Abstract
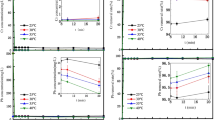
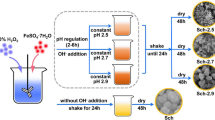
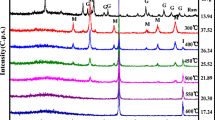
Iron hydroxides have received high attention in the treatment of chromium (Cr) polluted wastewater. In this study, the obtained chemical (or biological) pincushion-schwertmannite spheres had a diameter of 2 − 5 μm (0.5–1 μm), and akaganéite rods had a length of 300–500 nm (100–150 nm) at an axial ratio of about 3. The average diameters (μm) of their agglomerated particles in solutions were 20.6–32.5 (only 0.480 for Aka-Chem). Schwertmannites and akaganéites were used to investigate Cr(VI) adsorption behaviors in aqueous solutions by batch experiments, under various reaction times, initial Cr(VI) and adsorbent levels, pH values, temperature and anions of NO3−, Cl−, CO32−, SO42−, and H2PO4−. Adsorption data well fitted to pseudo-second-order rate model (R2 = 0.999), and Langmuir (R2 = 0.954–0.988) and Freundlich (R2 = 0.984–0.996) isothermal models at pH 7.0. Maximum Cr(VI) adsorption capacities were 119/133 for Sch-Chem/Sch-Bio, and 14.6/83.6 for Aka-Chem/Aka-Bio. The H2PO4− than SO42−/CO32− had a stronger effect on Cr(VI) adsorption. Adsorbents with pHZPC of near to 4.0 still had a good Cr(VI) removal ability at pH 3.0–8.0. The possible Cr(VI) adsorption mechanisms by FTIR and XPS results for schwertmannite and akaganéite were electrostatic attractions and ion exchanges between hydroxyl (or sulfate) and chromate ions. The Cr(VI) adsorption of optimal schwertmannite and bioakaganéite was a spontaneous, endothermic and random process at the temperatures of 288–318 K. They had a good regeneration ability for Cr(VI) adsorption, and removal ratios could reach to about 80% of original values (60–70% in aqueous solution with 60 mg/L Cr(VI) and pH7.0, and 35–50% in wastewater with 120 mg/L Cr(VI) and about pH4.0), after three cycles. Herein, schwertmannite/bioakaganéite have a promising application in treatment of acidic/neutral wastewater with chromate.
Graphical Abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Anah L, Astrini N (2017) Influence of pH on Cr(VI) ions removal from aqueous solutions using carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel as adsorbent. Earth Environ Sci 60:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/60/1/012010
Antelo J, Fiol S, Gondar D, Lopez R, Arce F (2012) Comparison of arsenate, chromate and molybdate binding on schwertmannite: surface adsorption vs anion-exchange. J Colloid Interf Sci 386:338–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.07.008
Arcos-Casarrubias JA, Cruz-Diaz MR, Cardoso-Martinez J, Vazquez-Arenas J, Caballero-Dominguez FV (2018) Chromium adsorption into a macroporous resin based on vinylpyridine-divinylbenzene copolymers: thermodynamics, kinetics, and process dynamic in a fixed bed column. Adsorption 24:105–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-017-9925-y
Cao XH, Guo J, Mao JD, Lan YQ (2011) Adsorption and mobility of Cr(III)-organic acid complexes in soils. J Hazard Mater 192:1533–1538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.076
Carlson JJ, Kawatra SK (2013) Factors affecting zeta potential of iron oxides. Miner Process Ext Met Rev 34:269–303. https://doi.org/10.1080/08827508.2011.604697
Ding BT, Wang XM, Feng K, Fu JR, Liang JR, Zhou LX (2022) Efficient adsorption of Cr(VI) in acidic environment by nano-scaled schwertmannite prepared through pH regulation: characteristics, performances, and mechanism. Environ Sci Pollut R 176:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21257-z
Ebrahim S, Shokry A, Ibrahim H, Solimar M (2016) Polyaniline/akaganéite nanocomposite for detoxification of noxious Cr(VI) from aquatic environment. J Polym Res 23:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-016-0977-6
Eskandarpour A, Onyang MS, Tanahashi M, Ochieng A, BandoY IK, Okido M, Asai S (2008) Magnetic fixed-bed column for Cr(VI) removal from aqueous solution using schwertmannite. Isij Int 48:240–244. https://doi.org/10.2355/isi**ternational.48.240
Gan M, Sun SJ, Zheng ZH, Tang HJ, Sheng JR, Zhu JY, Liu XX (2015a) Adsorption of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) by AlPO4 modified biosynthetic schwertmannite. Appl Surf Sci 356:986–997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.08.200
Gan M, Zheng ZH, Sun SJ, Zhu JY, Liu XX (2015b) The influence of aluminum chloride on biosynthetic schwertmannite and Cu(II)/Cr(VI) adsorption. Rsc Adv 5:94500–94512. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra17316g
Gupta VK, Pathania D, Agarwal S, Sharma S (2013) Removal of Cr(VI) onto Ficus carica biosorbent from water. Environ Sci Pollut R 20:2632–2644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1176-6
