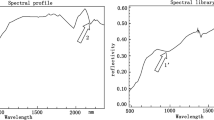
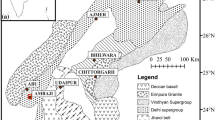
Abstract
Hyperspectral imaging technology has been used for biochemical analysis of Earth’s surface exploiting the spectral reflectance signatures of various materials. The new-generation Italian PRISMA (PRecursore IperSpettrale dellaMissione Applicativa) hyperspectral satellite launched by the Italian space agency (ASI) provides a unique opportunity to map various materials through spectral signature analysis for recourse management and sustainable development. In this study PRISMA hyperspectral satellite imagery–based multiple spectral indices were generated for rapid pollution assessment at Ghazipur and Okhla landfill sites in Delhi, India. It was found that the combined risk score for Okhla landfill site was higher than the Ghazipur landfill site. Various manmade materials identified, exploiting the hyperspectral imagery and spectral signature libraries, indicated presence of highly saline water, plastic (black, ABS, pipe, netting, etc.), asphalt tar, black tar paper, kerogen BK-Cornell, black paint and graphite, chalcocite minerals, etc. in large quantities in both the landfill sites. The methodology provides a rapid pollution assessment tool for municipal landfill sites.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai W, Liu S, Liao H et al (2022) Application of hyperspectral imaging technology in the rapid identification of microplastics in farmland soil. Sci Total Environ 807:151030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151030
Alam P, Sharholy M, Ahmad K (2020) A study on the landfill leachate and its impact on groundwater quality of Ghazipur area, New Delhi, India. In: Kalamdhad AS (ed) Recent Developments in Waste Management. Springer, Singapore, pp 345–358
Ali SM, Pervaiz A, Afzal B et al (2014) Open dum** of municipal solid waste and its hazardous impacts on soil and vegetation diversity at waste dum** sites of Islamabad city. J King Saud Univ - Sci 26:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2013.08.003
Angmo S, Shah S (2021) Impact of Okhla, Bhalswa and Ghazipur municipal waste dumpsites (landfill) on groundwater quality in Delhi. Curr World Environ 16:210–220. https://doi.org/10.12944/CWE.16.1.21
Apaza H, Chévez L, Loro H (2014) Near-infrared hyperspectral imaging spectroscopy to detect microplastics and pieces of plastic in almond flour. Int J Comput Syst Eng 15:90–93
Banerjee A (2021) Impact of municipal solid waste landfill on surrounding environment: A case study. In: Patel S, Solanki CH, Reddy KR, Shukla SK (eds) Proceedings of the Indian Geotechnical Conference 2019. Springer Singapore, Singapore, pp 249–260
Bansal S, Biswas S (2015) A case study on characteristics of soild waste & leachate treatment of Okhla landfill- New Delhi. Int J Res Engg & Tech 04:175–181
Chen C-W, Tseng Y-S, Mukundan A, Wang H-C (2021) Air pollution: sensitive detection of PM2.5 and PM10 concentration using hyperspectral imaging. Appl Sci:11:4543. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11104543
Cheng XF, Song TT, Chen Y et al (2017) Retrieval and analysis of heavy metal content in soil based on measured spectra in the Lan** Zn-Pb mining area, western Yunnan Province. Acta Petrol Mineral 36:60–69
Choe E, van der Meer F, van Ruitenbeek F, van der Werff H, de Smeth B, Kim K-W (2008) Map** of heavy metal pollution in stream sediments using combined geochemistry, field spectroscopy, and hyperspectral remote sensing: a case study of the Rodalquilar mining area, SE Spain. Remote Sens Environ 112:3222–3233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2008.03.017
DPCC (Delhi Pollution Control Committee) water laboratory report no. DPCC/W/LF/2021/3193 dated 24 June 2021
Gamal E, Khdery G, Morsy A, Ali M, Hashim A, Saleh H (2020) Hyperspectral indices for discriminating plant diversity in Wadi Al-Afreet, Egypt. Plant Archives 20:3361-3371Gao, BC (1996) NDWI: a Normalized Difference Water Index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens Environ 58:257–266
Gill J, Faisal K, Shaker A, Yan WY (2019) Detection of waste dum** locations in landfill using multi-temporal Landsat thermal images. Waste Manag Res 37:386–393. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X18821808
Gong C, Wang X, Chen RB et al (2016) Study on heavy metal element content in the coastal saline soil by hyperspectral remote sensing. Remote Sens Technol Appl 25:169–177
Hazem T, El-Hamid A, Hong G (2020) Hyperspectral remote sensing for extraction of soil salinization in the northern region of Ningxia. Model Earth Syst Environ 6:2487–2493
Huete AR (1998) A Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index (SAVI). Remote Sens Environ 25:295–309
Iacoboaea C, Petrescu F (2013) Landfill monitoring using remote sensing: a case study of Glina, Romania. Waste Manag Res J Int Solid Wastes Public Clean Assoc ISWA 31:1075–1080. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X13487585
Joshi R, Ahmed S, Kumar S (2018) Seasonal variation of leachate quality at active landfill sites in Delhi, India. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1680/jmuen.17.00039
Khan MJ, Khan HS, Yousaf A et al (2018) Modern trends in hyperspectral image analysis: a review. IEEE Access 6:14118–14129. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2812999
Khosravi V, Ardejani FD, Gholizadeh A, Saberioon M (2021) Satellite imagery for monitoring and map** soil chromium pollution in a mine waste dump. Remote Sens 13:1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13071277
