Abstract
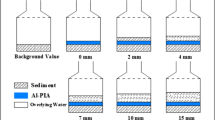
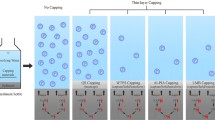
A biological aluminum–based P-inactivation agent (BA-PIA) has been developed and demonstrated to effectively remove nitrogen and phosphorus; however, whether it can control the release of nitrogen and phosphorus in sediment still needs study. This study aimed to examine the effect of BA-PIA on controlling sediment nitrogen and phosphorus release. BA-PIA was prepared by artificial aeration. The use of BA-PIA in controlling nitrogen and phosphorus release was studied using water and sediment from a landscape lake in static simulation experiments. The sediment microbial community was analyzed using high-throughput sequencing. Static simulation showed that the reduction rates of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) by BA-PIA were 66.8 ± 1.46% and 96.0 ± 0.98%, respectively. In addition, cap** of BA-PIA promotes the conversion of easily released nitrogen (free nitrogen) in the sediment to stable nitrogen (acid-hydrolyzable nitrogen). The content of weakly adsorbed phosphorus and iron-adsorbed phosphorus in the sediment was reduced. The relative abundance of nitrifying bacteria, denitrifying bacteria, and microorganisms carrying phosphatase genes (such as Actinobacteria) in the sediment increased by 109.78%. The cap** of BA-PIA not only effectively removed the nitrogen and phosphorus in water but greatly reduced the risk of nitrogen and phosphorus release from sediment. BA-PIA was able to make up for the deficiency of the aluminum-based phosphorus-locking agent (Al-PIA) that only removes phosphorus, giving it improved application prospects.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al-Tahmazi T, Babatunde AO (2016) Mechanistic study of P retention by dewatered waterworks sludges. Environ Technol Inno 6:38–48
Amin R, Reuther J, Bera A, Wohlleben W, Mast Y (2012) A novel GlnR target gene, nnaR, is involved in nitrate/nitrite assimilation in Streptomyces coelicolor. Microbiology 158:1172–1182
Borisenko GV, Makkaveev EP, Stunzhas PA (2021) Concentration and diffusion of nutrients in the interpore–bottom water system of the ob river estuary. Oceanology 61(1):25–33
Chai B, Wang S, Li S, Lei X, Li M (2021) Roles of bacterial biomass, physiology and community in sediment phosphorus solubilizing at varying hydrostatic pressures. J Clean Prod 282:124531
Chen T, Zou Z, Li J (2017) Transfer and transformation of 15NO3− in bioretention and effect of danish grass in the process. Environ Eng 35:60–64
Ding S, Sun Q, Chen X, Liu Q, Wang D, Lin J, Zhang C, Tsang DCW (2018) Synergistic adsorption of phosphorus by iron in lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock): new insight into sediment phosphorus immobilization. Water Res 134:32–43
Fraser T, Lynch DH, Entz MH, Dunfield KE (2015) Linking alkaline phosphatase activity with bacterial phoD gene abundance in soil from a long-term management trial. Geoderma 257:115–122
Gao L, Zhang L, Hou J, Wei Q, Fu F, Shao H (2013) Decomposition of macroalgal blooms influences phosphorus release from the sediments and implications for coastal restoration in Swan Lake, Shandong, China. Ecol Eng 60:19–28
Gui F, Yu G, Wang L (2014) Numerical simulation of exogenous source nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) loading from upstream watershed into the Taihu lake. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin 23(09):1265–1274
He T, Li Z, Sun Q, Xu Y, Ye Q (2016) Heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by Pseudomonas tolaasii Y-11 without nitrite accumulation during nitrogen conversion. Bio Technol 200:493–499
Hy A, Pan Y, Ming KC, Wei LD (2020) Use of lanthanum/aluminum co-modified granulated attapulgite clay as a novel phosphorus (P) sorbent to immobilize P and stabilize surface sediment in shallow eutrophic lakes - ScienceDirect. Chem Eng J 385
Kim G, Jeong W, Choi S, Khim J (2007) Sand cap** for controlling phosphorus release from lake sediments. Environ Technol 28(4):381–389
Le LT, Lee S, Bui XT, Jahng D (2020) Suppression of nitrite-oxidizing bacteria under the combined conditions of high free ammonia and low dissolved oxygen concentrations for mainstream partial nitritation. Environ Technol Inno 20:101135–201146
Li S, Zhou Z, Yang S, Liu S, Li F, Yuan B (2019) The efficiency of controlling the phosphorus release from the sediment using calcined modified water purification plant sludge (C-WTPS). J Lake Sci 31:961–968
Li B, Zhou Z, Ravi N, Hu Z, Guo D, Chen J (2021a) Combined remediation of eutrophic water by phoslock® and aerobic denitrifying bacteria. Environ Sci 42:1861–1869
Li J, Deng K, Zhang W, Sang C, Zhao Y, Xu R (2021b) Effects of amendment of glucose on fertilizer nitrogen transformation and acidification in ultisol cropland. Acta Pedol Sinica 58(1):162–168
Lin C, Li S, Zhu B, Liu S, Li T (2021) Al-PHOSLOCK thin-layer cap** to control phosphorus release from sediment: effect of hydraulic retention time and phosphorus migration/transformation mechanism. J Soils Sediments 21:2474–2482
Liu X, **e D, Li K, Zhou J, Wang H (2013) Influence of application of bio-energizer to sediment microbial community and the content of nitrogen and phosphorus element. China Environ Sci 33:87–92