Hsini A, Benafqir M, Naciri Y, Laabd M, BouzianiA E-Z, Lakhmiri R, El Alem N, Albourine A (2021) Synthesis of an arginine-functionalized polyaniline@FeOOH composite with high removal performance of hexavalent chromium ions from water: Adsorption behavior, regeneration and process capability studies. Co-Lloid Surface A 617:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126274
Kaprara E, Pinakidou F, Paloura EC, Zouboulis AL, Mitrakas M (2018) Continuous flow process of Cr(VI) removal from drinking water through reduction onto FeOOH by inorganic sulfur reductants. Water Sci Tech-W Sup 18:734−744. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2017.152
Li Y, Qin C, Zhang J, Lan YQ, Zhou LX (2014) Cu(II) catalytic reduction of Cr(VI) by tartaric acid under the irradiation of simulated solar light. Environ Eng Sci 31:447–452. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2013.0407
Li B, Zhang L, Yin WZ, Lv SH, Li P, Zheng XY, Wu JH (2020) Effective immobilization of hexavalent chromium from drinking water by nano-FeOOH coating activated carbon: Adsorption and reduction. J Environ Manage 277:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111386
Li XF, Guo CL, ** XH, He CC, Yao Q, Lu GN, Dang Z (2021) Mechanisms of Cr(VI) adsorption on schwertmannite under environmental disturbance: changes in surface complex structures. J Hazard Mater 416:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125781
Liu YY, Liu XM, Zhao YP, Dionysiou DD (2017) Aligned α-FeOOH nanorods anchored on a graphene oxide-carbon nanotubes aerogel can serve as an effective Fenton-like oxidation catalyst. Appl Catal B-Environ 213:74–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.05.019
Lu JB, Xu K, Yang JM, Hao YR, Cheng F (2017) Nano iron oxide impregnated in chitosan bead as a highly efficient sorbent for Cr(VI) removal from water. Carbohyd Polym 173:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.05.070
Mao N, Yang LQ, Zhao GH, Li XL, Li XF (2012) Adsorption performance and mechanism of Cr(VI) using magnetic PS-EDTA resin from micro-polluted waters. Chem Eng J 200:480–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.082
Obregon S, Mendoza-Resendez R, Luna C (2017) Facile synthesis of ultrafine akaganeite nanoparticles for the removal of hexavalent chromium: adsorption properties, isotherm and kinetics. J Nanosci Nanotechno 17:4471–4479. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2017.14198
Qiu Y, Zhang Q, Gao B, Li M, Fan ZX, Sang WJ, Hao HR, Wei XN (2020) Removal mechanisms of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) by biochar supported nanosized zero-valent iron: Synergy of adsorption, reduction and transformation. Environ Pollut 265:1–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115018
Rakhunde R, Deshpande L, Juneja HD (2012) Chemical speciation of chromium in water: a Review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:776–810. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2010.534029
Schwertmann U, Cornell RM (2000) Iron oxides in the laboratory: preparation and characterization, 2nd, completely revised and enlarged edition. Mineral Mag 61:740–741. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527613229
Senamart N, Deekamwong K, Wittayakun J, Prayoonpokarach S, Chanlek N, Poo-arporn Y, Wannapaiboon S, Kidkhunthod P, Loiha S (2022) Structural elucidation of hexavalent Cr adsorbed on surfaces and bulks of Fe3O4 and α-FeOOH. Rsc Adv 12:25578–25586. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2ra03676b
Ulatowska J, Stala L, Polowczyk L (2021) Comparison of Cr(VI) adsorption using synthetic schwertmannite obtained by Fe3+ hydrolysis and Fe2+ oxidation: Kinetics, isotherms and adsorption mechanism. Int J Mol Sci 22:1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158175
Wang CY, Liu N, Li C, Jiang TT, Chen WJ, Wang LH, Zhang XL (2017) Adsorption of Cr(VI) on the MWCNTs/attapulgite composites. China Environ Sci 37:2179–2186
Wang T, Zhang PC, Ni SJ, Huang Y, Qiu KH, Li JF, Zhang M, Yin HS, Li JC (2019) Synthesis of nano-akaganeite powder and its chromium adsorption behavior. Ferroelectrics 540:184–192. https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2018.1454747
Wang XM, Ying H, Zhao WT, Feng XH, Tan WF, Beyer KA, Huang QY, Liu F, Zhu MQ (2021) Molecular-Scale Understanding of sulfate exchange from schwertmannite by chromate versus arsenate. Environ Sci Technol 55:5857–5867. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c07980
Wu SJ, Lu JW, Ding ZC, Li N, Fu FL, Tang B (2016) Cr(VI) removal by mesoporous FeOOH polymorphs: performance and mechanism. Rsc Adv 6:82118–82130. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra14522a
Wu H, Wang C, Kwon J, Choi Y, Lee J (2021) Synthesis of 2D and 3D hierarchical β-FeOOH nanoparticles consisted of ultrathin nanowires for efficient hexavalent ch-romium removal. Appl Surf Sci 543:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148823
