Abstract
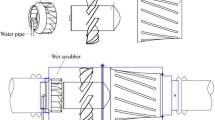
This study explores the synergistic removal effect of various schemes based on demisters on boiler flue gas dust on a pilot-scale experimental bench. The results show that the dust removal efficiency is 28.43–51.30% when demisters are put into operation alone; the larger the inlet dust concentration of demisters is, the higher the dust removal efficiency will be; but it still cannot reach the 10 mg/Nm3 ultra-low emission standard. The dust removal efficiency is 93.13% when wet electro-static precipitator and demisters are put into operation simultaneously. Furthermore, the outlet dust concentration is lower than 5 mg/Nm3, and the dust removal efficiency of the demisters themselves increases to 67.28%, which has shown a significant improvement compared with operation alone. The dust removal efficiency is 70.98–78.37% when the water-washing layer and demisters are put into operation simultaneously. Moreover, the outlet dust concentration reaches the standard of 10 mg/Nm3 when the liquid–gas ratio (L/G) is more than 3.5. This research shows that when the inlet dust concentration is ≤ 35 mg/Nm3, the method of “water-washing layer + demisters” can be used as an equivalent alternative to the wet electro-static precipitator when L/G ≥ 3.5, which has reference value for reducing the construction cost of ultra-low emission reformation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Bao J, Yang L, Guo W, Song S, Geng J (2012a) Improving the removal of fine particles in the WFGD system by adding wetting agents. Energy Fuels 26:4924–4931. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef3007195
Bao J, Yang L, Song S, **ong G (2012b) Separation of fine particles from gases in wet flue gas desulfurization system using a cascade of double towers. Energy Fuels 26:2090–2097. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef201868q
Chen Z, Zhan L, Zhao J, Sun S, Yao Y (2016) Application of wet electrostatic precipitator in 1000 MW coal-fired power plant. International Society for Electrostatic Precipitation (ICESP 2016). https://isesp.org/isesp_conferences. Accessed 2022-06-02
Du Q, Cui Z, Dong H, Gao J, Li D, Yu J, Liu Y (2019) Field measurements on the generation and emission characteristics of PM2.5 generated by industrial layer burning boilers. J Energy Inst 92:1251–1261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2018.10.009
El-Dessouky H, Alatiqi I, Ettouney H, Al-Deffeeri N (2000) Performance of wire mesh mist eliminator. Chem Eng Process 39:129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0255-2701(99)00033-1
Guo Z, Hao Y, Tian H et al (2022) Field measurements on emission characteristics, chemical profiles, and emission factors of size-segregated PM from cement plants in China. Sci Total Environ 818:151822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151822
Hao W, Yang L (2016) Removal of fine particles from coal combustion by heterogeneous condensational enlargement in wet flue gas desulfurization. In: Yue, G., Li, S. (eds) Clean Coal Technology and Sustainable Development. ISCC 2015. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-2023-0_54
Hu J, Yang S, Zhong L, Yang Y, Hu X, Xue X (2018) Application of cyclone gas cap water washing device in ultra clean discharge treatment technology of exhaust gas. E3S Web Conf 53:04035. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20185304035
Jiang M, Li B (2019) Pollutant emission and energy consumption analysis of environmental protection facilities in ultra-low emission coal-fired power units. IOP Conf. Ser Earth Environ. Sci. 401:012010. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/401/1/012010
Jiang P, Khishgee S, Alimujiang A, Dong H (2020) Cost effective approaches for reducing carbon and air pollution emissions in the power industry in China. J Environ Manag 264:110452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110452
Li J, Zhao X, He Y, Liu H (2016) Research on technical route of flue gas ultra-low emission for coal-fired power plant (ICESP 2016). https://isesp.org/isesp_conferences. Accessed 2022-06-02
Liang Y, Li Q, Ding X, Wu D, Wang F, Otsuki T, Cheng Y, Shen T, Li S, Chen J (2020) Forward ultra-low emission for power plants via wet electrostatic precipitators and newly developed demisters: filterable and condensable particulate matters. Atmos Environ 225:117372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2020.117372
Liu J, Yang L, **ong G, Lu B, **n C (2011) Experimental investigation on the improving removal of fine particles in LIFAC flue gas desulfurization by heterogeneous condensation. J Fuel Chem Technol 39:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5813(11)60007-8
Liu C, Li J, Yang C, Diao Z, Wang C (2019) A composite absorption liquid for simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification in flue gas. Chin J Chem Eng 27:2566–2573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2019.04.013
Liu H, Tan Q, Jiang X, Ma S, Liao W, Yang F, Huang F (2020) Comprehensive evaluation of flue gas desulfurization and denitrification technologies of six typical enterprises in Chengdu, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:45824–45835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10460-5
Nie P, Zhang H, Wang Y (2013) Causes analysis of wet flue gas desulphurization stack rainout for the thermal powerplant without GGH and its countermeasures. Adv| Mater Res 724:1306–1309. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.724-725.1306
Parker KR (1997) Why an electrostatic precipitator? In: Parker KR (ed) Applied electrostatic precipitation. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1553-4_1