Kumari P, Kaur A, Gupta NC (2018) Extent of groundwater contamination due to leachate migration adjacent to unlined landfill site of Delhi. Environ Claims J 31:160–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/10406026.2018.1543825
Kumar S, George KJ (2015) Hyperspectral remote sensing in characterizing soil salinity severity using svm technique - a case study of alluvial plains. Int J Adv Remote Sens GIS 4:1344–1360
Kuriakose T, Ramanathan AL, Sankar K, Rawat M, Sahoo M (2016) Characterizing waste dump effects on ground water through electrical resistivity sounding around Okhla landfill site, New Delhi, India. J Appl Geochem 18:457–463
Mor S, Ravindra K, Dahiya RP, Chandra A (2006) Leachate characterization and assessment of groundwater pollution near municipal solid waste landfill site. Environ Monit Assess 118:435–456. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1505-7
Naveen BP, Malik RK (2017) Assessment of leachate pollution index for Delhi landfill sites, India. OAIJSE 2(9):98-101. ISSN (Online) 2456-3293
Ottavianelli G, Hobbs S, Smiith R, Bruno D (2005) Assessment of hyperspectral and SAR remote sensing for solid waste landfill management. Proc. of the 3rd ESA CHRIS/Proba Workshop, 21-23 March, ESRIN, Frascati, Italy (ESA SP-593, June 2005)
Segal D (1982) Theoretical basis for differentiation of ferric-iron bearing minerals, using Landsat MSS data. Proceedings of symposium for remote sensing of environment, 2nd Thematic Conference on Remote Sensing for Exploratory Geology, Fort Worth, TX pp. 949-951.
Serranti S, Bonifazi G (2012) Pollution level detection in dump clay liners by hyperspectral imaging. Int J Environ Waste Manag 10:163–176. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJEWM.2012.048363
Serranti S, Palmieri R, Bonifazi G, Cózar A (2018) Characterization of microplastic litter from oceans by an innovative approach based on hyperspectral imaging. Waste Manag 76:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.03.003
Shan J, Zhao J, Liu L et al (2018) A novel way to rapidly monitor microplastics in soil by hyperspectral imaging technology and chemometrics. Environ Pollut Barking Essex 1987 238:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.03.026
Shan J, Zhao J, Zhang Y et al (2019) Simple and rapid detection of microplastics in seawater using hyperspectral imaging technology. Anal Chim Acta 1050:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.11.008
Sharma A, Gupta AK, Ganguly R (2018) Impact of open dum** of municipal solid waste on soil properties in mountainous region. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 10:725–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2017.12.009
Sinha N (2014) Environmental impact of solid waste (Okhla – landfill site). J Basic ApplEng Res 1:75–77
Swati, Ghosh P, Thakur IS (2017) An integrated approach to study the risk from landfill soil of Delhi: chemical analyses, in vitro assays and human risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 143:120–128
Tripathi A, Singh A, Capt MM (2021) Environmental impacts of Ghazipur landfill on its surroundings. Int Res J Eng Tech 08(02):1178–1184
Vincent RK (1994) Remote sensing for solid waste landfills and hazardous waste sites. Photogramm Eng Remote Sens 60:979–982
Wu J, Liu Y, Wang J, He T (2010) Application of Hyperion data to land degradation map** in the Hengshan region of China. Int J Remote Sens 31:5145–5161. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160903302940
Yeilagi S, Rezapour S, Asadzadeh F (2021) Degradation of soil quality by the waste leachate in a Mediterranean semi-arid ecosystem. Sci Rep 11:11390. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-90699-1
Zhang Y, Wang X, Shan J et al (2019) Hyperspectral imaging based method for rapid detection of microplastics in the intestinal tracts of fish. Environ Sci Technol 53:5151–5158. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b07321
Zhang Y, Wu L, Ren H et al (2020) Map** water quality parameters in urban rivers from hyperspectral images using a new self-adapting selection of multiple artificial neural networks. Remote Sens 12:336. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12020336
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to Italian Space Agency (ASI) for providing the satellite hyperspectral imagery free of cost. PC acknowledges the fellowship received from University of Queensland - Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Academy of Research, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, India.
Availability of data and materials
All data has been included in the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript. PC acknowledges the fellowship received from University of Queensland - Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Academy of Research, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AD contributed to the conception, design, material/data preparation and analysis of the study. AD and PC wrote the first draft. BL and SS supervised the study, analysed the data and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dutta, A., Chaudhary, P., Sharma, S. et al. Satellite hyperspectral imaging technology as a potential rapid pollution assessment tool for urban landfill sites: case study of Ghazipur and Okhla landfill sites in Delhi, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 116742–116750 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22421-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-22421-1