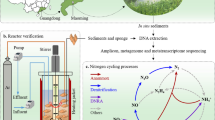
Abstract
A reservoir is an important source of methane (CH4), which is consumed by aerobic methane-oxidizing bacteria (MOB), representing the main CH4 sink in water. The central urban area of Chongqing in the Three Gorges Reservoir (TGR) area was selected as the study area in 2021. High-throughput sequencing was used to analyze the community structure and abundance of MOBs. The results showed that Methylocystis (Type II) was the dominant MOB in water, whereas Methylococcus (Type I) and Methylocystis co-dominated the sediments. High water temperature in the study area largely accounted for the predominance of Type II MOBs in the two habitats. Moreover, the influence of environmental factors on MOB community and its interspecific relationship were significantly regulated by the operation of the TGR. In the low-water-level period, NO2−-N and CO2 concentration significantly correlated with Methylocystis, whereas in the high-water-level period, the higher discharge and velocity weakened the influence of all environmental factors on Methylocystis. In addition, the scouring of sediments by increasing discharge in the high-water-level period caused a significant decrease in dissolved CH4 concentration. The decrease in substrate increased interspecific competition within the MOB community, especially between different types of MOBs, in the high-water-level period.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Ai J, Lu Y, Zhong X et al (2022) The community characteristics and functions of methanotrophs in karst Lake Caohai, Guizhou Plateau. J Lake Sci 34(3). https://doi.org/10.18307/2022.0317
Bastviken D, Ejlertsson J, Tranvik L (2002) Measurement of methane oxidation in lakes: a comparison of methods. Environ Sci Technol 36:3354–3361. https://doi.org/10.1021/es010311p
Blees J, Niemann H, Wenk CB et al (2014) Micro-aerobic bacterial methane oxidation in the chemocline and anoxic water column of deep south-alpine Lake Lugano (Switzerland). Limnol Oceanogr 59:311–324. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2014.59.2.0311
Borrel G, Jezequel D, Biderre-Petit C et al (2011) Production and consumption of methane in freshwater lake ecosystems. Res Microbiol 162:832–847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2011.06.004
Bowman J (2006) The methanotrophs—the families Methylococcaceae and Methylocystaceae. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (Eds.), The prokaryotes: volume 5: proteobacteria: alpha and beta subclasses. Springer, New York, pp. 266–289
Bowman J (2014) The family Methylococcaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes. Springer, Berlin, pp 411–440
Bussmann I, Hackbusch S, Schaal P et al (2017) Methane distribution and oxidation around the Lena Delta in summer 2013. Biogeosciences 14(21):4985–5002. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-14-4985-2017
Canelhas MR, Denfeld BA, Weyhenmeyer GA (2016) Methane oxidation at the water-ice interface of an ice-covered lake. Limnol Oceanogr. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10288
Crevecoeur S, Ruiz-Gonzalez C, Prairie YT et al (2019) Large-scale biogeography and environmental regulation of methanotrophic bacteria across boreal inland waters. Mol Ecol 28:4181–4196. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15223
D’Acunha B, Johnson MS (2019) Water quality and greenhouse gas fluxes for stormwater detained in a constructed wetland. J Environ Manage 231:1231–1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.106
Deemer BR, Harrison JA, Li S et al (2016) Greenhouse gas emissions from reservoir water surfaces: a new global synthesis. Bioscience 66:949–964. https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/biw117
Deutzmann JS, Schink B (2011) Anaerobic oxidation of methane in sediments of Lake Constance, an oligotrophic freshwater lake. Appl Environ Microb 77(13):4429–4436. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00340-11
Freilich S, Kreimer A, Meilijson I et al (2010) The largescale organization of the bacterial network of ecological co-occurrence interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 38:3857–3868. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq118
Graef C, Hestnes AG, Svenning MM et al (2011) The active methanotrophic community in a wetland from the high Arctic. Environ Microbiol Rep 3:466–472. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1758-2229.2010.00237.x
