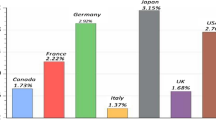
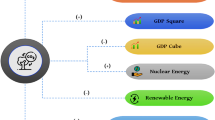
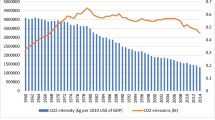
Abstract
Given the importance of energy efficiency in environmental degradation, the effects of energy efficiency and renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption on global environmental pollution were investigated. For this purpose, panel data from 107 countries from 1996 to 2014 were examined. In addition, the present study also tested the well-known environmental Kuznets curve (EKC). The long-run relations were estimated by applying a panel quantile regression (PQR) approach, which is useful for finding heterogeneous effects at lower- and upper-level quantiles of CO2 emissions. The empirical results indicated that energy efficiency had a significantly negative impact on CO2 emissions with low intensity at higher-level quantiles.
Furthermore, the impact of renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption on environmental degradation was significantly negative and positive across all quantiles, respectively. The empirical results provide evidence supporting an inverted U-shaped nexus between GDP and CO2, whereby the EKC is found valid. Hence, energy efficiency improvement and renewable energy consumption policies must align with strategies to curb environmental degradation.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abrevaya J, Dahl CM (2008) The effects of birth inputs on birthweight: evidence from quantile estimation on panel data. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics 26(4):379–397
Ajmi, Ahdi Noomen, Shawkat Hammoudeh, Duc Khuong Nguyen, and João Ricardo Sato. 2015. “On the relationships between CO2 emissions, energy consumption and income: the importance of time variation.” Energy Economics 49: 629–38. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140988315000444.
———. 2020b. “Heterogeneous effects of energy efficiency and renewable energy on carbon emissions: evidence from develo** countries.” Journal of Cleaner Production 247: 119122. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652619339927.
Akram R, Majeed MT et al (2020a) Asymmetric effects of energy efficiency and renewable energy on carbon emissions of BRICS economies: evidence from nonlinear panel autoregressive distributed lag model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(15):18254–18268
Akram R, Chen F et al (2020c) Heterogeneous effects of energy efficiency and renewable energy on carbon emissions: evidence from develo** countries. J Clean Prod 247:119122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119122
Akram R et al (2021) Heterogeneous effects of energy efficiency and renewable energy on economic growth of BRICS countries : a fixed effect panel quantile regression analysis. Energy 215:119019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119019
Allard A, Takman J, Uddin GS, Ahmed A (2018) The N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve: an empirical evaluation using a panel quantile regression approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(6):5848–5861. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0907-0
Al-Mulali U, Ozturk I, Solarin SA (2016) Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in seven regions: the role of renewable energy. Ecol Ind 67:267–282
Amin, Azka, Eyup Dogan, and Zeeshan Khan. 2020. “The impacts of different proxies for financialization on carbon emissions in top-ten emitter countries.” Science of The Total Environment 740: 140127. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969720336482.
Anwar, Ahsan, Muhammad Siddique, Eyup Dogan, and Arshian Sharif. 2021. “The moderating role of renewable and non-renewable energy in environment-income nexus for ASEAN countries: evidence from method of moments quantile regression.” Renewable Energy 164: 956–67. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960148120315536.
Apergis N, Ben M, Ben S (2018) Does renewable energy consumption and health expenditures decrease carbon dioxide emissions ? Evidence for sub-Saharan Africa countries. Renewable Energy 127:1011–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.05.043
Apergis, Nicholas, and James E Payne. 2012. “Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption-growth nexus: evidence from a panel error correction model.” Energy Economics 34(3): 733–38. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140988311000909.
Bah MM, Azam M (2017) Investigating the relationship between electricity consumption and economic growth: evidence from South Africa. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 80:531–537
Baltagi, Badi H, and ** X Wu. 1999. “Unequally spaced panel data regressions with AR (1) disturbances.” Econometric Theory: 814–23.
