Abstract
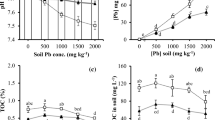
The present study, investigated the influence of the natural tea saponin (TS) obtained by microwave-assisted extraction and citric acid (CA) by commercially enhancing lead ion (Pb(II)) uptake by Salvia virgata Jacq. The Pb(II) tolerance was compared, and the growth of plants and Pb(II) accumulation characteristics of S. virgata with chemical agents TS and CA were studied for their phytoextraction potential of Pb(II) from artificially contaminated soil of 0–100 mg kg−1 different concentrations under pot conditions. The different morphophysiological parameters of S. virgata such as growth, biomass, chlorophylls, and carotenoids were significantly changed under different Pb(II) stress and TS and CA concentrations. To evaluate the removal efficiency of the studied plant, the bioconcentration factor (BCF) or enrichment coefficient (EC), translocation factor (TF), and tolerance index (TI) values were also calculated and compared with the control. Phytotoxic effects were observed at 100 mg kg−1; added Pb(II) treatments caused significant decreases of 33.05% in the biomass of S. virgata compared to the control. All the obtained results showed that the concentrations of Pb(II) being compared revealed a highest uptake (286 ± 5.2 mg kg−1) of 100 mg kg−1. The concentration of available Pb(II)-assisted TS and CA increased by 9.1–28.4% compared to the control. Based on these findings, S. virgata might be cultivated and used as a hyperaccumulator in the removal of Pb(II) from the contaminated soils, and appropriate application of TS and CA can enhance phytoremediation of Pb(II)-contaminated soil by other hyperaccumulator plants.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study is available for sharing from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abou-Elwafa SF, Amin AA, Shehzad T (2019) Genetic map** and transcriptional profiling of phytoremediation and heavy metals responsive genes in sorghum. Ecotox Environ Safe 173:366–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.022
Al Chami Z, Cavoski I, Mondelli D, Miano T (2013) Effect of compost and manure amendments on zinc soil speciation, plant content, and translocation in an artificially contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(7):4766–4776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1439-2
Cay S (2016) Enhancement of cadmium uptake by Amaranthus caudatus, an ornamental plant, using tea saponin. Environ Monit Assess 188(6):320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5334-z
Cay S, Uyanik A, Engin MS, Kutbay HG (2015) Effect of EDTA and tannic acid on the removal of Cd, Ni, Pb and Cu from artificially contaminated soil by Althaea rosea Cavan. Int J Phytoremediat 17(6):568–574. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2014.935285
Cay S, Engin MS, Uyanik A, Cay C, Guney S (2019) Phytoremediation of cadmium in soil and hydroponics by Tradescantia fluminensis. Carpath J Earth Env 14(2):269–274. https://doi.org/10.26471/cjees/2019/014/078
Dowom SA, Abrishamchi P, Radjabian T, Salami SA (2017) Enhanced phenolic acids production in regenerated shoot cultures of Salvia virgata Jacq. after elicitation with Ag+ ions, methyl jasmonate and yeast extract. Ind Crop Prod 103:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.03.043
Engin MS, Uyanik A, Cay S, Icbudak H (2010) Effect of the adsorptive character of filter papers on the concentrations determined in studies involving heavy metal ions. Adsorpt Sci Technol 28(10):837–846. https://doi.org/10.1260/0263-6174.28.10.837
Farid M, Ali S, Rizwan M, Ali Q, Abbas F, Bukharie SAH, Saeed R, Wu L (2017) Citric acid assisted phytoextraction of chromium by sunflower; morphophysiological and biochemical alterations in plants. Ecotox Environ Safe 145:90–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.07.016
Fatima A, Farid M, Alharby HF, Bamagoos AA, Rizwan M, Ali S (2020) Efficacy of fenugreek plant for ascorbic acid assisted phytoextraction of copper (Cu); a detailed study of Cu induced morpho-physiological and biochemical alterations. Chemosphere 251:126424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126424
Hosseini SS, Lakzian A, Halajnia A, Razavi BS (2021) Optimization of EDTA and citric acid for risk assessment in the remediation of lead contaminated soil. Rhizosphere-Neth 17:100277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2020.100277
Kara SG, Ulger M, Kahraman A (2021) Phytochemical analysis, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Salvia virgata mericarps. Bot Serb 45(2):223–231. https://doi.org/10.2298/Botserb2102223g
Kraus TEC, Dahlgren RA, Zasoki RJ (2003) Tannins in nutrient dynam-ics of forest ecosystems–a review. Plant Soil 256:41–46
KrishnaRaj S, Dan TV, Saxena PK (2000) A fragrant solution to soil remediation. Int J Phytoremediat 2(2):117–132. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510008500034
Liu KH, Guan XJ, Li CM et al (2022) Global perspectives and future research directions for the phytoremediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil: a knowledge map** analysis from 2001 to 2020. Front Env Sci Eng 16(6):73. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-021-1507-2
Ma C, Liu FY, Hu B, Wei MB, Zhao JH, Zhang HZ (2019) Quantitative analysis of lead sources in wheat tissue and grain under different lead atmospheric deposition areas. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(36):36710–36719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06825-0