Poullikkas A (2015) Review of design, operating, and financial considerations in flue gas desulfurization systems. Energy Technol Policy 2:92–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/23317000.2015.1064794
Shahrestani M, Rahimi A (2019) Evaluation of electrical energy consumption in UV/H2O2 advanced oxidation process for simultaneous removal of NO and SO2. Environ Eng Res 24:389–396. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2018.276
Sun Z, Wang S, Zhou Q (2010) Experimental study on desulfurization efficiency and gas–liquid mass transfer in a new liquid-screen desulfurization system. Appl Energy 87:1505–1512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2009.09.007
Tomaszewski A, Przybylinski T, Kapica P, Lackowski M (2020) Influence of the spray scrubber geometry on the efficiency of dust removal-theoretical predictions and CFD analysis. J Appl Fluid Mech 13:1055–1066. https://doi.org/10.36884/jafm.13.04.30926
Wang Y, James P (1998) The calculation of wave-plate demister efficiencies using numerical simulation of the flow field and droplet motion. Chem Eng Res Des 76:980–985. https://doi.org/10.1205/026387698525630
Wang W, Li Z, Lyu J, Zhang H, Yue G, Ni W (2019) An overview of the development history and technical progress of China’s coal-fired power industry. Front Energy 13:417–426. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11708-019-0614-2
Wu H, Pan D, Jiang Y, Huang R, Hong G, Yang B, Peng Z, Yang L (2016) Improving the removal of fine particles from desulfurized flue gas by adding humid air. Fuel 184:153–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.07.024
Wu Q, Gu M, Du Y, Zeng H (2019) Synergistic removal of dust using the wet flue gas desulfurization systems. R Soc Open Sci 6:181696. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.181696
Xu Y, Yang Z, Zhang J (2017) Study on performance of wave-plate mist eliminator with porous foam layer as enhanced structure. Part I: Numerical simulation. Chem Eng Sci 171:650–661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2017.05.031
Yang L, Bao J, Yan J, Liu J, Song S, Fan F (2010) Removal of fine particles in wet flue gas desulfurization system by heterogeneous condensation. Chem Eng J 156:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.09.026
Yang L, Xu M, Wang J, Song L, Wang J (2021) Experimental and numerical analysis of a demister with vortex generators. Chin J Chem Eng 33:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2020.07.045
Yi H, Zhong T, Liu J, Yu Q, Zhao S, Gao F, Zhou Y, Wang S, Tang X (2021) Emissions of air pollutants from sintering flue gas in the Bei**g-Tian**-Hebei area and proposed reduction measures. J Clean Prod 304:126958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126958
You L, Zhu Y (2021) Efficient coordinated dust removal technology and economic analysis of desulfurization system under ultra-low emission situation. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ. Sci. 701:012003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/701/1/012003
Yuan C, Su S, Xu R, Liang S, Cheng H, Yao Z, Jiang L, Wang Z (2022) Effect of wet flue gas desulfurization on the concentrations and component profiles of condensable particulate matter from ultralow emission coal-fired power plants. Atmos Pollut Res 13:101376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2022.101376
Zhao H, Zheng C, Džapo H, Liu S, Guo Y, Gao X, Wu T (2019) A perspective on the applications of energy-cyber-physical systems (e-CPSs) in ultra-low emission coal-fired power plants. Energy Procedia 158:6139–6144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2019.01.497
Zhao Y, Zhang J, Wang Z (2020) Cost analysis of environmental protection price of coal-fired plants in China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:18729–18742. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08467-z
Zhang X (2015) Analysis of flue gas pollutants deep-removal technology in coal-fired power plants. Front Eng Manag 1:336–340. https://doi.org/10.15302/J-FEM-2014061
Zhang G, Zhang L, Wang J, Hu E (2017) Improving acoustic agglomeration efficiency by addition of sprayed liquid droplets. Powder Technol 317:181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.04.058
Zhong L, Yang Y, Hu J, Hu X, Liu Y, Xue X (2018) The industrial application of water washing device for aerosol condensation in ultra low flue gas emission. E3S Web Conf 53:02015. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/20185302015
Zu K, Yao Y, Cai M, Zhao F, Cheng D (2017) Modeling and experimental study on acoustic agglomeration for dust particle removal. J Aerosol Sci 114:62–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2017.09.001
Funding
This work was supported by the Aerospace Technology Application Industry R&D Project of The Sixth Research Institute of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (No. 2019F0020YXTB) and the Key Science and Technology Project of China National Coal Group CORP. (No. 17–37).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yi **ang conducted data analysis and wrote and revised the manuscript. Di Wu conducted the experiments and revised the manuscript. Guohua Yang revised the manuscript. Yanyan Chen reviewed the data. Wenhao Lyu conducted supplementary experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
The authors declare consent to participate.
Consent for publication
The authors declare consent to publish.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
**ang, Y., Wu, D., Yang, G. et al. Pilot study on demister-based dust removal methods for boiler flue gas. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 37570–37578 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24840-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-24840-6