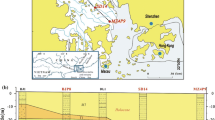
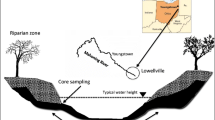
Abstract
Groundwater level fluctuation is a common natural phenomenon that causes alternate changes in oxygen, moisture, and biogeochemical processes in sediments. Microbes are sensitive to these environmental changes. Therefore, a specific microbial community is proposed to form in the groundwater fluctuation zone (GFZ). The vertical distributions of microbial abundance, diversity, and functional microbes and genes in sediment profiles were investigated, focusing on the GFZ, using high-throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing, qPCR, and the Functional Annotation of Prokaryotic Taxa (FAPROTAX) approach. The relationships between chemical variables and microbial community structure were investigated by redundancy analysis (RDA). Results showed that the microbial abundance and microbial community richness and diversity were higher in the sediments of the GFZ. The nitrate reducers prefer to stay just below the groundwater level in the GFZ. The predominant microbes in the GFZ functioned as nitrifiers and Fe-oxidizers. The specific community in the GFZ is mainly related to NO3− and Fe(III) in the sediment. Consequently, the biochemical processes nitrification and Fe- and Mn-oxidation sequentially happen above the nitrate-reduction zone near the groundwater level in the GFZ. These results provide new knowledge in the biogeochemistry cycle of the GFZ and its disturbance on the vertical distribution and transport of biogenic elements and contaminants.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Braun B, Schroder J, Knecht H, Szewzyk U (2016) Unraveling the microbial community of a cold groundwater catchment system. Water Res 107:113–126
Bryant LD, Little JC, Burgmann H (2012) Response of sediment microbial community structure in a freshwater reservoir to manipulations in oxygen availability. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 80(1):248–263
Chen R, Liu H, Zhang P, Zhao L, Ding K, Yuan S (2019) Attenuation of Fe(III)-reducing bacteria during table fluctuation of groundwater containing Fe2+. Sci Total Environ 694:133660
Chen X, Lu J, Zhu J, Liu C (2020) Characteristics of denitrifying bacteria in different habitats of the Yongding River wetland. China J Environ Manage 275:111273
Crump BC, Kling GW, Bahr M, Hobbie JE (2003) Bacterioplankton community shifts in an arctic lake correlate with seasonal changes in organic matter source. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(4):2253–2268
Deemer BR, Harrison JA (2019) Summer redox dynamics in a eutrophic reservoir and sensitivity to a summer’s end drawdown event. Ecosystems 22(7):1618–1632
Di Canito A, Zampolli J, Orro A, D’Ursi P, Milanesi L, Sello G, Steinbuchel A, Di Gennaro P (2018) Genome-based analysis for the identification of genes involved in o-xylene degradation in Rhodococcus opacus R7. BMC Genomics 19(1):587
Ehrlich HL, Newman DK (2015) Geomicrobiology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Elken E, Heinaru E, Joesaar M, Heinaru A (2020) Formation of new PHE plasmids in pseudomonads in a phenol-polluted environment. Plasmid 110:102504
Farnsworth CE, Voegelin A, Hering JG (2012) Manganese oxidation induced by water table fluctuations in a sand column. Environ Sci Technol 46(1):277–284
Field EK, Kato S, Findlay AJ, MacDonald DJ, Chiu BK, Luther GW, Chan CS (2016) Planktonic marine iron oxidizers drive iron mineralization under low-oxygen conditions. Geobiology 14(5):499–508
Froelich PN, Klinkhammer GP, Bender ML, Luedtke NA, Heath GR, Cullen D, Dauphin P, Hammond D, Hartman B, Maynard V (1979) Early oxidation of organic matter in pelagic sediments of the eastern equatorial Atlantic: suboxic diagenesis. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 43(7):1075–1090
Gruber N, Galloway JN (2008) An Earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 451(7176):293–296
Gulay A, Musovic S, Albrechtsen HJ, Al-Soud WA, Sorensen SJ, Smets BF (2016) Ecological patterns, diversity and core taxa of microbial communities in groundwater-fed rapid gravity filters. ISME J 10(9):2209–2222
Hu A, Wang H, Li J, Liu J, Chen N, Yu CP (2016) Archaeal community in a human-disturbed watershed in southeast China: diversity, distribution, and responses to environmental changes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(10):4685–4698
Huang J, Yang J, Jiang H, Wu G, Liu W, Wang B, **ao H, Han J (2020) Microbial responses to simulated salinization and desalinization in the sediments of the Qinghai-Tibetan Lakes. Front Microbiol 11:1772
