Abstract
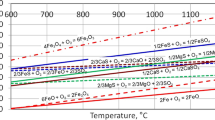
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is a toxic pollutant and its fixation is a high cost but imperative task for sulfide metallurgy industry. Although being a mature technology for on-line fixation of SO2 by limestone injection in coal-fired boilers, its application is rarely investigated in the sulfide metallurgy plant. Extending this technology to the metallurgy industry is highly plausible, but with the feasibility and practicability waiting to be uncovered. Herein, feeding CaO into the rotary volatilization kiln as SO2-fixation agent is demonstrated to be an efficient in-furnace desulfurization strategy for zinc smelting plant. The sulfur distribution within the entire smelting process is systematically analyzed, determining that the critical procedure for pressuring the desulfurization system is the rotary volatilization kiln. The thermodynamics analysis shows that addition of CaO is feasible for SO2 fixation by forming CaS or restraining the reductive decomposition of SO42−. The industrial tests, including the online monitoring of kiln flue gas and kiln slag analysis, validate the thermodynamics analysis, realizing a 24.6% reduction of SO2 in the flue gas by converting gaseous SO2 to solid CaS via feeding 20% CaO. The present study highlights an effective strategy for on-line fixing the SO2, being a potential way for relieving the desulfurization pressures in zinc sulfide metallurgy plant.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abo Atia T, Spooren J (2020) Microwave assisted chloride leaching of zinc plant residues. J Hazard Mater 398:122814
Bang KH, Kang YB (2022) Recycling red mud to develop a competitive desulfurization flux for Kanbara Reactor (KR) desulfurization process. J Hazard Mater 440:129752
Cao L, Liao Y-l, Shi G-c, Zhang Y, Guo M-y (2019) Leaching behavior of zinc and copper from zinc refinery residue and filtration performance of pulp under the hydrothermal process. Int J Min Metall Mater 26:21–32
Cheng J, Zhou J, Liu J, Zhou Z, Huang Z, Cao X, Zhao X, Cen K (2003) Sulfur removal at high temperature during coal combustion in furnaces: a review. Prog Energ Combust 29:381–405
Chutia L, Ojha N, Girach I, Pathak B, Sahu LK, Sarangi C, Flemming J, da Silva A, Bhuyan PK (2022) Trends in sulfur dioxide over the Indian subcontinent during 2003–2019. Atmo Environ 284:119189
Dong Y, Li Y, Zhang L, Cui L, Zhang B, Dong Y (2017) Novel method of ultralow SO2 emission for CFB boilers: combination of limestone injection and activated carbon adsorption. Energ Fuels 31:11481–11488
Hanif MA, Ibrahim N, Abdul Jalil A (2020) Sulfur dioxide removal: an overview of regenerative flue gas desulfurization and factors affecting desulfurization capacity and sorbent regeneration. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 27:27515–27540
Iberahim N, Sethupathi S, Bashir MJK, Kanthasamy R, Ahmad T (2022) Evaluation of oil palm fiber biochar and activated biochar for sulphur dioxide adsorption. Sci Total Environ 805:150421
Jiang G-M, Peng B, Liang Y-J, Chai L-Y, Wang Q-W, Li Q-Z, Hu M (2017) Recovery of valuable metals from zinc leaching residue by sulfate roasting and water leaching. T Nonferr Metal Soc 27:1180–1187
Li M, Peng B, Chai L, Peng N, Yan H, Hou D (2012) Recovery of iron from zinc leaching residue by selective reduction roasting with carbon. J Hazard Mater 237–238:323–330
Li C, McLinden C, Fioletov V, Krotkov N, Carn S, Joiner J, Streets D, He H, Ren X, Li Z, Dickerson RR (2017) India is overtaking China as the world’s largest emitter of anthropogenic sulfur dioxide. Sci Rep 7:14304
Li B, Wang K, Zhu B (2020a) Study on energy-saving operation technology of environmental protection facilities of ultra-low emission coal-fired unit. Energ Rep 6:1356–1364
Li G, Wang J, Rao M, Luo J, Zhang X, You J, Peng Z, Jiang T (2020b) Coprocessing of stainless-steel pickling sludge with laterite ore via rotary kiln-electric furnace route: enhanced desulfurization and metal recovery. Process Saf Environ 142:92–98
