Abstract
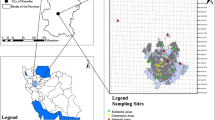
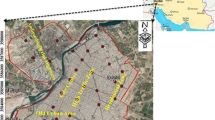
Anthropogenic activities in and around the urban highways followed by aerodynamic processing generate street dusts, which can cause adverse health effects through different exposure pathways. Hence, considering the high degree of industrialization, concomitant unplanned urbanization, and rapid demographic augmentation, street dust samples from an urban city (Gazipur, Bangladesh) were investigated in terms of potentially toxic elements (using ICP-MS) to evaluate their ecological and health risks. Mean concentrations (± SD) of lead (Pb), copper (Cu), chromium (Cr), cadmium (Cd), zinc (Zn), nickel (Ni), and arsenic (As) in the analyzed air-dried samples were 40.9 ± 13.6, 44.9 ± 15.4, 83.3 ± 19.0, 9.1 ± 5.4, 239.1 ± 34.7, 33.5 ± 10.4, and 2.1 ± 0.8 mg/kg, respectively with heterogeneous distribution which were 0.2 (As) to 82.7 (Cd) times higher than the available internationally recommended limits. Element-specific environmental indices revealed that contamination levels followed the descending order as Cd > Zn > Cu > Pb > Cr > Ni > As, whereas individual ecological risks followed the descending order as Cd > Cu > Pb > Ni > Zn > Cr > As. Sampling site-specific composite indices indicated that sampling sites with high loadings of traffic, population, industrialization, and urbanization were mostly polluted. Multivariate statistical approaches also deduced the similar origins of the studied elements. In terms of the investigated elements, the study site possessed high potential ecological risks, although non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks through different pathway’s exposures seem insignificant, where children are more vulnerable than adults.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdel-Latif NM, Saleh IA (2012) Heavy metals contamination in roadside dust along major roads and correlation with urbanization activities in Cairo, Egypt. J Am Sci 8(6):379–389
Abrahim GMS, Parker RJ (2008) Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary Auckland, New Zealand. Environ Monit Assess 136:227–238
Adamiec E, Jarosz-Krzemińska E (2019) Human health risk assessment associated with contaminants in the finest fraction of sidewalk dust collected in proximity to trafficked roads. Sci Rep 9:16364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52815-0
Ahmed MFU (2012) Gazipur District. In: Islam, Sirajul; Miah, Sajahan; Khanam, Mahfuza; Ahmed, Sabbir (eds). Banglapedia: the National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh (Online ed.). Dhaka, Bangladesh: Banglapedia Trust, Asiatic Society of Bangladesh
Ahmed F, Ishiga H (2006) Trace metal concentrations in street dusts of Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Atmos Environ 40:3835–3844
Ahmed MS, Biswas MMH, Mottalib MA, Alam MN, Khan M (2019) Translocation of heavy metals from industry into vegetables and crops through water and soil of Mokesh Beel in Bangladesh and their impact on human body. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 13(5):59–71
Ahmed FT, Khan AHAN, Khan R, Saha SK, Alam FA, Dafader NC, Sultana S, Elius IB, Mamun SA (2021) Characterization of Arsenic contaminated groundwater from central Bangladesh: irrigation feasibility and preliminary health risks assessment. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 15:100433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100433
Ahsan MA, Satter F, Siddique MAB, Akbor MA, Shamim A, Shajahan M, Khan R (2019) Chemical and physicochemical characterization of effluents from the tanning and textile industries in Bangladesh with multivariate statistical approach. Environ Monit Assess 191:575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7654-2
Ali MM, Ali MK, Islam MS, Rahman MZ (2016) Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 5:27–35
