Abstract
This study is hinged on analyzing factors such as agriculture and globalization (de jure trade and financial) that threaten a sustainable environment using two proxies of ecological footprint: carbon and noncarbon ecological footprint in the Philippines while controlling for the influence of fossil to GDP, economic growth, urban population, and financial development using the autoregressive distributed lag (ARDL) framework. The result provides evidence of long‐run stable state among the variables. The result validates inverted U‐shaped pattern of EKC involving relationship between agricultural development and ecological footprint for the Philippines indicating that initially, ecological footprint increases as the agriculture develops and then declines as the agriculture matures to generate efficiency and low carbon. In addition, this study explores elasticities of the variables using ARDL, FMOLS, DOLS, and CCR procedure and found that de jure financial globalization exerts positive influence on ecological footprint in the long run. De jure trade globalization is found to be negative and significant in the long run. It is also found that agricultural level operates below the threshold level required to maximize the growth benefits of agricultural system towards mitigating environmental sustainability. Further empirical result shows a positive relationship between economic growth, fossil fuel, urban-population growth, and ecological footprint, and negative insignificant relationship between credit to private sector and ecological footprint. The government should optimize the use of agricultural land through well-articulated economic integration strategy fashioned to pave way for cleaner and low-carbon technologies sources like solar, geothermal, biomass, biogas, tidal power, photovoltaic, and wind energy in the agricultural production to avoid further deterioration of the environment.




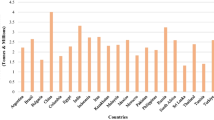
Source: author’s design







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdunnur (2020) Nexus of fisheries and agriculture production and urbanization on ecological footprint: new evidence from Indonesian economy. Int J Energy Econ Policy 2020 10(3):190–195
Adedoyin FF, Alola AA, Bekun FV (2020) (2020) The nexus of environmental sustainability and agro-economic performance of Sub-Saharan African countries. Heliyon 6:e04878
Adedoyin FF, Bein MA, Gyamfi BA, Bekun FV (2021) Does agricultural development induce environmental pollution in E7? A myth or reality. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13586-2
Adeleye BN, Adedoyin F, Nathaniel S (2020) The criticality of ICT-trade nexus on economic and inclusive growth. Inf Technol Dev 1–21
Adusei M, Adeleye N (2020) Credit information sharing and non‐performing loans: the moderating role of creditor rights protection. Int J Finance Econ 1–14
Agbanike TF, Nwani C, Uwazie UI, Anochiwa LI, Enyoghasim MO (2019) Banking sector development and energy consumption in Nigeria: exploring the causal relationship and its implications. Afr Dev Rev 31(3):292–306
Agboola MO, Bekun FV (2019) Does agricultural value added induce environmental degradation empirical evidence from an agrarian country. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:27660–27676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05943-z
Ahmed Z, Wang Z, Mahmood F, Hafeez M, Ali H (2019) Does globalization increase the ecological footprint? Empirical evidence from Malaysia. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:18565–18582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05224-9
Aluko OA, Opoku EEO, Ibrahim M (2021) Investigating the environmental effect of globalization: insights from selected industrialized countries. J Environ Manag 281:111892
Amegavi GB, Langnel Z (2020) Globalization, electricity consumption and ecological footprint: an autoregressive distributive lag (ARDL) approach. Sustainable Cities and Society (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2020.102482.