Li J, Wang Y, Yin P, Huang J, Wu Z, Cao R, Wang L, Zeng Q, Pan X, Li G, Zhou M (2021) The burden of sulfur dioxide pollution on years of life lost from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a nationwide analysis in China. Environ Res 194:110503
Liangxiong H, Li Z, Yuan S (2011) Pollution spillover in developed regions in China-based on the analysis of the industrial SO2 emission. Energy Procedia 5:1008–1013
Likus-Cieslik J, Socha J, Gruba P, Pietrzykowski M (2020) The current state of environmental pollution with sulfur dioxide (SO2) in Poland based on sulfur concentration in Scots pine needles. Environ Pollut 258:113559
Lin H-F, Weng W, Zhong S-P, Qiu G-Z (2022) Enhanced recovery of zinc and lead by slag composition optimization in rotary kiln. T Nonferr Metal Soc 32:3110–3122
Liu X, Lin B, Zhang Y (2016) Sulfur dioxide emission reduction of power plants in China: current policies and implications. J Clean Prod 113:133–143
Long H-M, Wu X-J, Chun T-J, Di Z-X, Wang P, Meng Q-M (2016) A pilot-scale study of selective desulfurization via urea addition in iron ore sintering. Int J Min Met Mater 23:1239–1243
Ng KH (2021) Reduction of hazardous SO2 into elemental sulphur over chicken eggshells-derived calcium-based redox agent: a systematic step-by-step thermodynamic analysis and process validations. J Clean Prod 278:123927
Peng N, Peng B, Chai L, Liu W, Li M, Yuan Y, Yan H, Hou D-K (2012) Decomposition of zinc ferrite in zinc leaching residue by reduction roasting. Procedia Environ Sci 16:705–714
Qu J, Chen X, **e H, Gao S, Wang D, Yin H (2022) Anode electrolysis of sulfides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119:e2202884119
Rathnayake M, Julnipitawong P, Tangtermsirikul S, Toochinda P (2018) Utilization of coal fly ash and bottom ash as solid sorbents for sulfur dioxide reduction from coal fired power plant: life cycle assessment and applications. J Clean Prod 202:934–945
Shen X-y, Liang Y-y, Shao H-m, Sun Y, Liu Y, Zhai Y-c (2020) Extraction and kinetic analysis of Pb and Sr from the leaching residue of zinc oxide ore. Int J Min Met Mater 28:201–209
Shi C-b, Huang Y, Zhang J-x, Li J, Zheng X (2021) Review on desulfurization in electroslag remelting. Int J Min Met Mater 28:18–29
Weng W, **ao J, Shen Y, Liang X, Lv T, **ao W (2021) Molten salt electrochemical modulation of iron-carbon-nitrogen for lithium-sulfur batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 60:24905–24909
Weng W, Jiang B, Wang Z, **ao W (2020) In situ electrochemical conversion of CO2 in molten salts to advanced energy materials with reduced carbon emissions. Sci Adv 6: eaay9278
Xu Y, Masui T (2009) Local air pollutant emission reduction and ancillary carbon benefits of SO2 control policies: application of AIM/CGE model to China. Eur J Oper Res 198:315–325
Zeng B, Zhou W, Zhou M (2021) Forecasting the concentration of sulfur dioxide in Bei**g using a novel grey interval model with oscillation sequence. J Clean Prod 311:127500
Zhao X, Deng C, Huang X, Kwan MP (2017) Driving forces and the spatial patterns of industrial sulfur dioxide discharge in China. Sci Total Environ 577:279–288
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the sample analysis by Suyu Chen and Lei Yang in Zi** School of Geology and Mining, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350108, China.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Basic Research and Development Program (No. 2022YFC3900801) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (51874101, 52274349).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, W., Zhang, W., Lin, H. et al. Fixing sulfur dioxide by feeding calcine oxide into the rotary volatilization kiln in zinc smelting plant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 43768–43777 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25164-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25164-9