Guérin F, Abril G (2007) Significance of pelagic aerobic methane oxidation in the methane and carbon budget of a tropical reservoir. J Geophys Res 112:G03006. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006JG000393
Lei D, Liu J, Zhang JW et al (2019) Methane oxidation in the water column of **angxi Bay, Three Gorges Reservoir. Clean: Soil, Air, Water 47:1800516. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201800516
Li Z, Lu LH, Guo JS et al (2017) Responses of spatial-temporal dynamics of bacterioplankton community to largescale reservoir operation: a case study in the Three Gorges Reservoir. China Sci Rep 7:42469. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42469
Li Z, Lu LH, Lv PY et al (2020) Imbalanced stoichiometric reservoir sedimentation regulates methane accumulation in China’s Three Gorges Reservoir. Water Resour Res 56:e2019WR026447. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019WR026447
Liu Y, Zhang J, Zhao L et al (2015) Aerobic and nitrite-dependent methane-oxidizing microorganisms in sediments of freshwater lakes on the Yunnan Plateau. Appl Microbiol Biot 99:2371–2381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6141-5
Liu T, Zhang AN, Wang J et al (2018) Integrated biogeography of planktonic and sedimentary bacterial communities in the Yangtze River. Microbiome 6(1):16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-017-0388-x
Liu J, **ao SB, Wang CH et al (2021) Spatial and temporal variability of dissolved methane concentrations and diffusive emissions in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Water Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117788
Liu D, Mo YL, Peng C et al (2022) The impact of different electron acceptors on methane oxidation and the key microbial players in the soil of the Jialing River riparian wetland. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin. https://doi.org/10.11870/cjlyzyyhj202210012
Lu LH, Li XR, Li Z et al (2021) Aerobic methanotrophs in an urban water cycle system: community structure and network interaction pattern. Sci Total Environ 772:145045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145045
Matoušů A, Osudar R, Šimek K et al (2017) Methane distribution and methane oxidation in the water column of the Elbe estuary, Germany. Aquat Sci 79:443–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-016-0509-9
Musenze RS, Fan L, Grinham A et al (2016) Methane dynamics in subtropical freshwater reservoirs and the mediating microbial communities. Biogeochemistry 128:233–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-016-0206-8
Oswald K, Milucka J, Brand A et al (2015) Light-dependent aerobic methane oxidation reduces methane emissions from seasonally stratified lakes. Plos One 10(7). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132574
Qin Y, Gou YJ, Yu ZT et al (2021) Effects of environmental factors on the methane and carbon dioxide fluxes at the middle of Three Gorges Reservoir. J Water Clim Change. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2021.081
Qin Y, Huang H, Li Z et al (2021) Research progress of aerobic methane oxidation process in inland waters. J Lake Sci 33(4):1004–1017. https://doi.org/10.18307/2021.0404
Qin Y, Tang Q, Lu LH et al (2021) Changes in planktonic and sediment bacterial communities under the highly regulated dam in the mid-part of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Appl Microbiol Biot 105:839–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11047-3
Qin Y, Ouyang CY, Gou YJ et al (2022) The characteristics and influencing factors of dissolved methane concentrations in Chongqing’s central urban area in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20822-w
Raghoebarsing AA, Pol A, van de Pas-Schoonen KT et al (2006) A microbial consortium couples anaerobic methane oxidation to denitrification. Nature 440:918–921. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04617
Reis PCJ, Thottathil SD, Ruiz-González C et al (2020) Niche separation within aerobic methanotrophic bacteria across lakes and its link to methane oxidation rates. Environ Microbiol 22:738–751. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14877
Ruiz-González C, Proia L, Ferrera I et al (2013) Effects of large river dam regulation on bacterioplankton community structure. Fems Microbiol Ecol 84(2):316–331. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6941.12063
Saunois M, Stavert AR, Poulter B et al (2020) The global methane budget 2000–2017. Earth Syst Sci 12:1561–1623. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-12-1561-2020
