Abstract
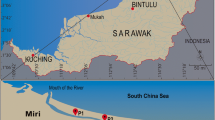
The rapid development of coastal aquaculture in recent decades has led to excessive discharge of organic matter and nutrients into surrounding waters, which could result in eutrophication and potentially affect metal cycling. In our study, the influence of algal organic matter on metal accumulation was examined in three coastal sediment cores taken from a tropical region, Hainan Island, China. Overall, metal pollution adjacent to aquaculture ponds remained at low levels on the coast, except Zn, Cd, and Sn were moderately to highly enriched in the Dongjiao sediments. The δ13C values and the atomic C/N ratios indicated a major contribution of phytoplankton to sedimentary organic matter at the Dongjiao site. Moreover, both the algae-derived organic matter and effluent nitrogen were significantly associated with the enriched Zn, Cd, and Sn, suggesting that nutrient-induced phytoplankton growth and its organic matter may act as a “biological pump” to enhance the accumulation of metals. Wastewater treatment for aquaculture ponds should include the control of algal organic matter.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Alzahrani DA, Selim EMM, El-Sherbiny MM (2018) Ecological assessment of heavy metals in the grey mangrove (Avicennia marina) and associated sediments along the red sea coast of Saudi Arabia. Oceanologia 60(4):513–526
Bao H, Wu Y, Unger D, Du J, Herbeck LS, Zhang J (2013) Impact of the conversion of mangroves into aquaculture ponds on the sedimentary organic matter composition in a tidal flat estuary (Hainan Island, China). Cont Shelf Res 57:82–91
Bharadwaj SA, Patnaik S, Browdy LC, Lawrence LA (2014) Comparative evaluation of an inorganic and a commercial chelated copper source in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) fed diets containing phytic acid. Aquaculture 422-423:63–68
Bhattacharya BD, Nayak DC, Sarkar SK, Biswas SN, Rakshit D, Ahmed MK (2015) Distribution of dissolved trace metals in coastal regions of indian Sundarban mangrove wetland: a multivariate approach. J Clean Prod 96:233–243
Biao X, Kai** Y (2007) Shrimp farming in China: operating characteristics, environmental impact and perspectives. Ocean Coast Manag 50(7):538–550
Birth G (2003) A scheme for assessing human impacts on coastal aquatic environments using sediments. In: Woodcoffe CD, Furness RA (eds) Coastal GIS 2003. Wollongong University Papers in Center for Maritime Policy, Australia, p 14
Bouwman L, Beusen A, Gilbert PM, Overbeek C, Pawlowski M, Herrera J, Mulsow S, Yu R, Zhou M (2013) Mariculture: significant and expanding cause of coastal nutrient enrichment. Environ Res Lett 8:04402
Burford MA, Williams KC (2001) The fate of nitrogenous waste from shrimp feeding. Aquaculture 198:79–93
Burford MA, Costanzo SD, Dennison WC, Jackson CJ, Jones AB, McKinnon AD, Preston NP, Trott LA (2003) A synthesis of dominant ecological processes in intensive shrimp ponds and adjacent coastal environments in NE Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 46:1456–1469
Carbonell G, Ramos C, Tarazona JV (1998) Metals in shrimp culture areas from the Gulf of Fonseca, Central America. I. Sediments. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 60:252–259
Carrie J, Wang F, Sanei H, Macdonald RW, Outridge PM, Stern GA (2009) Increasing contaminant burdens in an Arctic fish, burbot (Lota lota), in a warming climate. Environ Sci Technol 44:316–322
Cheng Z, Man YB, Nie XP, Wong MH (2013) Trophic relationships and health risk assessments of trace metals in the aquaculture pond ecosystem of Pearl River Delta, China. Chemosphere 90(7):2142–2148
Chu B, Chen X, Li Q, Yang Y, Mei X, He B, Li H, Tan L (2015) Effects of salinity on the transformation of heavy metals in tropical estuary wetland soil. Chem Ecol 31(2):186–198
Clark MW, McConchie D, Lewis DW, Saenger P (1998) Redox stratification and heavy metal partitioning in Avicennia-dominated mangrove sediments: a geochemical model. Chem Geol 149(3-4):147–171
Costanzo SD, O’Donohue MJ, Dennison WC (2004) Assessing the influence and distribution of shrimp pond effluent in a tidal mangrove creek in north-east Australia. Mar Pollut Bull 48:514–525
Dong D, Nelson YM, Lion LW, Shuler ML, Ghiorse WC (2000) Adsorption of Pb and Cd onto metal oxides and organic material in natural surface coatings as determined by selective extractions: new evidence for the importance of Mn and Fe oxides. Water Res 34:427–436
Duan D, Ran Y, Cheng H, Chen JA, Wan G (2014) Contamination trends of trace metals and coupling with algal productivity in sediment cores in Pearl River Delta, South China. Chemosphere 103:35–43
Duan D, Zhang D, Yang Y, Wang J, Chen JA, Ran Y (2017) Source, composition, and environmental implication of neutral carbohydrates in sediment cores of subtropical reservoirs, South China. Biogeosciences 14(18):4009