Mahar A, Wang P, Ali A et al (2016) Challenges and opportunities in the phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soils: a review. Ecotox Environ Safe 126:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.12.023
Malar S, Manikandan R, Favas PJC, Sahi SV, Venkatachalam P (2014) Effect of lead on phytotoxicity, growth, biochemical alterations and its role on genomic template stability in Sesbania grandiflora: a potential plant for phytoremediation. Ecotox Environ Safe 108:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.05.018
Mattina MI, Lannucci-Berger W, Musante C, White JC (2003) Concurrent plant uptake of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from soil. Environ Pollut 124(3):375–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00060-5
Moameri M, Khalaki MA (2019) Capability of secale montanum trusted for phytoremediation of lead and cadmium in soils amended with nano-silica and municipal solid waste compost. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(24):24315–24322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0544-7
Pires-Lira MF, de Castro EM, Lira JMS, de Oliveira C, Pereira FJ, Pereira MP (2020) Potential of Panicum aquanticum Poir (Poaceae) for the phytoremediation of aquatic environments contaminated by lead. Ecotox Environ Safe 193:110336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110336
Pu SY, Cai XY, Wang WJ, et al. (2021) NTA-assisted mineral element and lead transportation in Eremochloa ophiuroides (Munro) Hack. Environ Sci Pollut Reshttps://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17306-8
Rajendran S, Priya TAK, Khoo KS et al (2022) A critical review on various remediation approaches for heavy metal contaminants removal from contaminated soils. Chemosphere 287:132369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132369
Ramana S, Biswas AK, Singh AB, Ajay Ahirwar NK, Rao AS (2015) Tolerance of ornamental succulent plant crown of thorns (Euphorbia milli) to chromium and its remediation. Int J Phytoremediat 17(4):363–368. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2013.862203
Saifullah Ghafoor A, Zia MH et al (2010) Comparison of organic and inorganic amendments for enhancing soil lead phytoextraction by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Int J Phytoremediat 12(7):633–649. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226511003753953. Pii 923448543
Senkal BC, Uskutoglu T, Cesur C, Ozavci V, Dogan H (2019) Determination of essential oil components, mineral matter, and heavy metal content of Salvia virgata Jacq. grown in culture conditions. Turk J Agric For 43(4):395–404. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1812-84
Sharifi K, Rahnavard A, Saeb K, Fahimi FG, Tavana A (2022) Ability of Urtica dioica L. to adsorb heavy metals(Pb, Cd, As, and Ni) from contaminated soils. Soil Sediment Contam 2(1):51–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2022.2052263
Smical AI, Hotea V, Oros V, Juhasz J, Pop E (2008) Studies on transfer and bioaccumulation of heavy metals from soil into lettuce. Environ Eng Manag J 7(5):609–615. https://doi.org/10.30638/eemj.2008.085
Witham FHB, Blaydes DF, Devlin RM (1971) Experiments in plant physiology. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York
Wu HH, Wei WX, Xu CB et al (2020) Polyethylene glycol-stabilized nano zero-valent iron supported by biochar for highly efficient removal of Cr(VI). Ecotox Environ Safe 188:109902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109902
**a HL, Chi XY, Yan ZJ, Cheng WW (2009) Enhancing plant uptake of polychlorinated biphenyls and cadmium using tea saponin. Bioresource Technol 100(20):4649–4653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.04.069
Xu QX, Liu XR, Zhao JW et al (2018) Feasibility of enhancing short-chain fatty acids production from sludge anaerobic fermentation at free nitrous acid pretreatment: role and significance of tea saponin. Bioresource Technol 254:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.084
Xue ZJ, Wu MJ, Hu HX, Kalkhajeh YK (2021) Cadmium uptake and transfer by Sedum plumbizincicola using EDTA, tea saponin, and citric acid as activators. Int J Phytoremediat 23(10):1052–1060. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.1874290
Zaheer IE, Ali S, Rizwan M, Farid M, Shakoor MB, Gill RA, Najeeb U, Iqbal N, Ahmad R (2015) Citric acid assisted phytoremediation of copper by Brassicanapus L. Ecotox Environ Safe 120:310–317
Zayed A, Lytle CM, Qian JH, Terry N (1998) Chromium accumulation, translocation and chemical speciation in vegetable crops. Planta 206(2):293–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004250050403
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All of the scientific studies in this article were carried out by the author, Seydahmet Cay, and he critically revised the manuscript, commented on the drafts of the manuscript, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Elena Maestri
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cay, S. Assessment of tea saponin and citric acid–assisted phytoextraction of Pb-contaminated soil by Salvia virgata Jacq. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 49771–49778 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25809-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25809-9