Mikami Y, Nittami T, Kurisu F (2013) Effect of endogenous carbon source on biological denitrification rate. J Water Environ Technol 11(1):1–9
Myllynen K, Ojutkangas E, Nikinmaa M (1997) River water with high iron concentration and low pH causes mortality of lamprey roe and newly hatched larvae. Eco Environ Safe 36(1):43
Rydin E (2000) Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Res 34(7):2037–2042
State Environmental Protection Administration (SEPA) of China (2002) Monitoring and analyzing methods of water and wastewater, 4th edn. China Environment Science Press, Bei**g
Varjo E, Liikanen A, Salonen VP, Martikainen PJ (2003) A new gypsum-based technique to reduce methane and phosphorus release from sediments of eutrophied lakes: (Gypsum treatment to reduce internal loading). Water Res 37(1):1–10
Vlerken FV (1998) Chances for biological techniques in sediment remediation. Water Sci Technol 37:345–353
Wang S, Jiang X, Zhong L, ** X, Sun S (2010) Seasonal occurrence characteristics of ifdrent forms of nitrogen in the sediments of Chaohu lake. Environ Sci 31(04):946–953
Wang Y, Li S, Liu S, Li F, Zhou Z (2022a) Three kinds of active thin-layer cap** materials for reducing the phosphorus load in eutrophic water body: comparison in dynamic experiment. Environ Sci and Pollut R 29(11):16427–16435
Wang Y, Yuan S, Liu S, Li F, Zhou Z (2022b) Effect of aluminum-based P-inactivation agent (Al-PIA) cap** on bacterial community in sediment. J Soils Sediments 22(4):1344–1354
Wang Y, Yuan S, Liu S, Li F, Zhou Z (2023) Removal efficacy and mechanism of nitrogen and phosphorus by biological aluminum-based P-inactivation agent (BA-PIA). J Environ Sci 127:187–196
Wu T, Qin B, Brookes JD, Yan W, Ji X, Feng J (2019) Spatial distribution of sediment nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Taihu from a hydrodynamics-induced transport perspective. Sci Total Environ 650:1554–1565
Yu Y, Chen C, Wu Y, Yu L (2015) The effect of covering on sediment in a canyon type lake under the anaerobic condition. Environ Eng 33(2):53–57
Yuan X, Cui X, Yin J, Li N, Wang M, Shen D (2020) Application of quorum sensing in bioaugmentation for denitrification process with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Sci Circumst 40(05):1661–1666
Zekker I, Rikmann E, Tenno T, Vabamäe P, Kroon K, Loorits L, Saluste A, Taavo T (2012) Effect of HCO3− concentration on anammox nitrogen removal rate in a moving bed biofilm reactor. Environ Technol 33(20):2263–2271
Zekker I, Rikmann E, Tenno T, Kroon K, Seiman A, Loorits L, Fritze H, Tuomivirta T, Priit V, Raudkivi M, Mandel A, Tenno T (2015) Start-up of low-temperature anammox in UASB from mesophilic yeast factory anaerobic tank inoculum. Environ Technol 36(2):214–225
Zhan Y, Yu Y, Lin J, Wu X, Zhao Y (2020) Assessment of iron-modified calcite/zeolite mixture as a cap** material to control sedimentary phosphorus and nitrogen liberation. Environ Sci and Pollut R 27(4):1–17
Zhou Z, Huang T, Yuan B (2016) Nitrogen reduction using bioreactive thin-layer cap** (BTC) with biozeolite: A field experiment in a eutrophic river. J Environ Sci 42:1119–1125
Zhou Z, Liu Q, Li S, Li F, Zou J, Liao X, Yuan B, Sun W (2018) Characterizing the correlation between dephosphorization and solution pH in a calcined water treatment plant sludge. Environ Sci Pollut R 25:18510–18518
Zhou Z, Lin C, Li S, Liu S, Li F, Yuan B (2022) Four kinds of cap** materials for controlling the phosphorus and nitrogen release from contaminated sediment: comparison in static simulation experiment. Front Environ Sci Eng 16(3):1–9
Zhu B, Li S, Lin C, Liu S, Li F, Zhou Z (2021) The effect of secondary cap** on the control of phosphorus release from sediment by activated thin-layer cap** with Al-PIA. Environ Sci and Pollut R 28(14):18062–18069
Zhuo T, Ding Y, Wan Q, Li S, Chai B, Lei X (2021) Effects of hydrostatic pressure on phosphorus transformation at the water-sediment interface of a deep reservoir: novel insights into bacterial community and functional genes. J Soils Sediments 21(10):3367–3379
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Fund of China (Grant No. 51878300), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China (Grant No. 2019J01052), and the Science and Technology Project Foundation of **amen City (Grant No. 3502Z20203044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yichao Wang: writing—original draft, visualization, formal analysis. Xue** Tang: investigation, data curation. Chunming Gong: investigation, writing—review and editing. Chen Huang: validation, writing—review and editing. **aohai Wu: validation, writing—review and editing. Fei Li: writing—review and editing. Zhenming Zhou: conceptualization, resources, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
The participant has consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, ., Tang, X., Gong, C. et al. Effect of controlling nitrogen and phosphorus release from sediment using a biological aluminum–based P-inactivation agent (BA-PIA). Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 86425–86436 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28521-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-28521-w