Abstract
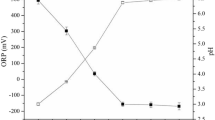
Lanthanum-modified drinking water treatment sludge (DTSLa) and thermal-modified drinking water treatment sludge (TDTS) were prepared from drinking water treatment sludge(DTS). The adsorption properties of DTSLa and TDTS on phosphate in water and the effects on the controlled release and morphology of phosphorus in sediment at different dosages (0%, 2.5%, 5%) were discussed. Combining with SEM, BET, XRD, FTIR, and XPS characterization methods, the immobilization mechanism of DTSLa and TDTS on phosphorus in sediment was explored. The addition of TDTS can transform NH4Cl-P (loosely sorbed P), BD-P (bicarbonate–dithionite extractable P), and Org-P (organic P) into stable NaOH-rP (metal oxide-bound P) in sediment, and the conversion amount will increase with the increase of TDTS supplemental amount. DTSLa converted NH4Cl-P, BD-P, Org-P, and NaOH-rP to more stable HCl-P (calcium-bound P). At the same time, the content of WSP (water-soluble phosphorus) and olsen-P (NaHCO3 extractable P) in sediment can be reduced by the addition of DTSLa and TDTS, reducing the risk of the release of phosphorus from the sediment to the overlying water. In addition, phosphorus can be directly removed from the interstitial water by DTSLa and TDTS, so as to reduce the phosphorus concentration gradient between the overlying water and the interstitial water, thus inhibiting the release of phosphorus from interstitial water to overlying water. The results showed that DTSLa is better than TDTS in terms of its adsorption capacity and adsorption effect on endogenous phosphorus in water, so DTSLa is more suitable to be used as a sediment conditioner to control the phosphorus content in water and sediment.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data used for this work are publicly available.
References
Berg U, Neumann T, Donnert D, Nuesch R, Stuben D (2004) Sediment cap** in eutrophic lakes-efficiency of undisturbed calcite barriers to immobilize phosphorus. Appl Geochem 19:1759–1771
Beutel MW, Leonard TM, Dent SR, Moore BC (2008) Effects of aerobic and anaerobic conditions on P, N, Fe, Mn, and Hg accumulation in waters overlaying profundal sediments of an oligo-mesotrophic lake. Water Res 42:1953–1962
Copetti D, Finsterle K, Marziali L, Stefani F, Tartari G, Douglas G, Reitzel K, Spears BM, Winfield IJ, Crosa G, Haese PD, Yasseri S, Lurling M (2016) Eutrophication management in surface waters using lanthanum modified bentonite: A review. Water Res 97:162–174
Dong SX, Wang YI, Zhao YW, Zhou XH, Zheng HI (2017) La3+/La(OH)(3) loaded magnetic cationic hydrogel composites for phosphate removal: effect of lanthanum species and mechanistic study. Water Res 126:433–441
D’Haese PC, Douglas G, Verhulst A, Neven E, Behets GJ, Vervaet BA, Finsterle K, Lürling M, Spears B (2019) Human health risk associated with the management of phosphorus in freshwaters using lanthanum and aluminium. Chemosphere 220:213–286
He YX, Zhang LM, An X, Wan GP, Zhu WJ, Luo YM (2019) Enhanced fluoride removal from water by rare earth (La and Ce) modified alumina: adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and mechanism. J Food Process Technol 688:184–198
He LWZ, Chen Y, Sun F, Li YJ, Huang W, Yang SS (2022) Controlled release of phosphorus using lanthanum-modified hydrochar synthesized from water treatment sludge: adsorption behavior and immobilization mechanism. J Water Process Eng 50:103319
Ippolito JA, Barbarick KA, Elliott HA (2011) Drinking water treatment residuals: a review of recent uses. J Environ Qual 40:1–12
Jeppesen E, Sondergaard M, Jensen JP, Havens KE, Anneville O, Carvalho L, Coveney MF et al (2005) Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading - an analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshwater Biol 50:1747–1771
