Abstract
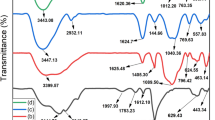
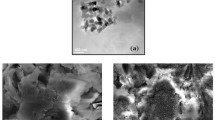
The abundant release of toxic heavy metals into wastewater has been a serious threat to human health, aquatic environments, plants, and animals; thus, it is critical to purify wastewater of these pollutants through a proper treatment process. A novel hydrogel compound was synthesized using partially hydrolyzed polyacrylamide (PHPAm) and functionalized Fe3O4-coated magnetic nanoparticles (PHPAm/Fe3O4@SiO2-SH) that is efficient in removal of mercury and lead from wastewater. This new magnetic nanoadsorbent is characterized using scanning electron microscope, Fourier-transform infrared, thermogravimetric analysis, vibrating sample magnetometer, and energy-dispersive X-ray analysis. The central composite design under response surface methodology (CCD-RSM) was applied in designing the experiments to optimize the main parameters affecting the adsorption capacity: initial concentration (77.50 mg L−1), pH (6.11 and 6.48), adsorbent dosage (25 mg), and contact time (115 and 106 min) for both Hg2+ and Pb2+ adsorption, respectively. Quadratic models were used for variable predictions and analysis of variance was applied to evaluate the statistical parameters and investigate the interactions of the variables. The high determination coefficient (R2 0.99) for both metals indicates a good correlation between actual and predicted response values. Additionally, thermodynamic modeling showed an endothermic and exothermic for Hg2+ and Pb2+, respectively, and also the spontaneous nature of both metals’ adsorption process within the temperature range of 288–318 K. Mercury and lead kinetic studies were in agreement with pseudo-second-order modeling, and the equilibrium results revealed that the Langmuir isotherm best fit the experimental data with maximum adsorption capacities of 256.41 and 227.27 (mg g−1) for Hg2+ and Pb2+, respectively. Overall, PHPAm/Fe3O4@SiO2-SH is thought to have highly promising potential for investigating heavy metals in wastewater treatment, and will make important contributions to similar studies that may be conducted in the future.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Adam AM, Saad HA, Atta AA, et al (2021) Pb ( II ), Cd ( II ) and Sn ( II ) heavy metals from wastewater using novel metal – carbon-based composites
Al-Jlil SA, Alsewailem FD (2009) Saudi Arabian clays for lead removal in wastewater. Appl Clay Sci 42:671–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLAY.2008.03.012
Amin MT, Alazba AA, Shafiq M (2017) Nonspontaneous and multilayer adsorption of malachite green dye by Acacia nilotica waste with dominance of physisorption. Water Sci Technol 76:1805–1815. https://doi.org/10.2166/WST.2017.366
Aschner M, Aschner JL (1990) Mercury neurotoxicity: mechanisms of blood-brain barrier transport. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 14:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0149-7634(05)80217-9
Asfaram A, Ghaedi M, Agarwal S et al (2015) Removal of basic dye Auramine-O by ZnS:Cu nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon: optimization of parameters using response surface methodology with central composite design. RSC Adv 5:18438–18450. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra15637d
Barakat MA (2011) New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arab J Chem 4:361–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.07.019
Berlin M, Zalups RK, Fowler BA (2009) Mercury. Handbook on the toxicology of metals: fourth edition 1:1013–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-59453-2.00046-9
Binandeh M, Rostamnia S, Karimi F (2019) Application of MNPs-IHSPN nanoparticles in really stabilization of biomolecules bio drugs In-vitro environment. 10.21203/rs.2.19616/v1
Borah D, Senapati K (2006) Adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solution onto pyrite. Fuel 85:1929–1934. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUEL.2006.01.012
Briggs D (2005) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Handbook of adhesion: second edition 621–622. https://doi.org/10.1002/0470014229.ch22
Churchill GA (2004) Using ANOVA to analyze microarray data. Biotechniques 37:173–177. https://doi.org/10.2144/04372TE01
Clarkson TW, Magos L, Greenwood MR (1972) The transport of elemental mercury into fetal tissues. Neonatology 21:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1159/000240512