Al-Khashman OA (2004) Heavy metal distribution in dust, street dust and soils from the work place in Karak Industrial Estate, Jordan. Atmos Environ 38:6803–6812
Al-Momani IF (2007) Trace Elements in Street and Household Dusts in Amman, Jordan. Soil Sediment Contam Int J 16(5):485–496
Al-Shidi HK, Sulaiman H, Al-Reasi HA, Jamil F, Aslam M (2020) Human and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in different particle sizes of road dust in Muscat, Oman. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09319-6
Ambade B, Litrupa (2012) Evaluation of heavy metal contamination 552 in road dust fallout of 553 Bhilai City. Int J Adv Eng Res Stud 1(554):81–83
Aminiyan MM, Baalousha M, Mousavi R, Aminiyan FM, Hosseini MM, Heydariyan A (2018) The ecological risk, source identification, and pollution assessment of heavy metals in road dust: a case study in Rafsanjan, SE Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:13382–13395
Aprile FM, Bouvy M (2008) Distribution and enrichment of heavy metals in sediments at the Tapacurá River Basin, Northeastern Brazil. Braz J Aquat Sci Technol 12(1):1–8
Bai J, **ao R, Cui B, Zhang K, Wang Q, Liu X, Gao H, Huang L (2011) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from the young and old reclaimed regions in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Environ Pollut 159(3):817–824
Baker F, Tasnim N, Tazim N, Sara HH, Pyuzza R, Ahmed SN, ult S, Haider M (2018) Understanding behavior of microcredit borrowers on solid waste management in Gazipur, Bangladesh. J Community Med Health Care 3(1):1024
BBS (2011) Statistics Division, Ministry of Planning, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh. BBS, Bangladesh
Bourliva A, Christophoridis C, Papadopoulou L, Giouri K, Papodopoulos A, Mitsika E, Fytianos K (2017) Characterization, heavy metal content and health risk assessment of urban road dusts from the historic center of the city of Thessaloniki, Greece. Environ Geochem Health 39:611–634
CEPA (1995) Chinese Environmental Protection Administration, Environmental Quality Standard for Soils (GB15618-1995), Bei**g, 1995.
Charlesworth S, Everett M, McCarthy R, Ordonez A, Miguel E (2003) A comparative study of heavy metal concentration and distribution in deposited street dusts in a large and a small urban area: Birmingham and Coventry, West Midlands, UK. Environ Int 29:563–573
Chatterjee A, Banerjee RN (1999) Determination of lead and other metals in a residential area of greater Calcutta. Sci Total Environ 227:175–185
Chen JS, Zhou JY (1992) Study of heavy metals in the water environment of China. China Environmental Science Press, Bei**g
Chen J, Wei F, Zheng WY, Adriano DC (1991) Background concentrations of elements in soils of China. Water Air Soil Pollut 57:699–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00282934
Chen H, Lu X, Li LY, Gao T, Chang Y (2014) Metal contamination in campus dust of **’an, China: a study based on multivariate statistics and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 484:27–35
Chen X, Liu M, Ma J, Liu X, Liu D, Chen Y, Li Y, Qadeer A (2017) Health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in housing units built on brownfields in a city in China. J Soils Sediments 17:1741–1750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-016-1625-9
Cheng HX, Li M, Zhao CD, Li K, Peng M, Qin AH, Cheng XM (2014) Overview of trace metals in the urban soil of 31 metropolises in China. J Geochem Explor 139:31–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.08.012
Cheng Z, Chen LJ, Li HH, Lin JQ, Yang ZB, Yang YX, Xu XX, **an JR, Shao JR, Zhu XM (2018) Characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals exposure via household dust from urban area in Chengdu, China. Sci Total Environ 619–620:621–629
CNEMC (1990) China National Environmental Monitoring Center, the backgrounds of soil environment in China. 1990. Environment Science Press of China.