**ong HX, Peng SN, Zhang BL (2022a) Cell-shape assemblage and nanostructure of akaganéite bioformed in FeCl2 solutions. Environ Sci Pollut R 29:75566–75574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21084-2
**ong HX, Xu SM, Zhu SB (2022b) Adsorption removal of arsenic from aqueous solutions and groundwater by isomeric FeOOH. Water Sci Technol 86:1653–1667. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2022.303
**ong HX, Hu D, Shi K, Zhu SB, Xu YQ (2023) Adsorptive removal of arsenic ions from contaminated water using low-cost schwertmannites and akaganéites. Mater Chem Phys 297:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127411
Xu CH, Cheng DD, Gao BY, Yin ZL, Yue QY, Zhao X (2012) Preparation and characterization of β-FeOOH-coated sand and its adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. Front Environ Sci Eng 6(4):4554–4562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-010-0275-1
Xu YQ, Yang M, Yao T, **ong HX (2014) Isolation, identification and arsenic-resistance of Acidithiobacillusferrooxidans HX3 producing schwertmannite. J Environ Sci 26:1463–1470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.05.012
Xu ZH, Jiang HM, Yu YQ, Xu JY, Liang JR, Zhou LX, Hu F (2017) Activation and β-FeOOH modification of sepiolite in one-step hydrothermal reaction and its simulated solar light catalytic reduction of Cr(VI). Appl Clay Sci 135:547–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.10.035
Xu D, Huang Y, Ma Q, Qian JZ, Guo X, Wu YQ (2023) A 3D porous structured cellulose nanofibrils-based hydrogel with carbon dots-enhanced synergetic effects of adsorption and photocatalysis for effective Cr(VI) removal. Chem Eng J 456:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.141104
Yang TT, Meng LR, Han SW, Hou JH, Wang SS, Wang XZ (2017) Simultaneous reductive and sorptive removal of Cr(VI) by activated carbon supported β-FeOOH. Rsc Adv 7:34687–34693. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra06440c
Yu CY, Zhang J, Wu XL, Lan YQ, Zhou LX (2014) Cr(VI) removal by biogenic schwertmannite in continuous flow column. Geochem J 48:1–7. https://doi.org/10.2343/geochemj.2.0278
Zhang D, Liu JX, Zhu SB, **ong HX, Xu YQ (2019a) Adsorption removal of Cr(VI) by isomeric FeOOH. Water Sci Technol 80:300–307. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2019.273
Zhang L, Fu FL, Tang B (2019b) Adsorption and redox conversion behaviors of Cr(VI) on goethite/carbon microspheres and akaganeite/carbon microspheres composites. Chem Eng J 356:151–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.08.224
Zhang Z, Guo GL, Li XT, Zhao QC, Bi X, Wu KN, Chen HH (2019c) Effects of hydrogen-peroxide supply rate on schwertmannite microstructure and chromium(VI) adsorption performance. J Hazard Mater 367:520–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.116
Zhang RR, Zeng Q, Guo P, Cui YQ, Sun YY (2020) Efficient capture of Cr(VI) by carbon hollow fibers with window-like structure. Environ Sci Pollut R 27:16763–16773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07939-6
Zhao JH, Lin W, Chang QG, Liu WJ, Wang SP, Lai YP (2012) Effects of operational conditions on the floc formation time and rate in magnesium hydroxide coagulation process. Desalin Water Treat 45:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.692022
Zhu JH, Wei SY, Gu HB, Rapole SB, Wang Q, Luo ZP, Haldolaarachchige N, Young DP, Guo ZH (2012) One-Pot synthesis of magnetic graphene nanocomposites decorated with Core@Double-shell nanoparticles for fast chromium removal. Environ Sci Technol 46:977–985. https://doi.org/10.1021/es2014133
Zhu LC, Liu YY, Li WM, Mou HY, Wang WY, Shi DZ, Wang T (2017) Adsorptive remediation of Cr(VI) contaminated groundwater with chemically synthesized schwertmannite. Environ Sci 38:629–639. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.201608044
Funding
The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: The authors received financial support by National Natural Science Foundations of China [41472034] and Natural Science General Fund of Jiangsu Province [BK20191444] for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Huixin **ong: conceptualization, methodology, validation, supervision, funding acquisition, writing—review and editing. Yang Liu: investigation, visualization, formal analysis, writing—original draft. Shuyue Wang: investigation, methodology, validation. Shibei Zhu: investigation, data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
All the authors agreed to be published.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
**ong, H., Liu, Y., Wang, S. et al. Schwertmannite and akaganéite for adsorption removals of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 62295–62311 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26348-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26348-z