Jia M, Bian X, Yuan S (2017) Production of hydroxyl radicals from Fe(II) oxygenation induced by groundwater table fluctuations in a sand column. Sci Total Environ 584–585:41–47
Jiang L, Zheng Y, Peng X, Zhou H, Zhang C, **ao X, Wang F (2009) Vertical distribution and diversity of sulfate-reducing prokaryotes in the Pearl River estuarine sediments. Southern China FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70(2):93–106
Kao CM, Chen CS, Tsa FY, Yang KH, Chien CC, Liang SH, Yang CA, Chen SC (2010) Application of real-time PCR, DGGE fingerprinting, and culture-based method to evaluate the effectiveness of intrinsic bioremediation on the control of petroleum-hydrocarbon plume. J Hazard Mater 178(1–3):409–416
Kao CM, Chen CY, Chen SC, Chien HY, Chen YL (2008) Application of in situ biosparging to remediate a petroleum-hydrocarbon spill site: field and microbial evaluation. Chemosphere 70(8):1492–1499
Kato S, Chan C, Itoh T, Ohkuma M (2013) Functional gene analysis of freshwater iron-rich flocs at circumneutral pH and isolation of a stalk-forming microaerophilic iron-oxidizing bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(17):5283–5290
Lai TV, Ryder MH, Rathjen JR, Bolan NS, Croxford AE, Denton MD (2021) Dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium increased with rising temperature. Biol Fert Soils 57(3):363–372
Li Z, Cupples AM (2021) Diversity of nitrogen cycling genes at a Midwest long-term ecological research site with different management practices. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105(10):4309–4327
Lipson DA, Raab TK, Parker M, Kelley ST, Brislawn CJ, Jansson J (2015) Changes in microbial communities along redox gradients in polygonized Arctic wet tundra soils. Environ Microbiol Rep 7(4):649–657
Liu C, Du Y, Chen K, Ma S, Chen B, Lan Y (2019) Contrasting exchanges of nitrogen and phosphorus across the sediment-water interface during the drying and re-inundation of littoral eutrophic sediment. Environ Pollut 255(Pt 3):113356
Liu Y, Ren Z, Qu X, Zhang M, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Peng W (2020) Microbial community structure and functional properties in permanently and seasonally flooded areas in Poyang Lake. Sci Rep 10(1):4819
Louca S, Parfrey LW, Doebeli M (2016) Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 353(6305):1272–1277
Lu L, Wan Z, Luo T, Fu Z, ** Y (2018) Polystyrene microplastics induce gut microbiota dysbiosis and hepatic lipid metabolism disorder in mice. Sci Total Environ 631–632:449–458
Ludemann H, Arth I, Liesack W (2000) Spatial changes in the bacterial community structure along a vertical oxygen gradient in flooded paddy soil cores. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(2):754–762
Lueder U, Druschel G, Emerson D, Kappler A and Schmidt C (2018) Quantitative analysis of O2 and Fe2+ profiles in gradient tubes for cultivation of microaerophilic Iron(II)-oxidizing bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 94(2): fix177
Ma J, Liu H, Zhang C, Ding K, Chen R, Liu S (2020) Joint response of chemistry and functional microbial community to oxygenation of the reductive confined aquifer. Sci Total Environ 720:137587
Matulich KL, Martiny JBH (2015) Microbial composition alters the response of litter decomposition to environmental change. Ecology 96(1):154–163
Meng L, Zuo R, Wang JS, Li Q, Du C, Liu X, Chen MH (2021) Response of the redox species and indigenous microbial community to seasonal groundwater fluctuation from a typical riverbank filtration site in Northeast China. Ecol Eng 159:106099
Meyerhof MS, Wilson JM, Dawson MN, Beman JM (2016) Microbial community diversity, structure and assembly across oxygen gradients in meromictic marine lakes. Palau Environ Microbiol 18(12):4907–4919
Nealson KH (1997) Sediment bacteria: who’s there, what are they doing, and what’s new? Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 25:403–434
Ollivier J, Towe S, Bannert A, Hai B, Kastl EM, Meyer A, Su MX, Kleineidam K, Schloter M (2011) Nitrogen turnover in soil and global change. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 78(1):3–16
Pronk GJ, Mellage A, Milojevic T, Smeaton CM, Engel K, Neufeld JD, Rezanezhad F, Van Cappellen P (2020) Carbon turnover and microbial activity in an artificial soil under imposed cyclic drainage and imbibition. Vadose Zone J 19(1):e20021
Saha UK, Sonon L, Biswas BK (2018) A comparison of diffusion-conductimetric and distillation-titration methods in analyzing ammonium- and nitrate-nitrogen in the KCl-extracts of georgia soils. Commun Soil Sci Plan 49(1):63–75
Shi J, Yang Y, Lu H, ** B, Li J, **ao C, Wang Y, Tang J (2021) Effect of water-level fluctuation on the removal of benzene from soil by SVE. Chemosphere 274:129796
