects of FDI, economic growth and energy consumption on carbon emissions in ASEAN-5: evidence from panel quantile regression. Econ Model 58:237–248
Funding
There is no funding for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The conception and design of the study were performed by Hêriş Golpîra and Cosimo Magazzino. Hêriş Golpîra, Heibatolah Sadeghi, and Cosimo Magazzino collected the data, carried out the experiments, summarized the results, and wrote the first draft manuscript. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This manuscript has not been submitted to any other publication for simultaneous consideration. The submitted work is original and it has not been published elsewhere in any form or language (partially or in full) unless the new work concerns an expansion of previous work. A single study has not been split up into several parts to increase the number of submissions and submitted to various publications or to one publication over time. Results have been presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification, or inappropriate data manipulation. We adhere to discipline-specific rules for acquiring, selecting, and processing data. No data, text, or theories by others are presented as if they were the author’s own (‘plagiarism’).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interest
I wish to confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Arshian Sharif
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Golpîra, H., Sadeghi, H. & Magazzino, C. Examining the Energy-Environmental Kuznets Curve in OECD Countries Considering their Population. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 94515–94536 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28923-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28923-w