Abstract
Studies have documented that per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) exposures are associated with thyroid hormones (TH) and lipid levels. This study investigates whether these effects interfere with each other. We analyzed data on 3954 adults in the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES; 2007–2012). TH disorder was defined using thyroid hormones. Serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, total cholesterol, and six types of PFAS were included. Weighted quantile sum (WQS) regression was used to estimate the overall effect of PFAS mixture on TH disorder and cholesterols, respectively. Potential confounders, including age, race, gender, education, household poverty, smoking, and alcohol drinking, were adjusted. PFAS mixture was associated increased risk for TH disorder (odds ratio = 1.21, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.02, 1.43), higher HDL cholesterol (linear coefficient = 1.31, 95% CI: 0.50, 2.11), and higher total cholesterol (linear coefficient = 5.30, 95% CI: 3.40, 7.21). TH disorder was associated with higher HDL cholesterol (linear coefficient = 2.30, 95% CI: 0.50, 2.11), but not total cholesterol. When adjusted for TH disorder, the effect estimates of PFAS mixture remain roughly unchanged on HDL cholesterol (linear coefficient = 1.13, 95% CI: 0.28, 1.98) and total cholesterol (linear coefficient = 5.61, 95% CI: 3.58, 7.63). Sex modified the effect of PFAS mixture on HDL cholesterol (P for interaction: 0.04) but did not change the interaction between PFAS and TH disorder on cholesterols. We corroborated the adverse health effects of PFAS exposure on TH and lipids; however, these two effects appear to be independent of and not interfere with each other.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
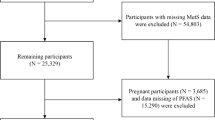
The data are available from the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007–2012.
References
Andersen ME, Hagenbuch B, Apte U, Corton JC, Fletcher T, Lau C, Longnecker MP (2021) Why is elevation of serum cholesterol associated with exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in humans? A workshop report on potential mechanisms. Toxicology 459:152845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2021.152845
Beggs KM, McGreal SR, McCarthy A, Gunewardena S, Lampe JN, Lau C, Apte U (2016) The role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha in perfluorooctanoic acid- and perfluorooctanesulfonic acid-induced hepatocellular dysfunction. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 304:18–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2016.05.001
Behr A-C, Plinsch C, Braeuning A, Buhrke T (2020) Activation of human nuclear receptors by perfluoroalkylated substances (PFAS). Toxicol in Vitro 62:104700
Boas M, Main KM, Feldt-Rasmussen U (2009) Environmental chemicals and thyroid function: an update. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 16(5):385–391. https://doi.org/10.1097/MED.0b013e3283305af7
Bobb JF, Valeri L, Claus Henn B, Christiani DC, Wright RO, Mazumdar M, Coull BA (2015) Bayesian kernel machine regression for estimating the health effects of multi-pollutant mixtures. Biostatistics 16(3):493–508
Calafat AM, Kuklenyik Z, Reidy JA, Caudill SP, Tully JS, Needham LL (2007) Serum concentrations of 11 polyfluoroalkyl compounds in the U.S. population: data from the national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES). Environmen Sci Technol 41(7):2237–2242. https://doi.org/10.1021/es062686m
Caporale N, Leemans M, Birgersson L, Germain P-L, Cheroni C, Borbély G, Cavallo F (2022) From cohorts to molecules: adverse impacts of endocrine disrupting mixtures. Science 375(6582):eabe8244
Carrico C, Gennings C, Wheeler DC, Factor-Litvak P (2015) Characterization of weighted quantile sum regression for highly correlated data in a risk analysis setting. J Agric Biol Environ Stat 20(1):100–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13253-014-0180-3
Chang SC, Thibodeaux JR, Eastvold ML, Ehresman DJ, Bjork JA, Froehlich JW, Butenhoff JL (2008) Thyroid hormone status and pituitary function in adult rats given oral doses of perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS). Toxicology 243(3):330–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2007.10.014
Cleeman JI, Grundy SM, Becker D, Clark LT, Cooper RS, Denke MA, Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (2001) Executive summary of the Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) expert panel on detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood cholesterol in adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). Jama-J Am Med Assoc 285(19):2486–2497. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.285.19.2486
Das KP, Wood CR, Lin MT, Starkov AA, Lau C, Wallace KB, Abbott BD (2017) Perfluoroalkyl acids-induced liver steatosis: effects on genes controlling lipid homeostasis. Toxicology 378:37–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2016.12.007
Dunder L, Lind PM, Salihovic S, Stubleski J, Karrman A, Lind L (2022) Changes in plasma levels of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are associated with changes in plasma lipids-a longitudinal study over 10 years. Environmental Research 211:112903. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112903