Jiang X, ** XC, Yao Y, Li LH, Wu FC (2008) Effects of biological activity, light, temperature and oxygen on phosphorus release processes at the sediment and water interface of Taihu Lake, China. Water Res 42:2251–2259
Kim LH, Choi E, Stenstrom MK (2003) Sediment characteristics, phosphorus types and phosphorus release rates between river and lake sediments. Chemosphere 50:53–61
Lurling M, van Oosterhout F (2013) Controlling eutrophication by combined bloom precipitation and sediment phosphorus inactivation. Water Res 47:6527–6537
Lurling M, Mackay E, Reitzel K, Spears BM (2016) Editorial – a critical perspective on geo-engineering for eutrophication management in lakes. Water Res 97:1–10
Lin JW, He SQ, Zhang HH, Zhan YH, Zhang ZB (2019) Effect of zirconium-modified zeolite addition on phosphorus mobilization in sediments. J Food Process Technol 646:144–157
Li XD, **e Q, Chen SH, **ng MC, Guan T, Wu DY (2019) Inactivation of phosphorus in the sediment of the Lake Taihu by lanthanum modified zeolite using laboratory studies. Environ Pollut 247:9–17
Lin JW, Wang H, Zhang YH, Zhang Z (2016) Evaluation of sediment amendment with zirconium-reacted bentonite to control phosphorus release. Environ Earth Sci 75:942
Li JPH, Zhou XH, Pang YQ et al (2017) Understanding of binding energy calibration in XPS of lanthanum oxide by in situ treatment. Phys Chem Chem Phys 21:22351–22358
Laakso J, Uusitalo R, Heikkinen J et al (2017) Phosphorus in agricultural constructed wetland sediment is sparingly plant available. J Plant Nutr and Soil Sc 180:554–562
Mallet M, Barthelemy K, Ruby C, Renard A, Naille S (2013) Investigation of phosphate adsorption onto ferrihydrite by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J Colloid Interface Sci 407:95–101
Muisa N, Nhapi I, Ruziwa W, Manyuchi MM (2020) Utilization of alum sludge as adsorbent for phosphorus removal in municipal wastewater: a review. J Water Process Eng 35:101187
Meis S, Spears BM, Maberly SC, O’Malley MB, Perkins RG (2012) Sediment amendment with Phoslock(R) in Clatto Reservoir(Dundee, UK): investigating changes in sediment elemental composition and phosphorus fractionation. J Environ Manage 93:185–193
Nguyen MD, Adhikari S, Mallya DS et al (2022) Reuse of aluminium-based water treatment sludge for phosphorus adsorption: evaluating the factors affecting and correlation between adsorption and sludge properties. Environ Technol Innov 27:102717–102717
Pu J, Wang SR, Ni ZK, Wu Y, Liu XF, Wu T, Wu HX (2021) Implications of phosphorus partitioning at the suspended particle-water interface for lake eutrophication in China’s largest freshwater lake. Poyang Lake Chemosphere 263:128334
Ribeiro DC, Martins G, Nogueira R, Brito AG (2014) Mineral cycling and pH gradient related with biological activity under transient anoxic-oxic conditions: effect on P mobility in volcanic lake sediments. Environ Sci Technol 48:9205–9210
Rydin E, Welch EB (1998) Aluminum dose required to inactivate phosphate in lake sediments. Water Res 32:2969–2976
Shen XX, Yuan NN, Wang CH (2020) The bioturbation effect of the snail Bellamya aeruginosa on phosphorus immobilisation by drinking water treatment residue in sediment: a long-term continuous flow test. J Environ Manage 266:110579
Su Y, Cui H, Li Q, Gao SA, Shang JK (2013) Strong adsorption of phosphate by amorphous zirconium oxide nanoparticles. Water Res 47:518–5026
Truong TV, Kim DJ (2021) Phosphate removal using thermally regenerated Al adsorbent from drinking water treatment sludge. Environ Res 196:110877
Totlani K, Mehta R, Mandavgane SA (2012) Comparative study of adsorption of Ni(II) on RHA and carbon embedded silica obtained from RHA. Chem Eng J 181:376–386
Wu BL, Fang LP, Fortner JD et al (2008) Highly efficient and selective phosphate removal from wastewater by magnetically recoverable La(OH)(3)/Fe3O4 nanocomposites. Water Res 126:179–188
Wang CH, Qi Y, Pei YS (2012) Laboratory investigation of phosphorus immobilization in lake sediments using water treatment residuals. Chem Eng J 209:379–385