Ben M, Ben S, Ozturk I (2017) Testing environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis : the role of renewable and non-renewable energy consumption and trade in OECD countries. Ecol Ind 60(2016):824–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.08.031
Bhargava A, Franzini L, Narendranathan W (1982) Serial correlation and the fixed effects model. Rev Econ Stud 49(4):533–549
Bhattacharya M, Awaworyi S, Reddy S (2017a) The dynamic impact of renewable energy and institutions on economic output and CO2 emissions across regions. Renewable Energy 111:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.03.102
Bhattacharya M, Churchill SA, Paramati SR (2017b) The dynamic impact of renewable energy and institutions on economic output and CO2 emissions across regions. Renewable Energy 111:157–167
Bildirici ME, Özaksoy F (2013) The relationship between economic growth and biomass energy consumption in some European countries. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy 5(2):23141
Bilgili F, Koçak E, Bulut Ü (2016) The dynamic impact of renewable energy consumption on CO2 emissions: a revisited environmental Kuznets curve approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 54:838–845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.080
———. 2021b. “The roles of economic growth and health expenditure on CO2 emissions in selected Asian countries: a quantile regression model approach.” Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13639-6.
Bilgili, Faik et al. 2021a. “The roles of economic growth and health expenditure on CO2 emissions in selected Asian countries: a quantile regression model approach.” Environmental Science and Pollution Research: 1–24.
Binder, Martin, and Alex Coad. 2011. “From average Joe’s happiness to miserable Jane and cheerful John: using quantile regressions to analyze the full subjective well-being distribution.” Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization 79(3): 275–90. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167268111000692.
Boontome P, Therdyothin A, Chontanawat J (2017) ScienceDirect ScienceDirect investigating the causal relationship between non-renewable assessing the feasibility of using the heat demand-outdoor and renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions temperature function for a long-term district heat demand. Energy Procedia 138:925–930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.10.141
Brini R (2021) Renewable and non-renewable electricity consumption, economic growth and climate change: evidence from a panel of selected African countries. Energy 223:120064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120064
Canay IA (2011) A simple approach to quantile regression for panel data. Economet J 14(3):368–386
Chang C-C (2010) A multivariate causality test of carbon dioxide emissions, energy consumption and economic growth in China. Appl Energy 87(11):3533–3537
Charfeddine L, Kahia M (2019) Impact of renewable energy consumption and financial development on CO2 emissions and economic growth in the MENA region: a panel vector autoregressive (PVAR) analysis. Renewable Energy 139:198–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.010
Cheng C, Ren X, Wang Z, Yan C (2019) Heterogeneous impacts of renewable energy and environmental patents on CO2 emission-evidence from the BRIICS. Sci Total Environ 668:1328–1338
Chong, Chin Hao et al. 2019. “The driving factors of energy-related CO2 emission growth in Malaysia: the LMDI decomposition method based on energy allocation analysis.” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 115(November 2018): 109356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109356.
Coad A, Rao RI, Value M (2006) A quantile regression analysis. Economics Bulletin 15(13):1–10
Cole, M A, A J Rayner, and J M Bates. 1997. “The environmental Kuznets curve: an empirical analysis.” Environment and Development Economics 2(4): 401–16. https://www.cambridge.org/core/article/the-environmental-kuznets-curve-an-empirical-analysis/B58C62C4A38CA2ADA8C20571342E11CD.
Cowan, Wendy N, Tsangyao Chang, Roula Inglesi-Lotz, and Rangan Gupta. 2014. “The nexus of electricity consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in the BRICS countries.” Energy Policy 66: 359–68. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301421513011087.
Danish RU, Khan S-U-D (2020) Relationship between energy intensity and CO2 emissions: Does economic policy matter? Sustain Dev 28(5):1457–1464. https://doi.org/10.1002/sd.2098
Danish Z, Zhang B, Wang Bo, Wang Z (2017) Role of renewable energy and non-renewable energy consumption on EKC: evidence from Pakistan. J Clean Prod 156:855–864
Danish MA, Baloch NM, Zhang JW (2019) Effect of natural resources, renewable energy and economic development on CO2 emissions in BRICS countries. Sci Total Environ 678:632–638
Danish, Syed Tauseef Hassan, et al. 2019. “Linking economic growth and ecological footprint through human capital and biocapacity.” Sustainable Cities and Society 47: 101516. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2210670719300459.
