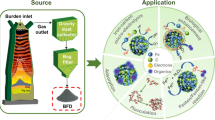
Abstract
To control the SO2 emission and achieve the target of “waste controlled by waste”, a novel desulfurization method with blast furnace dust slurry was proposed. The effects of reaction temperature, oxygen concentration, and solid–liquid ratio on SO2 removal efficiency were investigated. The optimal conditions were reaction temperature of 35 ℃, oxygen concentration of 10 vol.%, and solid–liquid ratio of 0.5 g/300 mL. Under the optimal conditions, the desulfurization efficiency reached 100% for 4 h. Response surface methodology (RSM) results showed that oxygen concentration significantly influenced the SO2 removal efficiency. Finally, the possible desulfurization mechanism of blast furnace dust was proposed based on the EDX, XRD, SEM–EDS, ICP, and IC. The blast furnace dust (main components are CaZn8(SO4)2(OH)12Cl2·(H2O)9, Mn6.927Si6O15·(OH)8, ZnO, Fe2O3) reacted with H+ to form Zn2+, Fe3+, and Mn2+ which shows a key effect on the SO2 liquid catalytic oxidation. This study provides a promising, feasible, and low-cost desulfurization technology by reusing blast furnace dust.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data analyzed during this study are included in this article.
References
Bao JC, **ao HL, Li K, Wang C, Song X, Sun X, Ning P, Luo YS (2020) Simultaneous NOx and SO2 removal during wet flue gas desulfurization, using copper smelter slag slurry combined with yellow phorphorus. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering 99:1334–1344. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.23925
Bao JC, Li K, Ning P, Wang C, Song X, Luo YS, Sun X (2021) Study on the role of copper converter slag in simultaneously removing SO2 and NOx using KMnO4/copper converter slag slurry. J Environ Sci 108:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.02.004
Dahlan I, Ahmad Z, Fadly M, Lee KT, Kamaruddin AH, Mohamed AR (2010) Parameters optimization of rice husk ash (RHA)/CaO/CeO2 sorbent for predicting SO2/NO sorption capacity using response surface and neural network models. J Hazard Mater 178:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.070
Dana M, Sobati MA, Shahhosseini S, Ansari A (2020) Optimization of a continuous ultrasound assisted oxidative desulfurization (UAOD) process of diesel using response surface methodology (RSM) considering operating cost. Chin J Chem Eng 28:1384–1396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2019.12.007
Flynn JH (1997) The ‘temperature integral’ - its use and abuse. Thermochim Acta 300:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0040-6031(97)00046-4
Hao RL, Wang XH, Zhao X, Xu MN, Zhao Y, Mao XZ, Yuan B, Zhang YX, Gao KL (2018) A novel integrated method of vapor oxidation with dual absorption for simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO: feasibility and prospect. Chem Eng J 333:583–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.191
Hao RL, Mao YM, Mao XZ, Wang Z, Gong YP, Zhang ZL, Zhao Y (2019) Cooperative removal of SO2 and NO by using a method of UV-heat/H2O2 oxidation combined with NH4OH-(NH4)2SO3 dual-area absorption. Chem Eng J 365:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.059
Hao RL, Song YC, Tian ZY, Li YH, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Gong YP, Ma Z, Qian Z (2020) Cooperative removal of SO2 and NO using a cost-efficient triple-area control method. Chem Eng J 383:123164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123164
Kılıç M, Pütün E, Pütün AE (2014) Optimization of Euphorbia rigida fast pyrolysis conditions by using response surface methodology. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 110:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2014.08.018
Li B, Wu H, Liu X, Zhu T, Liu F, Zhao X (2020) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO using a novel method with red mud as absorbent combined with O3 oxidation. J Hazard Mater 392:122270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122270
Li CY, Sheng YQ, Sun XY (2019a) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NOX by a combinationof red mud and coal mine drainage. Environ Eng Sci 36:444–452. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2018.0360
Li S, Yang JQ, Wang C, **e DL, Luo YM, Li K, He DD, Mei Y (2018) Removal of NOx from flue gas using yellow phosphorus and phosphate slurry as adsorbent. Energy Fuels 32:5279–5288. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b03964
Li YX, Xu QY, Guo RT, Wang ZY, Liu XY, Shi X, Qiu ZZ, Qin H, Jia PY, Qin Y, Pan WG (2019b) Removal of NO by using sodium persulfate/limestone slurry: modeling by response surface methodology. Fuel 254:115612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.06.020
Liu C, Li J, Yang C, Diao Z, Wang C (2019) A composite absorption liquid for simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification in flue gas. Chin J Chem Eng 27:2566–2573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2019.04.013
Meng ZH, Wang CY, Wang XR, Chen Y, Wu WF, Li HQ (2019) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NOx from flue gas using (NH4)2S2O3/steel slag slurry combined with ozone oxidation. Fuel 255:115760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115760
Nie YX, Li S, Wu CJ, Wang C, He DD, Mei Y (2018) Efficient removal of SO2 from flue gas with phosphate rock slurry and investigation of reaction mechanism. Ind Eng Chem Res 57:15138–15146. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b03223