Asici AA, Acar S (2018) How does environmental regulation affect production location of non-carbon ecological footprint. J Clean Prod 178(2018):927–936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.030
Balogh JM (2019) Agriculture-specific determinants of carbon footprint. Studies in Agricultural Economics 121(2019):166–170
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Driha OM, Bekun FV, Osundina OA (2019) Do agricultural activities induce carbon emissions? The BRICS experience. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:25218–25234
Bilandzija, D., Zgorelec, Z. & Kisic, I. (2016) Influence of tillage practices and crop type on soil CO2 emissions. Sustainability. Vol. 8(90); doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/su8010090
Briones ND (2005) Environmental sustainability issues in Philippine agriculture. Asian Journal of Agriculture and Development 2(1&2):67–78
Danish Ulucak, R. & Khan, S.U, (2020) Determinants of the ecological footprint: Role of renewable energy, natural resources, and urbanization. Sustain Cities Soc 54(2020):101996
Dinda S (2004) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol Econ 49(4):431–455
Doğan N (2018) The impact of agriculture on CO2 emissions in China. Panoeconomicus 62(2):257–271
Dogan N (2016) Agriculture and environmental Kuznets curves in the case of Turkey: evidence from the ARDL and bounds test. Agricultural Economics/ZemedelskaEkonomika 62(12):566–574
Engle RF, Granger CWJ (1987) Cointegration and error correction: representation, estimation and testing. Econometrica 55:251–276
Figge L, Oebels K, Offermans A (2016) The effects of globalization on ecological footprints: an empirical analysis. Environ Dev Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-016-9769-8
Friedrichs J, Inderwildi OR (2013) The carbon curse: are fuel rich countries doomed to high CO2 intensities? Energy Policy 62:1356–1365
Galic M, Bilandzija D, Percin A, Sestak I, Mesic M, Blazinkov M, Zgorelec Y (2019) Effects of agricultural practices on carbon emission and soil health. J Sustain Dev Energy Water Environ Syst 7(3):539–552. https://doi.org/10.13044/j.sdewes.d7.0271
Gill AR, Viswanathan KK, Hassan S (2017) The environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) and the environmental problem of the day. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. Vol
Godil DI, Sharif A, Rafique S, k Jermsittiparsert, K. (2020) The asymmetric effect of tourism, financial development, and globalization on ecological footprint in Turkey. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09937-0
Gokmenoglu KK, Taspinar N, Kaakeh M (2019) Agriculture-induced environmental Kuznets curve: the case of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06685-8
Gokmenoglu KK, Taspinar N (2018) Testing the agriculture-induced EKC hypothesis: the case of Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–13
Gregory AW, Hansen BE (1996) Residual-based tests for cointegration in models with regime shifts. Journal of Econometrics 70(1):99–126
Grossman GM, Krueger AB (1991) Environmental impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement. National Bureau of Economic Research working paper ser no. 3914:1–57. https://doi.org/10.3386/w3914.
Ibrahiem DM, Hanafy SA (2020) Dynamic linkages amongst ecological footprints, fossil fuel energy consumption and globalization: an empirical analysis. Manag Environ Qual 31(6):1549–1568
Jiang C, Ma X (2019) The impact of financial development on carbon emissions: a global perspective. Sustainability 11:5241. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11195241
Khan MK, Abbas F, Godil DI, Sharif A, Ahmed Z, Anser MK (2021) Moving towards sustainability: how do natural resources, financial development, and economic growth interact with the ecological footprint in Malaysia? A dynamic ARDL approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14686-9.
Kirikkaleli D, Adebayo TS, Khan Z, Ali S (2020) Does globalization matter for ecological footprint in Turkey? Evidence from dual adjustment approach. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11654-7.
Koengkan M, Fuinhas JA, Santiago R (2019) Asymmetric impacts of globalisation on CO2 emissions of countries in Latin America and the Caribbean. Environment Systems and Decisions. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-019-09752-0
Leal PH, Marques AC, Shahbaz M (2021) The role of globalisation, de jure and de facto, on environmental performance: evidence from develo** and developed countries. Environ Dev Sustain 23(2021):7412–7431
Lind JT, Mehlum H (2010) With or without U? The appropriate test for a U-shaped relationship. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 72(1):109–118
Ling CH, Ahmed K, Muhamad RB, Shahbaz M (2015) Decomposing the trade environment nexus for Malaysia: what do the technique, scale, composition, and comparative advantage effect indicate? Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:20131–20142
Liu X, Zhang S, Bae J (2017) The impact of renewable energy and agriculture on carbon dioxide emissions: investigating the environmental Kuznets curve in four selected ASEAN countries. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.086