Dogan E, Seker F (2016a) The influence of real output, renewable and non-renewable energy, trade and financial development on carbon emissions in the top renewable energy countries. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:1074–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.02.006
Dogan E, Turkekul B (2016) CO2 emissions, real output, energy consumption, trade, urbanization and financial development: testing the EKC hypothesis for the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):1203–1213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5323-8
Dong B, Wang F, Guo Y (2016) The global EKCs. Int Rev Econ Financ 43:210–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iref.2016.02.010
Dong K, Sun R, Hochman G (2017) Do natural gas and renewable energy consumption lead to less CO2 emission ? Empirical evidence from a panel of BRICS countries. Energy 141:1466–1478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.11.092
Dong K, Sun R, Dong X (2018a) CO2 emissions, natural gas and renewables, economic growth: assessing the evidence from China. Sci Total Environ 640:293–302
Dong K, Sun R, Jiang H, Zeng X (2018b) CO2 emissions, economic growth, and the environmental Kuznets curve in China: What roles can nuclear energy and renewable energy play? J Clean Prod 196:51–63
Engle RF, Manganelli S (2004) CAViaR: conditional autoregressive value at risk by regression quantiles. Journal of Business & Economic Statistics 22(4):367–381
EPA. 2009. Energy Efficiency as a Low-Cost Resource for Achieving Carbon Emissions Reductions. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-08/documents/ee_and_carbon.pdf.
Farrell MJ (1957) The measurement of productive efficiency. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A (general) 120(3):253–281
Fatima T, Shahzad U, Cui L (2020) Renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption, trade and CO2 emissions in high emitter countries: Does the income level matter? J Environ Plan Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/09640568.2020.1816532
Fattouh B, Harris L, Scaramozzino P (2008) Non-linearity in the determinants of capital structure: evidence from UK firms. Empirical Economics 34(3):417–438
Grossman, Gene M, and Alan B Krueger. 1991. “Environmental impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement.” National Bureau of Economic Research Working Paper Series No. 3914(3914): 1–57. http://www.nber.org/papers/w3914.
Hanif, Imran, Syed Muhammad Faraz Raza, Pilar Gago-de-Santos, and Qaiser Abbas. 2019. “Fossil fuels, foreign direct investment, and economic growth have triggered CO2 emissions in emerging Asian economies: some empirical evidence.” Energy 171: 493–501. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360544219300131.
Harris RDF, Tzavalis E (1999) Inference for unit roots in dynamic panels where the time dimension is fixed. Journal of Econometrics 91(2):201–226
Herzog, Tim. 2009. World Greenhouse Gas Emissions in 2005.
Hossain MS (2011) Panel estimation for CO2 emissions, energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and urbanization of newly industrialized countries. Energy Policy 39:6991–6999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2011.07.042
Hu B, Li Z, Zhang L (2019) Long-run dynamics of sulphur dioxide emissions, economic growth, and energy efficiency in China. J Clean Prod 227:942–949. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.170
Huang, Yuan, Huiming Zhu, and Zhongqingyang Zhang. 2020. “The heterogeneous effect of driving factors on carbon emission intensity in the Chinese transport sector: evidence from dynamic panel quantile regression.” Science of The Total Environment 727: 138578.
IEA (2020) Energy Technologies Perspectives 2020. International Energy Agency, Paris
Ike, George N, Ojonugwa Usman, Andrew Adewale Alola, and Samuel Asumadu Sarkodie. 2020a. “Environmental quality effects of income, energy prices and trade: the role of renewable energy consumption in G-7 countries.” Science of The Total Environment 721: 137813. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0048969720313255.
Ike, George N, Ojonugwa Usman, and Samuel Asumadu Sarkodie. 2020b. “Testing the role of oil production in the environmental Kuznets curve of oil producing countries: new insights from method of moments quantile regression.” Science of the Total Environment 711: 135208.
Inglesi-Lotz, Roula, and Eyup Dogan. 2018. “The role of renewable versus non-renewable energy to the level of CO2 emissions a panel analysis of sub-Saharan Africa’s Βig 10 electricity generators.” Renewable Energy 123: 36–43. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S096014811830185X.
Jalil A, Mahmud SF (2009) Environment Kuznets curve for CO2 emissions: a cointegration analysis for China. Energy Policy 37(12):5167–5172
Javid M, Khan M (2020) Energy efficiency and underlying carbon emission trends. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(3):3224–3236. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07019-4
Kocoglu, Mustafa, Ashar Awan, Ahmet Tunc, and Alper Aslan. 2021. “The nonlinear links between urbanization and CO2 in 15 emerging countries: evidence from unconditional quantile and threshold regression.” Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-676290/v1.
Koenker R (2004) Quantile regression for longitudinal data. J Multivar Anal 91(1):74–89
Koenker, Roger, and Gilbert Bassett Jr. 1978. “Regression quantiles.” Econometrica: 33–50.