Shi R, Xu S, Qi Z, Zhu Q, Huang H, Weber F (2019) Influence of suspended mariculture on vertical distribution profiles of bacteria in sediment from Daya Bay, Southern China. Mar Pollut Bull 146:816–826
Sinke AJC, Dury O, Zobrist J (1998) Effects of a fluctuating water table: column study on redox dynamics and fate of some organic pollutants. J Contam Hydrol 33(1–2):231–246
Smith CJ, Nedwell DB, Dong LF, Osborn AM (2007) Diversity and abundance of nitrate reductase genes (narG and napA), nitrite reductase genes (nirS and nrfA), and their transcripts in estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 73(11):3612–3622
Spietz RL, Williams CM, Rocap G, Horner-Devine MC (2015) A dissolved oxygen threshold for shifts in bacterial community structure in a seasonally hypoxic estuary. PLoS ONE 10(8):e0135731
Unno T, Kim J, Kim Y, Nguyen SG, Guevarra RB, Kim GP, Lee JH, Sadowsky MJ (2015) Influence of seawater intrusion on microbial communities in groundwater. Sci Total Environ 532:337–343
Vet WW, Dinkla IJ, Abbas BA, Rietveld LC and Loosdrecht MC (2012) Gallionella spp. in trickling filtration of subsurface aerated and natural groundwater. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(4): 904–912
Walters WA, Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Berg-Lyons D, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) PrimerProspector: de novo design and taxonomic analysis of barcoded polymerase chain reaction primers. Bioinformatics 27(8):1159–1161
Wang G, Huang W, Mayes MA, Liu X, Zhang D, Zhang Q, Han T, Zhou G (2019a) Soil moisture drives microbial controls on carbon decomposition in two subtropical forests. Soil Biol Biochem 130:185–194
Wang J, Wang D, Wang B (2019b) Soil bacterial diversity and its determinants in the riparian zone of the Lijiang River, China. Curr Sci India 117(8):1324–1332
Wilopo W and Putra DPE (2021) Groundwater recharge estimation using groundwater level fluctuation patterns in unconfined aquifer of Yogyakarta City, Indonesia. Kuwait J Sci 48(2)
Wu B, Liu F, Fang W, Yang T, Chen GH, He Z, Wang S (2021) Microbial sulfur metabolism and environmental implications. Sci Total Environ 778:146085
**a X, Cheng L, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Wang K, Ding A, Cai Z, Shi H, Zuo L (2020) Response of soil bacterial community and geochemical parameters to cyclic groundwater-level oscillations in laboratory columns. Vadose Zone J 19:e20011
**ang Y, Wang Y, Zhang C, Shen H, Wang D (2018) Water level fluctuations influence microbial communities and mercury methylation in soils in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. J Environ Sci (china) 68:206–217
Yan L, Hermans SM, Totsche KU, Lehmann R, Herrmann M, Kusel K (2021) Groundwater bacterial communities evolve over time in response to recharge. Water Res 201:117290
Ye F, Ma MH, Op den Camp HJM, Chatzinotas A, Li L, Lv MQ, Wu SJ, Wang Y (2018) Different recovery processes of soil ammonia oxidizers from flooding disturbance. Microb Ecol 76(4):1041–1052
Zhang H, Sun L, Li Y, Zhang W, Niu L, Wang L (2021) The bacterial community structure and N-cycling gene abundance in response to dam construction in a riparian zone. Environ Res 194:110717
Zhang YT, Tong M, Yuan SH, Qian A, Liu H (2020) Interplay between iron species transformation and hydroxyl radicals production in soils and sediments during anoxic-oxic cycles. Geoderma 370:114351
Zheng T, Deng Y, Wang Y, Jiang H, O’Loughlin EJ, Flynn TM, Gan Y, Ma T (2019) Seasonal microbial variation accounts for arsenic dynamics in shallow alluvial aquifer systems. J Hazard Mater 367:109–119
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41830862, 41672353, 41521001), Hubei Province for Innovative Research Groups (grant no. 2018CFA028), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan) (CUGCJ1803, CUGQY1928).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Junhao Shen: Conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, software, writing—original draft. Hui Liu: Supervision, project administration, funding acquisition, conceptualization, writing—review and editing. Huazhong Zhou: Writing—review and editing. Rong Chen: writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Robert Duran.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, J., Liu, H., Zhou, H. et al. Specific characteristics of the microbial community in the groundwater fluctuation zone. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 76066–76077 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21166-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21166-1