Mahmood H, Alkhateeb TTY, Al-Qahtani MMZ, Allam Z, Ahmad N, Furqan M (2019) Agriculture development and CO2 emissions nexus in Saudi Arabia. PLoS ONE 14(12):e0225865. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0225865
Managi S (2006) Are there increasing returns to pollution abatement? Empirical analytics of the environmental Kuznets curve in pesticides. Ecol Econ 58(3):617–636
Mrabet Z, Alsamara M (2016) Testing the Kuznets curve hypothesis for Qatar: a comparison between carbon dioxide and ecological footprint. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.039
Murshed M, Ferdaus J, Rashid S, Tanha MM, Islam J (2020) The environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for deforestation in Bangladesh: an ARDL analysis with multiple structural breaks. Energy, Ecology & Environment. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40974-020-00188-w
NaderiMahdei K, Bahrami A, Aazami M, Sheklabadi M (2015) Assessment of agricultural farming systems sustainability in Hamedan province: using ecological footprint analysis (case study: irrigated wheat). Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology. Vol
Naseem S, Ji GT, Kashif U (2020) Asymmetrical ARDL correlation between fossil fuel energy, food security, and carbon emission: providing fresh information from Pakistan. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09346-3
Okere KI, Onuoha FC, Muoneke OB, Oyeyemi AM (2021) Towards sustainability path in Argentina: the role of finance, energy mix, and industrial value-added in low or high carbon emission—application of DARDL simulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14756-y
Olaniyi CO, Oladeji SI (2020) Interplay between financial sector and institutional framework in the economic growth process of Kenya. Journal of Public Affairs e2562
Omoke PC, Nwani C, Effiong EL, Evbuomwan OO, Emenekwe CC (2020) The impact of financial development on carbon, non-carbon, and total ecological footprint in Nigeria: new evidence from asymmetric dynamic analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(2020):21628–21646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08382-3
Orhan A, Adebayo TS, Genç SY, Kirikkaleli D (2021) (2021) Investigating the linkage between economic growth and environmental sustainability in India: do agriculture and trade openness matter? Sustainability 13:4753. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13094753
Panayotou T (1993) Empirical tests and policy analysis of environmental degradation at diferent stages of economic development. Technol Environ Employ Geneva Int Labour World Empl (pp. 13–36)
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Economet 16(3):289–326
Phillips PC, Hansen BE (1990) Statistical inference in instrumental variables regression with I (1) processes. Rev Econ Stud 57(1):99–125
Rafindadi AA, Usman O (2019) Globalization, energy use, and environmental degradation in South Africa: startling empirical evidence from the Maki-cointegration test. J Environ Manag 244:265–275
Reynolds TW, Waddington SR, Anderson CL, Chew A, True Z, Cullen A (2015) Environmental impacts and constraints associated with the production of major food crops in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. Food Security 7:795–822
Rudolph A, Figge L (2017) Determinants of ecological footprints: what is the role of globalization? Ecol Ind 81(2017):348–361
Sabir S, Gorus MS (2019) The impact of globalisation on ecological footprint: empirical evidence from South Asian countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(32):33387–43339
Saikkonen P (1992) Estimation and testing of cointegrated systems by an autoregressive approximation. Economet Theor 8(1):1–27
Salari TE, Roumiani A, Kazemzadeh E (2021) Globalisation, renewable energy consumption, and agricultural production impacts on ecological footprint in emerging countries: using quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14204-x
Saud S, Chen S, Habeeb A, Sumayya, (2019) The role of financial development and globalization in the environment: accounting ecological footprint indicators for selected one-belt-one-road initiative countries. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119518
Selcuk M, Gormus S, Guven M (2021) Do agriculture activities matter for environmental Kuznets curve in the Next Eleven countries? Environ Sci Pollut Res 1–11
Shafik N, Bandyopadhyay S (1992) Economic growth and environmental quality: time series and cross-country evidence. Policy Res Work Pap Ser 18:55. https://doi.org/10.1108/14777830710778328
Shahbaz M, Tiwari AK, Nasir M (2013) The effects of financial development, economic growth, coal consumption and trade openness on CO2 emissions in South Africa. Energy Policy 61:1452–1459
Shahbaz M, Mallick H, Mahalik MK, Loganathan N (2015) Does globalization impede environmental quality in India? Ecol Ind 52(2015):379–393
Shahbaz M, Khan S, Ali A, Bhattacharya M (2017) The impact of globalization on CO2 emissions in China. Singap Econ Rev 62(4):929–957
Shahbaz M, Shahzad SJH, Mahalik MK (2018) Is globalization detrimental to CO2 emissions in Japan? New Threshold Analysis Environ Model Assess 23(5):557–568
Shahbaz M (2019) Globalisation-emissions nexus: testing the EKC hypothesis in Next-11 Countries. Munich Personal RePEc Archive. MPRA Paper No. 93959. Available at: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/93959/.
