Abstract
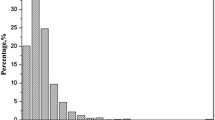
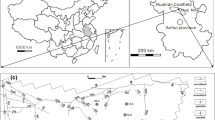
The coal found in the Longtan Formation of the Late Permian is widely distributed in Southwest China, including the northwestern Guizhou, southeastern Sichuan, and northern Yunnan regions. This coal typically has a high sulfur content. Eighty-two coal samples were collected from the coal strata in 11 counties spanning this area, including underground mine coal, native outcrop coal and man-made outcrop coal. The mercury, total fluorine, total sulfur, and sulfate contents and pH values were determined. The results showed that the average mercury content in native outcrop coal was 2233 ng/g, whereas that in underground mine coal was 306 ng/g, and the relative enrichment factor could reach 6.6. There was no significant difference in the total fluorine content among the three types of coals; furthermore, the total sulfur content in native outcrop coal and man-made outcrop coal was higher than that in underground mine coal because of the local policy, which strictly prohibits the mining of high-sulfur coal. Native outcrop coal is acidic, with a total average pH of 3.54 and an average sulfate content as high as 13,390 μg/g. In contrast, underground coal is almost neutral (average pH 7.33), with a low sulfate content (average 3221 μg/g). These characterizations indicate that native outcrop coal has been subjected to long-term weathering and the mercury enrichment is likely due to migration, oxidation, and precipitation of Hg from the underground coal seam and enriched in loose and pulverized coal particles. Further investigation is needed to determine whether other outcrop areas are affected by this phenomenon.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Belkin HE, Tewalt SJ, Finkelman RB, Zheng BS, Wu DS, Li SH (2006) Mercury in coal from the People’s Republic of China. Chin J Geochem 25(z1):52
Belkin HE, Finkelman RB, Zheng BS (1999) Human health effects of domestic combustion of coal a causal factor for arsenosis and fluorosis in rural China. Proceedings of Air Quality conference. McLean, VA: Energy and Environmental Research Center, University of North Dakota
Cao QY, Liang HD, Li CH, Yang L (2019) Analysis of mercury speciations in Late Permian coal from the border area of Yunnan, Guizhou and Sichuan provinces. China Environ Sci 39:377–384
Chang CY, Chen CY, Yin RS, Shen Y, Mao K, Yang ZG, Feng XB, Zhang H (2020) Bioaccumulation of Hg in rice leaf facilitates selenium bioaccumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L) leaf in the Wanshan Mercury Mine. Environ Sci Technol 54:3228–3236
Dai SF, Ren DY (2006) Fluorine concentration of coals in China—an estimation considering coal reserves. Fuel 85:929–935
Dai SF, Zeng RS, Sun YZ (2006) Enrichment of arsenic, antimony, mercury, and thallium in a Late Permian anthracite from **ngren, Guizhou, Southwest China. Int J of Coal Geol 66:217–226
Dai SF, Li WW, Tang YG, Zhang Y, Feng P (2007) The sources, pathway, and preventive measures for fluorosis in Zhi** County, Guizhou, China. Appl Geochem 22:1017–1024
Dai SF, Liu J, Ward CR (2016) Mineralogical and geochemical compositions of Late Permian coals and host rocks from the Guxu Coalfield, Sichuan Province, China, with emphasis on enrichment of rare metals. Int J of Coal Geol 166:71–95
Diehl SF, Goldhaber MB, Hatch JR (2004) Modes of occurrence of mercury and other trace elements in coals from the warrior field, Black Warrior Basin. Northwestern Alabama. Int J of Coal Geol 59:193–208
Ding ZH, Zheng BS, Finkelman RB, Belkin HE (2003) Discovery of a Hg-, Zn-, S-bearing mineral in coal. Geol Geochem 31:87–89
Feng XB, Qiu GL (2008) Mercury pollution in Guizhou, Southwestern China – an overview. Sci Total Environ 400:227–237
Feng XB, Hong YT, Ni JY, Zhou B, Wang Y (1998) Distribution and occurrence mode of Mercury in some coals of Guizhou Province and its environmental impact. Coal Geol Explor 26:12–14 (in Chinese)
Feng XB, Hong YT, Hong B (2001) Modes of occurrence of mercury in coal. Bull Minar Petrol Geochem 2:71–78
Feng XB, Chen JB, Fu XW (2013) Progress on environmental geochemistry of mercury. Bull Minar Petrol Geochem 32:503–530
Finkelman RB (2004) Potential health impacts of burning coal beds and waste banks. Int J of Coal Geol 59:19–24