Sawakuchi HO, Bastviken D, Sawakuchi AO et al (2016) Oxidative mitigation of aquatic methane emissions in large Amazonian rivers. Global Change Biol 22(3):1075–1085. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13169
Scheutz C, Kjeldsen P, Gentil E (2009) Greenhouse gases, radiative forcing, global warming potential and waste management–an introduction. Waste Manag Res 27:716–723. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X09345599
Semrau JD, DiSpirito AA, Yoon S (2010) Methanotrophs and copper. Fems. Microbiol Rev 34:496–531. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00212.x
Sundh I, Bastviken D, Tranvik LJ et al (2005) Abundance, activity, and community structure of pelagic methane-oxidizing bacteria in temperate lakes. Appl Environ Microb 71(11):6746–6752. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.11.6746-6752.2005
Tang Q, Xue XF, Wang H et al (2018) New knowledge of methanogens and methanotrophs in lake ecosystems. J Lake Sci 30:597–610. https://doi.org/10.18307/2018.0302
Thottathil SD, Reis PCJ, Del GPA (2018) The extent and regulation of summer methane oxidation in northern lakes. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 123:3216–3230. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JG004464
Tsubota J, Eshinimaev BT, Khmelenina VN et al (2005) Methylothermus thermalis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel moderately thermophilic obligate methanotroph from a hot spring in Japan. Int J Syst Evol Micr 55:1877–1884. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63691-0
Urmann K, Lazzaro A, Gandolfi I et al (2009) Response of methanotrophic activity and community structure to temperature changes in a diffusive CH4/O2 counter gradient in an unsaturated porous medium. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 69(2):202–212. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00708.x
Wang YF (2020) Methane metabolism and functional microorganisms in permafrost soils from the gas hydrate drilling area of Qilian Mountains. China University of Geosciences, China
Wang YM, Liu LM, Chen HH et al (2015) Spatiotemporal dynamics and determinants of planktonic bacterial and microeukaryotic communities in a Chinese subtropical river. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(21):9255–9266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6773-0
Yang YY, Chen JF, Tong TI et al (2019) Eutrophication influences methanotrophic activity, abundance and community structure in freshwater lakes. Sci Total Environ 662:863–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.307
Yang P, Yang H, Sardans J et al (2020) Large spatial variations in diffusive CH4 fluxes from a subtropical coastal reservoir affected by sewage discharge in southeast China. Environ Sci Technol 54:14192–14203. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c03431
Yun J, Zhuang G, Ma A et al (2012) Community structure, abundance, and activity of methanotrophs in the Zoige Wetland of the Tibetan Plateau. Microb Ecol 63:835–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-011-9981-x
Zhao W, Zhu KX, Huang WM et al (2013) Temporal-spatial patterns of methane emission flux and its influence factors in Hubei part of Three Gorges Reservoir. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 37(04):776–781. https://doi.org/10.7541/2013.95
Zheng W (2021) Study on Bacterial community structure and methane-oxidizing bacteria in the main section of the Yangtze River in Chongqing. ChongQing Jiaotong University, Chongqing, China
Zigah PK, Oswald K, Brand A et al (2015) Methane oxidation pathways and associated methanotrophic communities in the water column of a tropical lake. Limnol Oceanogr 60:553–572. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10035
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51609026) and the Research and Innovation Program for Graduate Students in Chongqing (CYS22402).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Changyue Ouyang and Yujia Gou: investigation, writing original draft, data curation, formal analysis, software. Yu Qin and Yue Liang: funding acquisition, editing and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Robert Duran
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ouyang, C., Qin, Y., Liang, Y. et al. Community structure and network interaction of aerobic methane-oxidizing bacteria in Chongqing’s central urban area in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 56368–56381 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26310-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26310-z