Kuznets S (1955) Economic Growth and Income Inequality. Routledge
Lancaster T (2000) The incidental parameter problem since 1948. Journal of Econometrics 95(2):391–413
Le, Thai-Ha, and Canh Phuc Nguyen. 2019. “Is energy security a driver for economic growth? Evidence from a Global Sample.” Energy Policy 129: 436–51. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301421519301211.
Le, Thai-Ha, Youngho Chang, and Donghyun Park. 2020. “Renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption, economic growth, and emissions: international evidence.” The Energy Journal 41(2).
Li, Guo, Abdulrasheed Zakari, and Vincent Tawiah. 2020. “Energy resource melioration and CO2 emissions in China and Nigeria: efficiency and trade perspectives.” Resources Policy 68: 101769. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301420720301458.
Liobikienė G, Butkus M (2017) Environmental Kuznets curve of greenhouse gas emissions including technological progress and substitution effects. Energy 135:237–248
López-Peña, Álvaro, Ignacio Pérez-Arriaga, and Pedro Linares. 2012. “Renewables vs. energy efficiency: the cost of carbon emissions reduction in Spain.” Energy Policy 50: 659–68. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301421512006635.
Mahapatra B, Irfan M (2021) Asymmetric impacts of energy efficiency on carbon emissions: a comparative analysis between developed and develo** economies. Energy 227:120485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120485
Marques, António Cardoso, José Alberto Fuinhas, and Carla Tomás. 2019. “Energy efficiency and sustainable growth in industrial sectors in European Union countries: a nonlinear ARDL approach.” Journal of Cleaner Production 239: 118045. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652619329154.
Mikayilov, Jeyhun I, Marzio Galeotti, and Fakhri J Hasanov. 2018. “The impact of economic growth on CO2 emissions in Azerbaijan.” Journal of Cleaner Production 197: 1558–72. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652618319280.
Moghadam HE, Vahid VD (2018) The impact of financial development and trade on environmental quality in Iran. Empirical Economics 54(4):1777–1799
Murshed Muntasir. 2021. “The environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for carbon and ecological footprints in South Asia: the role of renewable energy.” GeoJournal 6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10370-6
Narayan PK, Narayan S (2010) Carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: panel data evidence from develo** countries. Energy Policy 38(1):661–666
Narayan PK, Saboori B, Soleymani A (2016) Economic growth and carbon emissions. Econ Model 53:388–397
Neyman, Jerzy, and Elizabeth L Scott. 1948. “Consistent estimates based on partially consistent observations.” Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society: 1–32.
———. 2015b. “How effective are energy efficiency and renewable energy in curbing CO2 emissions in the long run? A heterogeneous panel data analysis.” Energy 82: 734–45. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360544215001085.
Ngoc, Bui Hoang, and Ashar Awan. 2021. “Does financial development reinforce ecological footprint in Singapore ? Evidence from ARDL and Bayesian analysis.” Environmental Science and Pollution Research (0123456789). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17565-5.
Odhiambo NM (2009) Electricity consumption and economic growth in South Africa: a trivariate causality test. Energy Economics 31(5):635–640
Özbuğday FC, Erbas BC (2015) How effective are energy efficiency and renewable energy in curbing CO2 emissions in the long run? A heterogeneous panel data analysis. Energy 82:734–745
Ozcan B, Tzeremes P, Dogan E (2019) Re-estimating the interconnectedness between the demand of energy consumption, income, and sustainability indices. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(26):26500–26516
Ozturk I, Aslan A, Kalyoncu H (2010) Energy consumption and economic growth relationship: evidence from panel data for low and middle income countries. Energy Policy 38(8):4422–4428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2010.03.071
Pablo-Romero María del P and Antonio Sánchez-Braza. 2017. “Residential energy environmental Kuznets curve in the EU-28.” Energy 125: 44–54
Pal D, Kumar S (2017) The environmental Kuznets curve for carbon dioxide in India and China: growth and pollution at crossroad. Journal of Policy Modeling 39(2):371–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpolmod.2017.03.005
Pandey S, Mishra M (2015) CO2 emissions and economic growth of SAARC countries: evidence from a panel var analysis. World Journal of Applied Economics 1(2):23–33
Pao H-T, Hsiao-Cheng Yu, Yang Y-H (2011) Modeling the CO2 emissions, energy use, and economic growth in Russia. Energy 36(8):5094–5100
Pata, Ugur Korkut. 2021. “Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption , economic complexity , CO2 emissions , and ecological footprint in the USA : testing the EKC hypothesis with a structural break.” : 846–61.