Finkelman RB, Orem W, Castranova V, Tatu CA, Belkin HE, Zheng BS, Lerch HE, Maharag SV, Bates AL (2002) Health impacts of coal and coal use: possible solutions. Int J of Coal Geol 50:425–433
Gao LB, Wang YP, Huang QW, Guo SQ (2017) Modes of occurrence and thermal stability of mercury in different samples from Guandi coal preparation plant. Fuel 200:22–30
Gao LL, Fu CC, Feng XB, Li ZG, Zhou SQ (2018) Mercury influence of a coal-fired power plant in East Guizhou on the ambient air and soil. Environ Monitin China 34:51–58 (in Chinese)
Hong XP, Liang HD, Zhang YF (2017) Acidity characteristic of efflorescent clay in late Permian coal-bearing strata in border area of Yunnan, Guizhou and Sichuan. Environ Chem 36:1831–1841 (in Chinese)
Hong XP, Liang HD, Zhang YF (2018) Evaluation of acidity in late Permian outcrop coals and its association with endemic fluorosis in the border area of Yunnan, Guizhou, and Sichuan in China. Environ Geochem Health 40:1093–1109
Li P, Feng XB, Qiu GL, Li ZG, Fu XW, Sakamoto M (2008) Mercury exposures and symptoms in smelting workers of artisanal mercury mines in Wuchuan, Guizhou, China. Environ Res 107:108–114
Li RY, Xu XH, Xu ZD, Ao M, Shang LH, Qiu GL, Tang XL (2016) Total mercury and methylmercury concentration and risk assessment in rice plants collected from a river watershed in a typical mercury mining area of Guizhou. Res Environ Sci 29:1829–1839
Li CH, Sun JC, Shi JY, Liang HD, Cao QY, Li ZW (2020) Mercury sources in a subterranean spontaneous combustion area. Ecotox Environ Safe 201:110863
Li Z , Feng X , Bi X , et al (2013) Heavy metals in the ground surface dust and agricultural soil in artisanal and medium-scale zinc smelting area in Northwest Guizhou Province, China[C]// International conference on heavy metals in the environment. solid state communications
Liang HD, Liang YC, Gardella JAJ, He P (2011) Potential release of hydrogen fluoride from domestic coal in endemic fluorosis area in Guizhou, China. Chin Sci Bull 56:2301–2303
Liang YC, Liang HD, Zhu SQ (2014) Mercury emission from coal seam fire at Wuda, Inner Mongolia, China. Atmos Environ 83:176–184
Liang YC, Liang HD, Zhu SQ (2016) Mercury emission from spontaneously ignited coal gangue hill in Wuda coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Fuel 182:525–530
Liang LC,Xu XH, Han JL, Xu ZD, Wu P, Guo JY, Qiu GL (2019) Characteristics, speciation, and bioavailability of mercury and methylmercury impacted by an abandoned coal gangue in southwestern China.[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26(36):37001–37011
Liu ZX, Feng ZC (2012) Theoretical study on adsorption heat of methane in coal. J China Coal Soci 37:648–654
Liu YL, Luo KL, Ling L (2013) Fluoride and sulfur dioxide indoor pollution situation and control in coal-burning endemic area in Zhaotong, Yunnan, China. Atmos Environ 77:725–737
Liu YH, Hong XP, Liang HD, Li ZH (2019) Weathering of coal-series clay-pyrite in the area of desulfurization in Guizhou Province. Environ Chem 38:1318–1327 (in Chinese)
Liu J, Meng B, Poulain AJ, Meng OY, Feng XB (2021) Stable isotope tracers identify sources and transformations of mercury in rice (Oryza sativa L.) growing in a mercury mining area. Fundam Res 1:259–268
Luo KL, Li HJ, Chen TB, Wang WZ, Bi SG, Wu XZ, Ni W, Wang LH (2008) Content of arsenic, selenium, mercury in the coal, food, clay and drinking water in the Zhaotong fluorosis area, eastern Yunnan Province. J China Coal Soc 33:289–294 (in Chinese)
Luo KL, Li HJ, Niu CX (2010) Fluorine and arsenic pollution route of grain in Yunnan/Guizhou coal-burning endemic fluorosis area. Geol Rev 56:289–298 (in Chinese)
Luo KL, Li L, Zhang SX (2011) Coal-burning roasted corn and chili as the cause of dental fluorosis for children in southwestern China. J Hazard Mater 185:1340–1347
Nguyen L, Zhang LM, Lin DW, Lin NH, Sheu GR (2016) Eight-year dry deposition of atmospheric mercury to a tropical high mountain background site downwind of the East Asian continent. Environ Pollut 255:113128
Pacyna JM, Travnikov O, De Simone F, Hedgecook IM, Sundseth K, Pacyma EG, Steenhuisen F, Pirrone N, Munthe J, Kindbom K (2016) Current and future levels of mercury atmospheric pollution on a global scale. Atmos Chem Phys 16:12495–12511