Davaulter V, Rognerud S (2001) Heavy metal pollution in sediments of the Pasvik River drainage. Chemosphere 42:9–18
Delibašić Š, Nedžla Đ-K, Mirela K, Indina K, Aldina V, Jasna H, Kristina H, Adina S, Samra S, Sabina Ž, Sabina G-S, Amela P, Arzija P (2020) Health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in street dust of federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 27:1296–1308. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2020.1826290
Du Y, Gao B, Zhou H, Ja X, Hao H, Yin S (2013) Health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dusts in urban parks of Bei**g, China. Procedia Environ Sci 18: 299–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2013.04.039
Duan ZB, Wang J, Zhang Y, Xuan B (2017) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in road dust from different functional areas in Guiyang, Southwest, China. Int J Environ Sci Edu 12(3):427–439. https://doi.org/10.12973/ijese.2017.01238a
Duong TTT, Lee BK (2011) Determining concentration level of heavy metal in road dust from busy traffic areas with different characteristics. J Environ Manag 92:554–562
Fahmida K, Islam MR (2018) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil of waste disposal site in Bangladesh: implication of spatial, seasonal variation and indices. In: Pradhan B (ed) GCEC 2017. GCEC 2017. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering, vol 9. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-8016-6_67
Faiz Y, Siddique N, Tufail M (2012) Pollution level and health risk assessment of road dust from an expressway, Islamabad, Pakistan. J Environ Sci Heal 47:818–829
Ferreira-Baptista L, Miguel ED (2005) Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: a tropical urban environment. Atmos Environ 39:4501–4512
Fu J, Zhao C, Luo Y, Liu C, Kyzas JZ, Luo Y, Zhao D, An S, Zhu H (2014) Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: their relations to environmental factors. J Hazard Mater 270:102–109
Guo W, Liu X, Liu Z, Li G (2010) Pollution and potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the sediments around Dongjiang Harbor, Tian**. Procedia Environ Sci 2:729–736
Guo G, Wu F, **e F, Zhang R (2012) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in urban soils from southwest China. J Environ Sci 24(3):410–418
Habib MA, Khan R (2021) Environmental impacts of coal-mining and coal-fired power-plant activities in a develo** country with global context. In: Spatial modeling and assessment of environmental contaminants (Chapter 24), Environmental challenges and solutions. Springer Nature, Switzerland AG. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-63422-3_24
Habib MA, Basuki T, Miyashita S, Bekelesi W, Nakashima S, Techato K, Khan R, Majlis ABK, Phoungthong K (2019a) Assessment of natural radioactivity in coals and coal combustion residues from a coal-based thermoelectric plant in Bangladesh: implications for radiological health hazards. Environ Monit Assess 191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-7160-y
Habib MA, Basuki T, Miyashita S, Bekelesi W, Nakashima S, Phoungthong K, Khan R, Rashid MB, Islam ARMT, Techato K (2019b) Distribution of naturally occurring radionuclides in soil around a coal-based power plant and their potential radiological risk assessment. Radiochim Acta 107(3):243–259. https://doi.org/10.1515/ract-2018-3044
Habib MA, Islam ARMT, Bodrud-Doza M, Mukta FA, Khan R, Siddique MAB, Phoungthong K, Techato K (2020) Simultaneous appraisals of pathway and probable health risk associated with trace metals contamination in groundwater from Barapukuria coal basin, Bangladesh. Chemosphere 242:125183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125183
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Han NMM, Latif MT, Othman M, Dominick D, Mohamad N, Juahir H, Tahir NM (2013) Composition of selected heavy metals in road dust from Kuala Lumpur city centre. Environ Earth Sci 72:849–859
Hossain MB, Islam MN, Alam MS, Hossen MZ (2019) Industrialisation Scenario at Sreepur of Gazipur, Bangladesh and physico-chemical properties of wastewater discharged from industries. Asian J Environ Ecol 9(4):1–14
Hossain MB, MN I, MS A, MZ H (2020) Seasonal variation of heavy metal concentrations in farm soils of Sreepur industrial area of Gazipur, Bangladesh: pollution level assessment. Am J Environ Sci 16(4):68–78