Duntas LH, Brenta G (2018) A renewed focus on the association between thyroid hormones and lipid metabolism. Front Endocrino 9:511. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00511
Fletcher T, Galloway TS, Melzer D, Holcroft P, Cipelli R, Pilling LC, Harries LW (2013) Associations between PFOA, PFOS and changes in the expression of genes involved in cholesterol metabolism in humans. Environ Int 57:2–10
Fragki S, Dirven H, Fletcher T, Grasl-Kraupp B, BjerveGutzkow K, Hoogenboom R, Luijten M (2021) Systemic PFOS and PFOA exposure and disturbed lipid homeostasis in humans: what do we know and what not? Critical Rev Toxicol 51(2):141–164. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408444.2021.1888073
Franco M, Chávez E, Pérez-Méndez O (2011) Pleiotropic effects of thyroid hormones: learning from hypothyroidism. J Thyroid Res. 321030. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/321030
Gao CX, Yang B, Guo Q, Wei LH, Tian LM (2015) High thyroid-stimulating hormone level is associated with the risk of develo** atherosclerosis in subclinical hypothyroidism. Horm Metab Res 47(3):220–224. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1394370
Jones PD, Hu WY, De Coen W, Newsted JL, Giesy JP (2003) Binding of perfluorinated fatty acids to serum proteins. Environ Toxicol Chem 22(11):2639–2649. https://doi.org/10.1897/02-553
Kato K, Wong LY, Jia LT, Kuklenyik Z, Calafat AM (2011) Trends in exposure to polyfluoroalkyl chemicals in the U.S. Population: 1999–2008. Environ Sci Technol 45(19):8037–8045. https://doi.org/10.1021/es1043613
Keil AP, Buckley JP, O’Brien KM, Ferguson KK, Zhao S, White AJ (2020) A quantile-based g-computation approach to addressing the effects of exposure mixtures. Environ Health Perspect 128(4):047004
Kim KI, Kim MA, Kim MK, Kim SH, Kim HS, Moon MK, Manage CKG (2016) 2015 Korean guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia: executive summary (english translation). Korean Circulation J 46(3):275–306. https://doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2016.46.3.275
Kim MJ, Moon S, Oh BC, Jung D, Ji K, Choi K, Park YJ (2018) Association between perfluoroalkyl substances exposure and thyroid function in adults: a meta-analysis. PloS One, 13(5):e0197244. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197244
Li CH, Ren XM, Ruan T, Cao LY, **n Y, Guo LH, Jiang G (2018) Chlorinated polyfluorinated ether sulfonates exhibit higher activity toward peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors signaling pathways than perfluorooctanesulfonate. Environ Sci Technol 52(5):3232–3239. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b06327
Lin CY, Chen PC, Lin YC, Lin LY (2009) Association among serum perfluoroalkyl chemicals, glucose homeostasis, and metabolic syndrome in adolescents and adults. Diabetes Care 32(4):702–707. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc08-1816
Liu FH, Hwang JS, Kuo CF, Ko YS, Chen ST, Lin JD (2018) Subclinical hypothyroidism and metabolic risk factors association: a health examination-based study in northern Taiwan. Biomed J 41(1):52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bj.2018.02.002
Long M, Ghisari M, Bonefeld-Jorgensen EC (2013) Effects of perfluoroalkyl acids on the function of the thyroid hormone and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(11):8045–8056. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1628-7
Lopez-Espinosa MJ, Mondal D, Armstrong B, Bloom MS, Fletcher T (2012) Thyroid function and perfluoroalkyl acids in children living near a chemical plant. Environ Health Perspect 120(7):1036–1041. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1104370
Luxia L, **gfang L, Songbo F, Xulei T, Lihua M, Weiming S, Pei S (2021) Correlation between serum TSH levels within normal range and serum lipid profile. Hormone Metabol Res 53(1):32–40. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1191-7953
Ma Y, Yang J, Wan Y, Peng Y, Ding S, Li Y, Xu S (2018) Low-level perfluorooctanoic acid enhances 3 T3–L1 preadipocyte differentiation via altering peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma expression and its promoter DNA methylation. J Appl Toxicol 38(3):398–407. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3549
Malin AJ, Lesseur C, Busgang SA, Curtin P, Wright RO, Sanders AP (2019) Fluoride exposure and kidney and liver function among adolescents in the United States: NHANES, 2013–2016. Environ Int 132:105012
Melzer D, Rice N, Depledge MH, Henley WE, Galloway TS (2010) Association between serum perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and thyroid disease in the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Environ Health Perspect 118(5):686–692. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.0901584
Olsen GW, Burris JM, Ehresman DJ, Froehlich JW, Seacat AM, Butenhoff JL, Zobel LR (2007) Half-life of serum elimination of perfluorooctanesulfonate, perfluorohexanesulfonate, and perfluorooctanoate in retired fluorochemical production workers. Environ Health Perspect 115(9):1298–1305. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.10009
Peppa M, Betsi G, Dimitriadis G (2011) Lipid abnormalities and cardiometabolic risk in patients with overt and subclinical thyroid disease. J Lipids 575840. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/575840
Porterfield SP (1994) Vulnerability of the develo** brain to thyroid abnormalities: environmental insults to the thyroid system. Environ Health Perspect 102 Suppl 2(Suppl 2), 125–130. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.94102125