Cui W, Meng Q, Feng Q et al (2019) Occurrence and release of cadmium, chromium, and lead from stone coal combustion. Intl J Coal Sci Technol 6:586–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/S40789-019-00281-4/FIGURES/4
Davis AP, Shokouhian M, Ni S (2001) Loading estimates of lead, copper, cadmium, and zinc in urban runoff from specific sources. Chemosphere 44:997–1009. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(00)00561-0
Demiral H, Demiral I, Tümsek F, Karabacakoǧlu B (2008) Adsorption of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution by activated carbon derived from olive bagasse and applicability of different adsorption models. Chem Eng J 144:188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2008.01.020
Demirel M, Kayan B (2012) Application of response surface methodology and central composite design for the optimization of textile dye degradation by wet air oxidation. Intl J Ind Chem 3:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/2228-5547-3-24
Ding Y, Zhu W, Xu Y, Qian X (2015) A small molecular fluorescent sensor functionalized silica microsphere for detection and removal of mercury, cadmium, and lead ions in aqueous solutions. Sensors Actuators B Chem 220:762–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.05.113
Du GH, Liu ZL, **a X, et al (2006) Characterization and application of Fe3O4/SiO2 nanocomposites. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 2006 39:3 39:285–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10971-006-7780-5
Ecer Ü, Yılmaz Ş, Şahan T (2020) Investigation of Mercury(II) and Arsenic(V) adsorption onto sulphur functionalised pumice: a response surface approach for optimisation and modelling. Int J Environ Anal Chem 00:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1838495
Erdemoǧlu M, Erdemoǧlu S, Sayilkan F et al (2004) Organo-functional modified pyrophyllite: preparation, characterisation and Pb(II) ion adsorption property. Appl Clay Sci 27:41–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLAY.2003.12.005
Faro LRF, Do Nascimento JLM, Alfonso M, Durán R (2001) In vivo effects of inorganic mercury (HgCl2) on striatal dopaminergic system. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 48:263–267. https://doi.org/10.1006/EESA.2000.2024
Flora SJS, Flora G, Saxena G (2006) Environmental occurrence , health effects and management of lead poisoning. 158–228
Gamage J, Weerahandi S (1998) Size performance of some tests in one-way ANOVA. Commun Stat Part B Simul Comput 27:625–640. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610919808813500
Gliozzo E (2021) Pigments — Mercury-based red (cinnabar-vermilion) and white (calomel) and their degradation products. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences 2021 13:11 13:1–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12520-021-01402-4
Gode F, Pehlivan E (2006) Removal of chromium(III) from aqueous solutions using Lewatit S 100: the effect of pH, time, metal concentration and temperature. J Hazard Mater 136:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2005.12.021
Goel J, Kadirvelu K, Rajagopal C, Garg VK (2005) Investigation of adsorption of lead, mercury and nickel from aqueous solutions onto carbon aerogel. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 80:469–476. https://doi.org/10.1002/JCTB.1212
Gunay Gurer A, Aktas K, Ozkaleli Akcetin M et al (2021) Adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics, and kinetic modeling of methylene blue onto novel carbonaceous adsorbent derived from bitter orange peels. Water Air Soil Pollut 232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05090-7
Guo X, Du B, Wei Q et al (2014) Synthesis of amino functionalized magnetic graphenes composite material and its application to remove Cr(VI), Pb(II), Hg(II), Cd(II) and Ni(II) from contaminated water. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.075
Gupta VK, Kumar R, Nayak A et al (2013) Adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution onto carbon nanotubes: a review. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 193–194:24–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CIS.2013.03.003
Hameed BH, Ahmad AL, Latiff KNA (2007) Adsorption of basic dye (methylene blue) onto activated carbon prepared from rattan sawdust. Dyes Pigments 75:143–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.05.039
Harvey B (2002) Managing elevated blood lead levels among young children : recommendations from the Advisory Committee on Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention
Järup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:167–182
Kim H-Y (2014) Analysis of variance (ANOVA) comparing means of more than two groups. Restor Dent Endo 39:74. https://doi.org/10.5395/RDE.2014.39.1.74
Kingston HM, Cain RD (2012) A new method to assess mercury emissions: a study of three coal-fired electric-generating power station configurations. 53:1318–1325. 10.1080/10473289.2003.10466300
Kinuthia GK, Ngure V, Beti D et al (2020) Levels of heavy metals in wastewater and soil samples from open drainage channels in Nairobi, Kenya: community health implication. Sci Rep 10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65359-5
Kushwaha AK, Gupta N, Chattopadhyaya MC (2014) Removal of cationic methylene blue and malachite green dyes from aqueous solution by waste materials of Daucus carota. J Saudi Chem Soc 18:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSCS.2011.06.011
Landaburu-Aguirre J, Pongrácz E, Perämäki P, Keiski RL (2010) Micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration for the removal of cadmium and zinc: use of response surface methodology to improve understanding of process performance and optimisation. J Hazard Mater 180:524–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2010.04.066
Landrigan PJ (2002) The worldwide problem of lead in petrol. Bull World Health Organ 80:768–768
Lindberg SE, Turner RR (1977) Mercury emissions from chlorine-production solid waste deposits. Nature 1977 268:5616 268:133–136. https://doi.org/10.1038/268133a0
Ma C, Li C, He N et al (2012) Preparation and characterization of monodisperse core-shell Fe 3O 4@SiO 2 microspheres and its application for magnetic separation of nucleic acids from E. coli BL21. J Biomed Nanotechnol 8:1000–1005. https://doi.org/10.1166/JBN.2012.1454
Matta G, Tchounwou P, Gjyli L (2015) lead and arsenic impact on environment and human health.pdf Cite this paper Related papers Heavy Met als and Human Healt h Simone Morais Elemnt mines urns neh Review: Environment al exposure t o mercury and it s t oxicopat hologic implicat ions for public
Merzouk B, Yakoubi M, Zongo I et al (2011) Effect of modification of textile wastewater composition on electrocoagulation efficiency. Desalination 275:181–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DESAL.2011.02.055
Najafi M, Rostamian R, Rafati AA (2011) Chemically modified silica gel with thiol group as an adsorbent for retention of some toxic soft metal ions from water and industrial effluent. Chem Eng J 168:426–432
Namasivayam C, Kadirvelu K (1999) Uptake of mercury ( II ) from wastewater by activated carbon from an unwanted agricultural solid by-product : coirpith. 37:79–84
Narimani A, Kordnejad F, Kaur P et al (2021) Rheological and thermal stability of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogel based on polyacrylamide/hydroxypropyl guar reinforced with graphene oxide for application in oil recovery. J Polym Eng 41:788–798. https://doi.org/10.1515/POLYENG-2021-0147/HTML
Naseem R, Tahir SS (2001) Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous/acidic solutions by using bentonite as an adsorbent. Water Res 35:3982–3986
National V (2010) Metal Pollution in ecosystems . Ecotoxicology Studies and Risk Assessment in the Marine Environment “ Metal Pollution in Ecosystems . Ecotoxicology Studies and Risk Assessment in the Marine Environment ”
Nordberg G, toxicologica FS-A pharmacologica et 1969 (1969) Distribution of inorganic mercury in the guinea pig brain. academia.edu
Pacyna EG, Pacyna JM (2002) Global emission of mercury from anthropogenic sources in 1995. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 2002 137:1 137:149–165. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015502430561
Peng W, Li H, Liu Y, Song S (2017) A review on heavy metal ions adsorption from water by graphene oxide and its composites. J Mol Liq 230:496–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MOLLIQ.2017.01.064
Pirrone N, Cinnirella S, Feng X et al (2010) Global mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic and natural sources. Atmos Chem Phys 10:5951–5964. https://doi.org/10.5194/ACP-10-5951-2010
Roto R, Yusran Y, Kuncaka A (2016) Magnetic adsorbent of Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 core-shell nanoparticles modified with thiol group for chloroauric ion adsorption. Appl Surf Sci 377:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APSUSC.2016.03.099