Hu X, Zhang Y, Ding Z, Wang T, Lian H, Sun Y, Wu J (2012) Bio-accessibility and health risk of arsenic and heavy metals (Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn and Mn) in TSP and PM2.5 in Nan**g, China. Atmos Environ 57:146–152
Huang J, Li F, Zeng G, Liu W, Huang X, **ao Z, Wu H, Gu Y, Li X, He X, He Y (2016) Integrating hierarchical bioavailability and population distribution into potential eco-risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust: a case study in **andao District, Changsha city, China. Sci Total Environ 541:969–976
Hughes MF (2002) Arsenic toxicity and potential mechanisms of action. Toxicol Lett 133(1):1–16
Idris AM, Fatima MS, Alqahtani T, Said O, Fawy KF (2018) Contamination level and risk assessment of heavy metal deposited in street dusts in Khamees-Mushait city, Saudi Arabia. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 26:495–511. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1520596
Islam MS, Tusher TR, Mustafa M, Mahmud S (2012) Effects of solid waste and industrial effluents on water quality of Turag River at Konabari industrial area, Gazipur, Bangladesh. Environ Sci Nat Resour 5(2):213–218
Islam M, Al-mamun A, Hossain F, Quraishi SB, Naher K, Khan R, Das S, Tamim U, Hossain SM, Nahid F (2017a) Contamination and ecological risk assessment of trace elements in sediments of the rivers of Sundarban mangrove forest, Bangladesh. Mar Pollut Bull 124:356–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.07.059
Islam MS, Proshad R, Ahmed S (2017b) Ecological risk of heavy metals in sediment of an urban river in Bangladesh. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 24(3):699–720
Islam ARMT, Islam HMT, Mia MU, Khan R, Habib MA, Bodrud-Doza M, Siddique MAB, Chu R (2020) Co-distribution, possible origins, status and potential health risk of trace elements in surface water sources from six major river basin, Bangladesh. Chemosphere 249:126180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126180
Jayarathne A, Egodawatta P, Ayoko GA, Goonetilleke A (2018) Assessment of ecological and human health risks of metals in urban road dust based on geochemical fractionation and potential bioavailability. Sci Total Environ 635:1609–1619
Jehan S, Seema AK, Said M, Rafiq A, Muhammad F, Sardar K, Abdullah K, Ali L (2018) Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in the Hattar industrial estate, Pakistan. Toxin Rev 39:68–77. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2018.1478858
Jiang X, Lu WX, Zhao HQ, Yang QC, Yang ZP (2014) Potential ecological risk assessment and prediction of soil heavy metal pollution around coal gangue dump. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci Discuss 2:1977–2010
Jiang YX, Chao S, Liu J, Yang Y, Chen Y, Zhang A, Cao H (2017) Source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil for a township in Jiangsu Province, China. Chemosphere 168:1658–1668
Jose J, Srimuruganandam B (2020) Investigation of road dust characteristics and its associated health risks from an urban environment. Environ Geochem Health 42:2819–2840
Kabir MH, Islam MS, Tusher TR, Hoq ME, Muliadi MSA (2020a) Changes of heavy metal concentrations in Shitalakhya river water of Bangladesh with seasons. Indones J Sci Tech 5(3):395–409
Kabir MH, Islam MS, Hoq ME, Tusher TR, Islam MS (2020b) Appraisal of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Shitalakhya River in Bangladesh using pollution indices, geo-spatial, and multivariate statistical analysis. Arab J Geosci 13(21):1135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-06072-5
Kabir MH, Tusher TR, Hossain MS, Islam MS, Shammi RS, Kormoker T, ProshadR IM (2020c) Evaluation of spatio-temporal variations in water quality and suitability of an ecologically critical urban river employing water quality index and multivariate statistical approaches: a study on Shitalakhya river, Bangladesh. Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 27:1388–1415. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2020.1848415
Kamani H, Mahvi AH, Sayedsalehi M, Jaafari J, Hoseini M, Safari JH, Dalvand A, Aslani H, Mirzaei N, Asrafi SD (2017) Contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in street dust of Tehran, Iran. Int J Environ Sci Technol 14:2675–2682