Duan D, Lan W, Chen F, Lei P, Pan K (2020) Neutral monosaccharides and their relationship to metal contamination in mangrove sediments. Chemosphere 251:126368
Ewoukem TE, Aubin J, Mikolasek O, Corson MS, Eyango MT, Tchoumboue J, van der Werf HMG, Ombredane D (2012) Environmental impacts of farms integrating aquaculture and agriculture in Cameroon. J Clean Prod 28:208–214
FAO (2016) The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture (SOFIA). Contributing to Food Security and Nutrition for All, Rome
Farmaki EG, Thomaidis NS, Pasias IN, Baulard C, Papaharisis L, Efstathiou CE (2014) Environmental impact of intensive aquaculture: investigation on the accumulation of metals and nutrients in marine sediments of Greece. Sci Total Environ 485:554–562
Gearing JN (1988) The use of stable isotope ratios for tracing the nearshore-offshore exchange of organic matter. In: In Coastal-offshore ecosystem interactions. Springer, Berlin, pp 69–101
Heaton TH (1986) Isotopic studies of nitrogen pollution in the hydrosphere and atmosphere: a review. Chem Geol: Isotope Geoscience Section 59:87–102
Hedges JI, Cowie GL, Richey JE, Quay PD, Benner R, Strom M, Forsberg BR (1994) Origins and processing of organic-matter in the Amazon River as indicated by carbohydrates and amino-acids. Limnol Oceanogr 39:743–761
Herbeck LS, Unger D (2013) Pond aquaculture effluents traced along back-reef waters by standard water quality parameters, d15N in suspended matter and phytoplankton bioassays. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 478:71–86
Herbeck LS, Sollich M, Unger D, Holmer M, Jennerjahn TC (2014) Impact of pond aquaculture effluents on seagrass performance in Ne Hainan, tropical china. Mar Pollut Bull 85(1):190–203
Herbeck LS, Krumme U, Andersen TJ, Jennerjahn TC (2019) Decadal trends in mangrove and pond aquaculture cover on Hainan (china) since 1966: mangrove loss, fragmentation and associated biogeochemical changes. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 233:106531
Hong AH, Hargan KE, Williams B, Nuangsaeng B, Huertos ML (2020) Examining molluscs as bioindicators of shrimp aquaculture effluent contamination in a Southeast Asian mangrove. Ecol Indic 115:106365
Jayachandran S, Chakraborty P, Ramteke D, Chennuri K, Chakraborty S (2018) Effect of pH on transport and transformation of Cu-sediment complexes in mangrove systems. Mar Pollut Bull 133:920–929
Jegatheesan V, Zeng C, Shu L, Manicom C, Steicke C (2007) Technological advances in aquaculture farms for minimal effluent discharge to oceans. J Clean Prod 15(16):1535–1544
Kainz M, Lucotte M, Parrish CC (2003) Relationships between organic matter composition and methyl mercury content of offshore and carbon-rich littoral sediments in an oligotrophic lake. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 60:888–896
Kalantzi I, Shimmield TM, Pergantis SA, Papageorgiou N, Black KD, Karakassis I (2013) Heavy metals, trace elements and sediment geochemistry at four Mediterranean fish farms. Sci Total Environ 444:128–137
Katya K, Lee S, Yun H, Dagoberto S, Browdy CL, Vazquez-Anon M, Bai SC (2016) Efficacy of inorganic and chelated trace minerals (Cu, Zn and Mn) premix sources in Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) fed plant protein based diets. Aquaculture 459:117–123
Lacerda LD, Santos JA, Madrid RM (2006) Copper emission factors from intensive shrimp aquaculture. Mar Pollut Bull 52:1823–1826
Lacerda LD, Soares TM, Costa BGB, Godoy MDP (2011) Mercury emission factors from intensive shrimp aquaculture and their relative importance to the Jaguaribe River Estuary, NE Brazil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 87:657–661
Lei P, Zhong H, Duan D, Pan K (2019) A review on mercury biogeochemistry in mangrove sediments: hotspots of methylmercury production? Sci Total Environ 680:140–150
Mendiguchía C, Moreno C, Manuelvez MP, Garciavargas M (2006) Preliminary investigation on the enrichment of heavy metals in marine sediments originated from intensive aquaculture effluents. Aquaculture 254(1):317–325
MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China) (2009) Background value of soil environment in China. China Environmental Monitoring Press, Bei**g (in Chinese)
Meyers PA (1994) Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter. Chem Geol 114:289–302
Ni Z, Wu X, Li L, Lv Z, Zhang Z, Hao A, Iseri Y, Kuka T, Zhang X, Wu W, Li C (2018) Pollution control and in situ bioremediation for lake aquaculture using an ecological dam. J Clean Prod 172:2256–2265
Ohta A, Imai N, Terashima S, Tachibana Y, Ikehara K, Katayama H, Noda A (2010) Factors controlling regional spatial distribution of 53 elements in coastal sea sediments in northern Japan: comparison of geochemical data derived from stream and marine sediments. Appl Geochem 25(3):357–376
Otero XL, Vidal-Torrado P, de Anta RMC, Macias F (2005) Trace elements in biodeposits and sediments from mussel culture in the Ria de Arousa (Galicia, NW Spain). Environ Pollut 136:119–134