Reinehr T (2010) Obesity and thyroid function. Mol Cell Endocrinol 316(2):165–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2009.06.005
Rigamonti E, Chinetti-Gbaguidi G, Staels B (2008) Regulation of macrophage functions by PPAR-α, PPAR-γ, and LXRs in mice and men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28(6):1050–1059
Shah AD, Bartlett JW, Carpenter J, Nicholas O, Hemingway H (2014) Comparison of random forest and parametric imputation models for imputing missing data using MICE: a CALIBER study. Am J Epidemiol 179(6):764–774
Steenland K, Tinker S, Frisbee S, Ducatman A, Vaccarino V (2009) Association of perfluorooctanoic acid and perfluorooctane sulfonate with serum lipids among adults living near a chemical plant. Am J Epidemiol 170(10):1268–1278. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwp279
Unal E, Akin A, Yildirim R, Demir V, Yildiz I, Haspolat YK (2017) Association of subclinical hypothyroidism with dyslipidemia and increased carotid intima-media thickness in children. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 9(2):144–149. https://doi.org/10.4274/jcrpe.3719
US Department of Health Human Services Centers for Disease Control Prevention (2005) Laboratory Procedure Manual. https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/2009-2010/labmethods/PFC_F_Polyfluorinated_Compounds_met.pdf. Accessed 18 July 2023
Vanden Heuvel JP, Thompson JT, Frame SR, Gillies PJ (2006) Differential activation of nuclear receptors by perfluorinated fatty acid analogs and natural fatty acids: a comparison of human, mouse, and rat peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha, -beta, and -gamma, liver X receptor-beta, and retinoid X receptor-alpha. Toxicol Sci 92(2):476–489. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfl014
Wan HT, Zhao YG, Wei X, Hui KY, Giesy JP, Wong CK (2012) PFOS-induced hepatic steatosis, the mechanistic actions on beta-oxidation and lipid transport. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820(7):1092–1101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.03.010
Webster GM, Rauch SA, Marie NS, Mattman A, Lanphear BP, Venners SA (2016) Cross-sectional associations of serum perfluoroalkyl acids and thyroid hormones in US adults: variation according to TPOAb and iodine status (NHANES 2007–2008). Environ Health Perspect 124(7):935–942
Weiss JM, Andersson PL, Lamoree MH, Leonards PEG, van Leeuwen SPJ, Hamers T (2009) Competitive binding of poly- and perfluorinated compounds to the thyroid hormone transport protein transthyretin. Toxicol Sci 109(2):206–216. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfp055
White SS, Fenton SE, Hines EP (2011) Endocrine disrupting properties of perfluorooctanoic acid. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 127(1–2):16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.03.011
Wolf CJ, Takacs ML, Schmid JE, Lau C, Abbott BD (2008) Activation of mouse and human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha by perfluoroalkyl acids of different functional groups and chain lengths. Toxicol Sci 106(1):162–171. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfn166
Wolf CJ, Schmid JE, Lau C, Abbott BD (2012) Activation of mouse and human peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPARalpha) by perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs): further investigation of C4–C12 compounds. Reprod Toxicol 33(4):546–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2011.09.009
Xu J, Shimpi P, Armstrong L, Salter D, Slitt AL (2016) PFOS induces adipogenesis and glucose uptake in association with activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 290:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.11.002
Yamamoto J, Yamane T, Oishi Y, Kobayashi-Hattori K (2015) Perfluorooctanoic acid binds to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and promotes adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 79(4):636–639. https://doi.org/10.1080/09168451.2014.991683
Yuan Y (2011) Multiple imputation using SAS software. J Stat Softw 45:1–25
Zhao M, Liu L, Wang F, Yuan Z, Zhang X, Xu C, Zhao J (2016) A worthy finding: decrease in total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in treated mild subclinical hypothyroidism. Thyroid 26(8):1019–1029. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2016.0010
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82203292, 82203461), the Medical Science and Technology Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (Grant No. 2019111811570248), and the Guangzhou Science and Technology Planning Project (Grant No. 202201011314).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LZ and ZCW conceived the study design and drafted the manuscript. RY and BL collected the data. WNC and JZ performed statistical analyses. RXL and WML critically revised the manuscript. All authors approved the version for publication. JJL supervised the whole manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Wang, Z., Yang, R. et al. The interference between effects of PFAS exposure on thyroid hormone disorders and cholesterol levels: an NHANES analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 90949–90959 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28739-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28739-8