Pilar L, Borovec K, Szeliga Z, Gorecki J (2021) Mercury emission from three lignite-fired power plants in the Czech Republic. Fuel Process Technol 212:106628
Pu HX, Luo KL, Zhang SX (2018) Risk assessment model for different foodstuff drying methods via AHP-FCE method: a case study of “coal-burning” fluorosis area of Yunan and Guizhou Province, China. Food Chem 263:74–80
Qin ZH, Yang ZB, Qin Y (2020) Geochemical characteristics of produced gas by CBM wells in western Guizhou. J China Coal Soc 45:712–720 (in Chinese)
Qiu H, Li JJ, Guo XQ, Xu Y, Cai DB (2018) Pollution characteristics of mercury in particulate matters around a coal-fired power plant in Guizhou Province in spring. Chin J Ecol 37:1545–1549
Ren DY, Zhao FH, Dai SF, Zhang JY, Luo KL (2006) The microelement geochemistry of coal. Science Press, Bei**g, p 272 (in Chinese)
Santos S, Machado R, Joana Neiva Correia M, Carvalho JR (2004) Treatment of acid mining waters. Miner Eng 17:225–232
Sun DJ (2011) Endemiology. People’s Medical Publishing House, Bei**g, pp 94–94
Tan H, He JL, Liang L, Lazoff S, Sommer J, **ao ZF, Lindgvist Q (2000) Atmospheric mercury deposition in Guizhou, China. Sci Total Environ 259:223–230
Tang XC, Wu XL, **a PH, Lin T, Huang XF, Zhang ZM, Zhang JC (2021) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and screening of accumulating plants around the Wanshan mercury mine in Northeast Guizhou Province, China. Enviro Sci Pollut Res 28:48837–48850
Tu R, Chen M, Li D (2018) The concentrations, distribution, and interrelation of mercury and selenium in human body in Wanshan mercury mining area. Chin J Ecol 37(5):1550–1555
Wang XB, Wang RX, Wei Q (2015) Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of Late Permian coals from the Mahe Mine, Zhaotong Coalfield, Northeastern Yunnan, China. Minerals 5:380–396
Wang XL, Ming J, Qiu B, Liao YF, Liao YD, Wei SF, Tu CL, Pan X (2019) Relationship between fluoride exposure, orthopedic injuries and bone formation markers in patients with coal-burning fluorosis. Chin J Appl Ecol 30:43–48 (in Chinese)
Wang XL, Li H, Lu Y, Lu JX, Shi SS (2022) Research status and prospect of methane adsorption and diffusion behavior in coal based on molecular simulation. China Energy Environ Prot 44:189–195
**a JC, Hu P, Wang JX (2016) Mercury pollution characteristics in Tongren Mercury Mining Area, Guizhou Province, China. Asian J Ecotoxicol 11:231–238
Yan JY, Wang C, Wang ZH (2019) Mercury concentration and speciation in mine wastes in Tongren mercury mining area, southwest China and environmental effects. Appl Geochem 106:112–119
Zhang JY, Ren DY, Xu DW, Liu JR, Dong B, Zhang CY (1999) The distribution of mercury in major associated minerals from coal beds in Southwestern Guizhou. Geol Rev 45:539–542 (in Chinese)
Zhang L, Wang SX, Wang L (2015) Updated emission inventories for speciated atmospheric mercury from anthropogenic sources in China. Environ Sci Technol 49:3185–3198
Zhao S, Duan Y, Yao T, Liu M, Lu JH, Tan HZ, Wang XB, Wu LT (2017) Study on the mercury emission and transformation in an ultra-low emission coal-fired power plant. Fuel 199:653–661
Zheng BS, Wu DS, Wang BB, Liu XJ, Wang MS (2005) Main geochemical processes that cause prevalence of coal-burning fluorosis. Chin J Endemiol 24:468–471 (in Chinese)
Zheng LG, Liu GJ, Qi CC, Chen YW, Zhang Y (2007) Study on environmental geochemistry of mercury in Chinese coals. J Univ Sci Technol China 37:953–963
Zheng L, Liu G, Chou CL (2008) Abundance and modes of occurrence of mercury in some low-sulfur coals from China. Int J Coal Geol 73:19–26
Zhou YP (1994) Occurrence and enrichmental factor of mercury from Laochang Coal mine. Coal Geol Explor 22:17–22 (in Chinese)
Zhou J, Wang Z, Zhang X, Zhang XS, Sun T (2017) Investigation of factors affecting mercury emission from subtropical forest soil: a field controlled study in southwestern China. J Geochem Explor 176:128–135
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Miss **g Lei for her assistance in the field work and Changqiu Zhao for his laboratory work.
Funding
This work was supported by the Anhui Natural Science Foundation Project (No. 2008085QD169), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41902172 and 41772157), and the Natural Science Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Anhui Province (No. KJ2020A1204).