Sahmoune MN (2018) Evaluation of thermodynamic parameters for adsorption of heavy metals by green adsorbents. Environ Chem Lett 17:697–704. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10311-018-00819-Z
Say R, Yilmaz N, Denizli A (2003) Biosorption of cadmium, lead, mercury, and arsenic ions by the fungus Penicillium purpurogenum. Sep Sci Technol 38:2039–2053. https://doi.org/10.1081/SS-120020133
Suzuki N, Yamamoto M, Watanabe K, et al (2004) Both mercury and cadmium directly influence calcium homeostasis resulting from the suppression of scale bone cells: the scale is a good model for the evaluation of heavy metals in bone metabolism. Journal of Bone and Mineral Metabolism 2004 22:5 22:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00774-004-0505-3
Tran HN, You SJ, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A, Chao HP (2017) Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Water Res 120:88–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.04.014
Tüzün I, Bayramoǧlu G, Yalçin E et al (2005) Equilibrium and kinetic studies on biosorption of Hg(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions onto microalgae Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Environ Manag 77:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.01.028
Van Tran V, Park D, Lee YC (2018) Hydrogel applications for adsorption of contaminants in water and wastewater treatment. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2018 25:25 25:24569–24599. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-018-2605-Y
Verma SR, Tonk IP (1983) Effect of sublethal concentrations of mercury on the composition of liver, muscles and ovary of Notopterus notopterus. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 1983 20:3 20:287–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284633
Wang Z, Xu J, Hu Y, Zhao H, Zhou J, Liu Y et al (2016) Functional nanomaterials: Study on aqueous Hg (II) adsorption by magnetic Fe3O4@ SiO2-SH nanoparticles. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 60:394–402
Wu FC, Liu BL, Wu KT, Tseng RL (2010) A new linear form analysis of Redlich-Peterson isotherm equation for the adsorptions of dyes. Chem Eng J 162:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.03.006
Zayed AM, Abdel Wahed MSM, Mohamed EA, Sillanpää M (2018) Insights on the role of organic matters of some Egyptian clays in methyl orange adsorption: isotherm and kinetic studies. Appl Clay Sci 166:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CLAY.2018.09.013
Zhang C, Sui J, Li J et al (2012) Efficient removal of heavy metal ions by thiol-functionalized superparamagnetic carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.062
Zhang C, Yu Z, Zeng G et al (2016) Phase transformation of crystalline iron oxides and their adsorption abilities for Pb and Cd. Chem Eng J 284:247–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2015.08.096
Zhang LY, Zhu XJ, Sun HW et al (2010) Control synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4–chitosan nanoparticles under UV irradiation in aqueous system. Curr Appl Phys 10:828–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CAP.2009.10.002
Zhang Y, Li X, Li Y (2015) Influence of solution chemistry on heavy metals removal by bioadsorbent tea waste modified by poly (vinyl alcohol). New pub: Balaban 53:2134–2143. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.861775
Zhang Y, Xu Q, Zhang S et al (2013) Preparation of thiol-modified Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles and their application for gold recovery from dilute solution. Sep Purif Technol 116:391–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2013.06.018
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Arvin Zist Pooya Lab for providing the necessary facilities to accomplish this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Elaheh Ebrahimpour performed the analysis, wrote the manuscript, and designed the figures. Ali Kazemi designed the study, interpreted the results, helped to shape the research, and supervised the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Angeles Blanco
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 196 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimpour, E., Kazemi, A. Mercury(II) and lead(II) ions removal using a novel thiol-rich hydrogel adsorbent; PHPAm/Fe3O4@SiO2-SH polymer nanocomposite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 13605–13623 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23055-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-23055-z