Paulo J, Bento C, Moutinho V (2016) CO2 emissions, non-renewable and renewable electricity production, economic growth, and International Trade in Italy. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 55:142–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.151
Pesaran MH (2007) A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. J Appl Economet 22(2):265–312. https://doi.org/10.1002/jae.951
Pesaran MH, Yamagata T (2008) Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. Journal of Econometrics 142(1):50–93
Le Quéré Corinne et al. 2019. “Drivers of declining CO2 emissions in 18 developed economies.” Nature Climate Change 9(3): 213–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-019-0419-7
Rahman, Mohammad Mafizur, and Eswaran Velayutham. 2020. “Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption-economic growth nexus: new evidence from South Asia.” Renewable Energy 147: 399–408. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0960148119313370.
Rahman MM, Kashem MA (2017) Carbon emissions, energy consumption and industrial growth in Bangladesh: empirical evidence from ARDL cointegration and Granger causality analysis. Energy Policy 110:600–608
Richmond, Amy K, and Robert Kaufmann. 2006. “Is there a turning point in the relationship between income and energy use and/or carbon emissions?” Ecological Economics 56(2): 176–89. https://econpapers.repec.org/RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:56:y:2006:i:2:p:176-189.
Riti JS, Shu Y (2016) Renewable energy, energy efficiency, and eco-friendly environment (R-E5) in Nigeria. Energy, Sustainability and Society 6(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13705-016-0072-1
Saidi, Kais, and Anis Omri. 2020. “Reducing CO2 emissions in OECD countries: do renewable and nuclear energy matter?” Progress in Nuclear Energy 126: 103425.
Saidi K, Hammami S (2015) The impact of co2 emissions and economic growth on energy consumption in 58 countries. Energy Rep 1:62–70
Sarkodie SA, Strezov V (2019) A review on environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis using bibliometric and meta-analysis. Sci Total Environ 649:128–145
Sarwar S, Chen W, Waheed R (2017) Electricity consumption, oil price and economic growth: global perspective. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 76:9–18
Shafiei, Sahar, and Ruhul A Salim. 2014. “Non-renewable and renewable energy consumption and CO2 emissions in oecd countries: a comparative analysis.” Energy Policy 66: 547–56. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301421513010872.
Shahbaz, Muhammad, Sakiru Adebola Solarin, Rashid Sbia, and Sadia Bibi. 2015. “Does energy intensity contribute to CO2 emissions? A Trivariate analysis in selected African countries.” Ecological Indicators 50: 215–24. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1470160X14005305.
Shahbaz, Muhammad et al. 2020. “The effect of renewable energy consumption on economic growth: evidence from the renewable energy country attractive index.” Energy 207: 118162.
Sharif A et al (2020) The renewable energy consumption-environmental degradation nexus in top-10 polluted countries: fresh insights from quantile-on-quantile regression approach. Renewable Energy 150:670–690
Sheikhzeinoddin, A., Tarazkar, M. H., Behjat, A., Al-mulali, U., & Ozturk, I. (2022). The nexus between environmental performance and economic growth: new evidence from the Middle East and North Africa region. Journal of Cleaner Production, 129892.
Sherwood B, Wang L (2016) Partially linear additive quantile regression in ultra-high dimension. Ann Stat 44(1):288–317
Shokoohi, Z., Dehbidi, N. K., & Tarazkar, M. H. (2022). Energy intensity, economic growth and environmental quality in populous Middle East countries. Energy, 239, 122164.
Sinha A, Bhattacharya J (2017) Estimation of environmental Kuznets curve for SO 2 emission : a case of Indian cities. Ecol Ind 72:881–894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.09.018
Sinha A, Muhammad Shahbaz FPM (2019) Environmental Kuznets curve (EKC): a manual Data Selection and Environmental Kuznets Curve Models - Environmental Kuznets Curve Models. Elsevier, Data Choice, Data Sources, Missing Data, Balanced and Unbalanced Panels. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-816797-7.00007-2
Sinha A, Shahbaz M (2018a) Estimation of environmental Kuznets curve for CO2 emission: role of renewable energy generation in India. Renewable Energy 119:703–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.12.058
Sovacool BK, Brown MA (2010) Competing dimensions of energy security: an international perspective. Annu Rev Environ Resour 35(1):77–108. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-environ-042509-143035
Soytas, Ugur, Ramazan Sari, and Bradley T Ewing. 2007. “Energy consumption, income, and carbon emissions in the United States.” Ecological Economics 62(3): 482–89. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921800906003430.