Nie YX, Li S, Dai JF, He DD, Mei Y (2020) Catalytic effect of Mn2+, Fe3+ and Mg2+ ions on desulfurization using phosphate rock slurry as absorbent. Chem Eng J 390:124568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124568
Pouladi B, Fanaei MA, Baghmisheh G (2019) Optimization of oxidative desulfurization of gas condensate via response surface methodology approach. J Cleaner Prod 209:965–977. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.283
Shi WX, Lin C, Chen W, Hong JL, Chang JC, Dong Y, Zhang YL (2017) Environmental effect of current desulfurization technology on fly dust emission in China. Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev 72:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.033
Song GL, **ao Y, Yang Z, Yang XT, Lyu QG (2021) A comparative experimental study on characteristics of ultra-low NOx emission and fly ash between Fugu bituminous and its semi-coke with post-combustion. Fuel Process Technol 211:106618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2020.106618
Sun D, **n G, Yao L, Yang L, Jiang X, Jiang W (2020) Manganese leaching in high concentration flue gas desulfurization process with semi-oxidized manganese ore. Chin J Chem Eng 28:571–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2019.09.006
Taheri Afarani H, Sadeghi M, Moheb A, Esfahani EN (2019) Optimization of the gas separation performance of polyurethane–zeolite 3A and ZSM-5 mixed matrix membranes using response surface methodology. Chin J Chem Eng 27:110–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2018.03.013
Wang BW, Yao SM, Peng YP (2020) Simultaneous desulfurization and denitrification of flue gas by pre-ozonation combined with ammonia absorption. Chin J Chem Eng 28:2457–2466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2020.05.001
Wang H, Yuan B, Hao RL, Zhao Y, Wang XP (2019) A critical review on the method of simultaneous removal of multi-air-pollutant in flue gas. Chem Eng J 378:122155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122155
Xu J, Wang N, Chen M, Zhou ZY, Yu HY (2020a) Comparative investigation on the reduction behavior of blast furnace dust particles during in-flight process in hydrogen-rich and carbon monoxide atmospheres. Powder Technol 366:709–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.03.025
Xu J, Wang N, Zhou ZY, Chen M, Wang PF (2020b) Experimental and numerical studies of the gas-molten reduction behavior of blast furnace dust particles during in-flight process. Powder Technol 361:226–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2019.08.050
Yang BC, Ma SX, Cui RJ, Sun SJ, Wang J, Li SC (2019a) Simultaneous removal of NOx and SO2 with H2O2 catalyzed by alkali/magnetism-modified fly ash: high efficiency, low cost and catalytic mechanism. Chem Eng J 359:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.11.068
Yang BC, Ma SX, Cui RJ, Wang J, Sun SJ, Li SC (2019b) Novel low-cost simultaneous removal of NO and SO2 with ·OH from decomposition of H2O2 catalyzed by alkali-magnetic modified fly ash. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:5339–5347. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b01014
Yuan B, Mao X, Wang Z, Hao R, Zhao Y (2020) Radical-induced oxidation removal of multi-air-pollutant: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 383:121162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121162
Zhang L, Gao Y, Yue Q, Zhang P, Wang Y, Gao B (2020) Prepartion and application of novel blast furnace dust based catalytic-ceramic-filler in electrolysis assisted catalytic micro-electrolysis system for ciprofloxacin wastewater treatment. J Hazard Mater 383:121215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121215
Zhao Y, Han YH, Wang TH, Sun ZH, Fang C (2019) Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NO from flue gas using iron-containing polyoxometalates as heterogeneous catalyst in UV-Fenton-like process. Fuel 250:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.03.151
Zhou BX, Wang T, Li C, Fu JP, Zhang Z, Song ZL, Ma CY (2020) Multi-objective optimization of the preparation parameters of the powdered activated coke for SO2 adsorption using response surface methodology. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 146:104776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2020.104776
Funding
This paper was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51968075) and the Young and Middle-aged Academic and Technical Leaders Reserve Talent Project of Yunnan (202105AC160054).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Binghua **e has written the manuscript; Na Geng, Qian Yu, Di He, Fang Wang, Tiancheng Liu, Jiyun Gao, ** Ning, and **n Song have helped in the critical revision; Lijuan Jia has conceived the study and edited the manuscript. The authors have read and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The work was performed in compliance with ethical standards. The landowners and the local authorities were informed of the experimental nature and the associated risks of the site treatment.
Consent to participate
All authors and stakeholders were informed and agreed to the protocol.
Consent to publish
All authors were allowed to read and approve the final manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
**e, B., Geng, N., Yu, Q. et al. Removal of SO2 from flue gas using blast furnace dust as an adsorbent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 15642–15653 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16842-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16842-7