Stock JH, Watson MW (1993) A simple estimator of cointegrating vectors in higher order integrated systems. Econometrica: journal of the Econometric Society 783–820
Subramaniam Y, Masron TA (2021) (2021) The impact of economic globalization on biofuel in develo** countries. Energy Conversion and Management: X. 10:100064
Suki NM, Sharif A, Afshan S, Suki NM (2020) Revisiting the environmental Kuznets curve in Malaysia: the role of globalization in sustainable environment. J Clean Prod 264:121669
Tamazian A, Chousa JP, Vadlamannati KC (2009) Does higher economic and financial development lead to environmental degradation: evidence from BRIC countries. Energy Policy 37(2009):246–253
Tenaw D, Beyene AD (2021) Environmental sustainability and economic development in sub-Saharan Africa: a modified EKC hypothesis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 143:110897
Uddin MMM (2020) What are the dynamic links between agriculture and manufacturing growth and environmental degradation? Evidence from different panel income countries. Environmental and Sustainability Indicators 7(2020):100041
Ulucak ZS, Ilkay SC, Ozcan B, Gedikli A (2020) (2020) Financial globalization and environmental degradation nexus: evidence from emerging economies. Resour Policy 67:101698
Usman O, Akadiri SS, Adeshola I (2020) Role of renewable energy and globalization on ecological footprint in the USA: implications for environmental sustainability. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09170-9
Wang J, Dong K (2019) What drives environmental degradation? Evidence from 14 Sub-Saharan African countries. Science of Total Environment 656(2019):165–173
Wang S, Li G, Fang C (2018) Urbanization, economic growth, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions: empirical evidence from countries with different income levels. Renew Sust Energ Rev 81:2144–2159
Wang L, Vo XV, Shahbaz M, Ak A (2020) (2020) Globalization and carbon emissions: is there any role of agriculture value-added, financial development, and natural resource rent in the aftermath of COP21? J Environ Manag 268:110712
Yurtkuran S (2021) The effect of agriculture, renewable energy production, and globalisation on CO2 emissions in Turkey: a bootstrap ARDL approach. Renewable Energy 171(2021):1236–1245
Zaidi SAH, Zafar MW, Shahbaz M, Hou F (2019) Dynamic linkages between globalisation, financial development and carbon emissions: evidence from Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. J Clean Prod 228(2019):533–543
Zivot E, Andrews DWK (2002) Further evidence on the great crash, the oil-price shock, and the unit-root hypothesis. J Bus Econ Statistics 20(1):25–44
Dietz T, Rosa EA (1997) Effects of population and affluence on CO2 emissions. Proc Nat Acad Sci 94(1):175–179. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.1.175
Leal PH, Marques AC (2019) Are de jure and de facto globalization undermining the environment? Evidence from high and low globalized EU countries. J Environ Manag 250:109460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109460
Charfeddine L, Yousef Al-Malk A, Al Korbi K (2018) Is it possible to improve environmental quality without reducing economic growth: Evidence from the Qatar economy. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 82:25–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.09.001
Okere KI, Onuoha FC, Muoneke, OB, Nwaeze NC (2022) Sustainability challenges in Peru: embossing the role of economic integration and financial development—application of novel dynamic ARDL simulation. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17756-0
Park JY (1992) Canonical Cointegrating Regressions. Econometrica 60(1):119. https://doi.org/10.2307/2951679
Pesaran HH, Shin Y (1998) Generalized impulse response analysis in linear multivariate models. Econ Lett 58(1):17–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-1765(97)00214-0
Narayan PK (2005) The saving and investment nexus for China: evidence from cointegration tests. Appl Econ 37(17):1979–1990. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036840500278103
Destek MA, Sarkodie SA (2019) Investigation of environmental kuznets curve for ecological footprint: the role of energy and financial development. Sci Total Environ 650:2483–2489
WDI (2018) World Development Indicators dataset. Available at: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/world-development-indicators/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
O.B. Muoneke: conceptualization, writing — original draft, investigation, supervision, project administration. K.I. Okere: data curation, formal analysis, methodology, software. N.C. Nwaeze: resources, validation, writing — review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muoneke, O.B., Okere, K.I. & Nwaeze, C.N. Agriculture, globalization, and ecological footprint: the role of agriculture beyond the tip** point in the Philippines. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 54652–54676 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19720-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19720-y