Wang CH, Gao SJ, Pei YS, Zhao QY (2013) Use of drinking water treatment residuals to control the internal phosphorus loading from lake sediments: laboratory scale investigation. Chem Eng J 225:93–99
Wang CH, Yuan NN, Pei YS, Jiang HL (2015) Aging of aluminum/iron-based drinking water treatment residuals in lake water and their association with phosphorus immobilization capability. J Environ Manage 119:178–185
Waajen G, van Oosterhout F, Douglas G, Lurling M (2016) Management of eutrophication in Lake De Kuil (The Netherlands) using combined flocculant – lanthanum modified bentonite treatment. Water Res 97:83–95
Wang CH, He R, Wu Y, Lurling M, Cai HY, Jiang HL, Liu X (2017) Bioavailable phosphorus (P) reduction is less than mobile P immobilization in lake sediment for eutrophication control by inactivating agents. Water Res 109:196–206
Wu BL, Wan J, Zhang YY, Pan BC, Lo IMC (2020) Selective phosphate removal from water and wastewater using sorption: process fundamentals and removal mechanisms. Environ Sci Technol 54:50–66
**ng XL, Chen MS, Wu YX, Tang YZ, Li C (2021) The decomposition of macrozoobenthos induces large releases of phosphorus from sediments. Environ Pollut 283:117104
Xu D, Ding SM, Sun Q, Zhong JC, Wu W, Jia F (2012) Evaluation of in situ cap** with clean soils to control phosphate release from sediments. J Food Process Technol 438:334–341
Yang MJ, Lin JW, Zhan YH, Zhang HH (2014) Adsorption of phosphate from water on lake sediments amended with zirconium-modified zeolites in batch mode. Ecol Eng 71:223–233
Yang MJ, Lin JW, Zhan YH, Zhu ZL, Zhang HH (2015a) Immobilization of phosphorus from water and sediment using zirconium-modified zeolites. Environ Sci Pollutr 22:3606–3619
Yin HB, Yang P, Kong M, Li W (2019) Use of lanthanum/aluminum co-modified granulated attapulgite clay as a novel phosphorus (P) sorbent to immobilize P and stabilize surface sediment in shallow eutrophic lakes. Chem Eng J 385:123395
Yang L, Wei J, Liu ZY, Wang JL, Wang DT (2015b) Material prepared from drinking waterworks sludge as adsorbent for ammonium removal from wastewater. Appl Surf Sci 330:228–236
Yang J, Dai Y, Zhu XY et al (2015c) Metal-organic frameworks with inherent recognition sites for selective phosphate sensing through their coordination-induced fluorescence enhancement effect. J Mater Chem A 3:7445–7452
Zhou Q, Gibson CE, Zhu Y (2001) Evaluation of phosphorus bioavailability in sediments of three contrasting lakes in China and the UK. Chemosphere 42:221–225
Zilius M, Giordani G, Petkuviene J, Lubiene I, Ruginis T, Bartoil M (2015) Phosphorus mobility under short-term anoxic conditions in two shallow eutrophic coastal systems ( Curonian and Sacca di Goro lagoons). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 164:134–146
Zhu XD, Liu YC, Qian F, Zhou C, Zhang SC, Chen JM (2014) Preparation of magnetic porous carbon from waste hydrochar by simultaneous activation and magnetization for tetracycline removal. Biores Technol 154:209–214
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fei Sun: conceptualization, data curation, writing—original draft. Liwenze He: resources, software, data curation. **gxiang Tang: visualization, writing—review & editing. Yanjun Li: validation, writing—review & editing. Yu Chen: methodology, project administration, supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All of the authors consent to publish this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, F., Chen, Y., He, L. et al. Comparative study of sediment phosphorus immobilization via the addition of lanthanum-modified and thermal-modified drinking water treatment sludge. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 76227–76245 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27960-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27960-9