Spiegel S, Brown B (2017) Heed local impact of coal mining. Nature 550(7674):43. https://doi.org/10.1038/550043a
Tamazian, Artur, Juan Piñeiro Chousa, and Krishna Chaitanya Vadlamannati. 2009. “Does higher economic and financial development lead to environmental degradation: evidence from BRIC countries.” Energy Policy 37(1): 246–53. https://econpapers.repec.org/RePEc:eee:enepol:v:37:y:2009:i:1:p:246-253.
Tarazkar MH, Dehbidi NK, Ansari RA, Pourghasemi HR (2021a) Factors affecting methane emissions in OPEC member countries: does the agricultural production matter? Environ Dev Sustain 23(5):6734–6748
Tarazkar MH, Dehbidi NK, Ozturk I, Al-Mulali U (2021b) The impact of age structure on carbon emission in the Middle East: the panel autoregressive distributed lag approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(26):33722–33734
Thompson A (2012) Water abundance and an EKC for water pollution. Econ Lett 117(2):423–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econlet.2012.06.014
Turner, Karen, and Nick Hanley. 2011. “Energy efficiency, rebound effects and the environmental Kuznets curve.” Energy Economics 33(5): 709–20. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0140988310002070.
Uddin MA, Ali MH, Masih M (2017) Political Stability and growth: an application of dynamic GMM and quantile regression. Econ Model 64:610–625
Ulucak, Recep, and Faik Bilgili. 2018. “A reinvestigation of EKC model by ecological footprint measurement for high, middle and low income countries.” Journal of Cleaner Production 188: 144–57. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S095965261830862X.
Ulucak, Recep, Ali Gokhan Yucel, and Emrah Kocak. 2019. “The process of sustainability : from past to present chapter 5 - the process of sustainability : from past to present.” (January).
UNEP. 2016. Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency in Develo** Countries: Contributions to Reducing Global Emissions. https://newclimate.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/onegigatonreport_2016.pdf.
Ur M, Rashid M (2017) Energy consumption to environmental degradation, the growth appetite in SAARC nations. Renewable Energy 111:284–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.03.100
Vieira, Nathália Duarte Braz, Luiz Augusto Horta Nogueira, and Jamil Haddad. 2018. “An Assessment of CO2 emissions avoided by energy-efficiency programs: a general methodology and a case study in Brazil.” Energy 142: 702–15. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0360544217317772.
Westerlund J (2007) Testing for error correction in panel data. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 69(6):709–748
Wooldridge, Jeffrey M. 2010. Econometric Analysis of Cross Section and Panel Data. MIT press.
**e, Qichang, **n Xu, and **aqing Liu. 2019. “Is there an EKC between economic growth and smog pollution in China? New evidence from semiparametric spatial autoregressive models.” Journal of Cleaner Production 220: 873–83. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652619305657.
Zafar MW, Mirza FM, Zaidi SAH, Hou F (2019) The nexus of renewable and nonrenewable energy consumption, trade openness, and CO2 emissions in the framework of EKC: evidence from emerging economies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(15):15162–15173
Zhang S (2019) Environmental Kuznets curve revisit in Central Asia: the roles of urbanization and renewable energy. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(23):23386–23398
Zhang B, Wang Bo, Wang Z (2017) Role of renewable energy and non-renewable energy consumption on EKC: evidence from Pakistan. J Clean Prod 156:855–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.203
Zhang, Jijian et al. 2021. “Measuring energy and environmental efficiency interactions towards CO2 emissions reduction without slowing economic growth in Central and Western Europe.” Journal of Environmental Management 279: 111704. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301479720316297.
Zhu H, Duan L, Guo Y, Keming Yu (2016) The effects of FDI, economic growth and energy consumption on carbon emissions in ASEAN-5: evidence from panel quantile regression. Econ Model 58:237–248
Zoundi Z (2017) CO2 emissions, renewable energy and the environmental Kuznets curve, a panel cointegration approach. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 72:1067–1075
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed equally to this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Roula Inglesi-Lotz
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awan, A., Kocoglu, M., Banday, T.P. et al. Revisiting global energy efficiency and CO2 emission nexus: fresh evidence from the panel quantile regression model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 47502–47515 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19101-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19101-5