Outridge PM, Sanei H, Stern GA, Hamilton PB, Goodarzi F (2007) Evidence for control of mercury accumulation rates in Canadian high Arctic lake sediments by variations of aquatic primary productivity. Environ Sci Technol 41:5259–5265
Paatero P (1997) Least squares formulation of robust non-negative factor analysis. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 37(1):23–35
Pan K, Wang WX (2012) Trace metal contamination in estuarine and coastal environments in China. Sci Total Environ 421:3–16
Poersch LH, Bauer W, Kersanach MW, Wasielesky W (2020) Assessment of trace metals, total organic carbon and total nitrogen of a shrimp farm system in Southern Brazil. Reg Stud Mar Sci 39:101452
Sanei H, Goodarzi F (2006) Relationship between organic matter and mercury in recent lake sediment: the physical–geochemical aspects. Appl Geochem 21(11):1900–1912
Schendel EK, Nordstrom SE, Lavkulich LM (2004) Floc and sediment properties and their environmental distribution from a marine fish farm. Aquac Res 35:483–493
Soto DX, Koehler G, Wassenaar LI, Hobson KA (2019) Spatio-temporal variation of nitrate sources to Lake Winnipeg using N and O isotope (δ15N, δ18O) analyses. Sci Total Environ 647:486–493
Stern GA, Sanei H, Roach P, Delaronde J, Outridge PM (2009) Historical interrelated variations of mercury and aquatic organic matter in lake sediment cores from a subarctic lake in Yukon, Canada: further evidence toward the algal-mercury scavenging hypothesis. Environ Sci Technol 43(20):7684–7690
Sun X, Fan D, Cheng P, Hu L, Sun X, Guo Z, Yang Z (2021) Source, transport and fate of terrestrial organic carbon from Yangtze River during a large flood event: insights from multiple-isotopes (δ13C, δ15N, Δ14C) and geochemical tracers. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 308:217–236
Vizzini S, Mazzola A (2006) Sources and transfer of organic matter in food webs of a Mediterranean coastal environment: evidence for spatial variability. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 66(3-4):459–467
Wolanski E, Spagnol S, Thomas S, Moore K, Alongi DM, Trott L, Davidson A (2000) Modelling and visualizing the fate of shrimp pond effluents in a mangrove-fringed tidal creek. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 50:85–97
Wu FC, Xu LB, Sun YG, Liao HQ, Zhao XL, Guo JY (2012) Exploring the relationship between polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and sedimentary organic carbon in three Chinese lakes. J Soils Sediments 12:774–783
**a F, Zhang C, Qu L, Song Q, Ji X, Mei K, Dahlgren RA, Zhang M (2020) A comprehensive analysis and source apportionment of metals in riverine sediments of a rural-urban watershed. J Hazard Mater 381:121230
Xu LB, Wu FC, Wan GJ, Liao HQ, Zhao XL, **ng BS (2011) Relationship between Pb-210(ex) activity and sedimentary organic carbon in sediments of 3 Chinese lakes. Environ Pollut 159:3462–3467
Zheng X, Huang L, Lin R, Du J (2015) Roles of epiphytes associated with macroalgae in benthic food web of a eutrophic coastal lagoon. Cont Shelf Res 110:201–209
Zheng X, Como S, Magni P, Huang L (2019) Spatiotemporal variation in environmental features and elemental/isotopic composition of organic matter sources and primary producers in the Yundang Lagoon (**amen, China). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(13):13126–13137
Zheng X, Como S, Huang L, Magni P (2020) Temporal changes of a food web structure driven by different primary producers in a subtropical eutrophic lagoon. Mar Environ Res 161:105128
Funding
This work was supported by the Hainan Provincial Basic and Applied Basic Research Fund for High-Level Talents in Natural Science (421RC662), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41676095, 42166006, 41503009), the Key R&D Program of Guangxi Province (GUIKE AB18126075), the Science and Technology Innovation Commission of Shenzhen (JCYJ20180507182227257, KQTD20180412181334790), and the State Key Laboratory of Organic Geochemistry, GIGCAS (SKLOG-201712).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shiquan Chen: Investigation, writing original draft, data curation, funding acquisition. Ke Pan: Conceptualization, writing review and editing, funding acquisition, project administration. Wenqin Li: Investigation, methodology, resources, data curation. Dandan Duan: Conceptualization, supervision, writing original draft, writing review and editing, project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: V.V.S.S. Sarma
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.02 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Pan, K., Li, W. et al. Influence of algal organic matter on metal accumulation in adjacent sediments of aquaculture from a tropical coast region. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 69717–69730 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20629-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20629-9