Khan R, Shirai N, Ebihara M (2015a) Chemical characteristics of R chondrites in the light of REE, Th, U and P abundances. Earth Planet Sci Lett 422:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2015.04.008
Khan R, Yokozuka Y, Terai S, Shirai N, Ebihara M (2015b) Accurate determination of Zn in geological and cosmochemical rock samples by isotope dilution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 30:506–514. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ja00344f
Khan R, Das S, Kabir S, Habib MA, Naher K, Islam MA, Tamim U, Rahman AKMR, Deb AK, Hossain SM (2019a) Evaluation of the elemental distribution in soil samples collected from ship-breaking areas and an adjacent island. J Environ Chem Eng 7(3):103189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.103189
Khan R, Parvez MS, Jolly YN, Haydar MA, Alam MF, Khatun MA, Sarker MMR, Habib MA, Tamim U, Das S, Sultana S, Islam MA, Naher K, Paul D, Akter S, Khan MHR, Nahid F, Huque R, Rajib M, Hossain SM (2019b) Elemental abundances, natural radioactivity and physicochemical records of a southern part of Bangladesh: implication for assessing the environmental geochemistry. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 12:100225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2019.100225
Khan R, Islam MS, Tareq ARM, Naher K, Islam ARMT, Habib MA, Siddique MAB, Islam MA, Das S, Rashid MB, Ullah AKMA, Miah MMH, Masrura SU, Bodrud-Doza M, Sarker MR, Badruzzaman ABM (2020) Elemental and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons distributions in the sediments of an urban river: influence of anthropogenic runoffs. Environ Nanotech Monit Manag 14:100318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100318
Khan R, Islam HMT, Islam ARMT (2021) Mechanism of elevated radioactivity in a freshwater basin: radiochemical characterization, provenance and associated hazards. Chemosphere 264:128459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128459
Kormoker T, Proshad R, Islam S, Ahmed S, Chandra K, Uddin M, Rahman M (2019) Toxic metals in agricultural soils near the industrial areas of Bangladesh: ecological and human health risk assessment. Toxin Rev:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2019.1650777
Li C et al (2008) Spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals in street dust in Shenyang city. Ecol Environ 17:560–564
Li HH, Chen LJ, Yu L, Guo ZB, Shan CQ, Lin JQ, Gu YG, Yang ZB, Yang YX, Shao JR, Zhu XM, Cheng Z (2017) Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of human exposure to oral bioaccessibility of heavy metals via urban street dusts from different functional areas in Chengdu, China. Sci Total Environ 586:1076–1084
Liu C, Cui J, Jiang G, Chen X, Wang L, Fang C (2013) Soil heavy metal pollution assessment near the largest landfill of China. Soil Sediment Contam 22(4):390–403. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2013.733447
Lu X, Wang L, Li LY, Lei K, Huang L, Kang D (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals in street dust of Baoji NW China. J Hazard Mat 173(1–3): 744–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.09.001
Luo XS, Yu S, Zhu YG (2012) Trace metal contamination in urban soils of China. Sci Total Environ 421–422:17–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.020
Ma Z, Chen K, Li Z, Bi J, Huang L (2016) Heavy metals in soils and road dusts in the mining areas of Western Suzhou, China: a preliminary identification of contaminated sites. J Soils Sediments 16:204–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1208-1
Maanan M, Saddik M, Maanan M, Chaibi M, Assobhei O, Zourarah B (2014) Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol Indic 48:616–626
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Mathur R, Balaram V, Satyanarayanan M, Sawant SS (2016) Assessment of heavy metal contamination of road dusts from industrial areas of Hyderabad, India. Environ Monit Assess 188:514
Men C, Liu R, Xu F, Wang Q, Guo L, Shen Z (2018) Pollution characteristics, risk assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in road dust in Bei**g, China. Sci Total Environ 612:138–147
Muller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 2:109–118
Murakam M, Nakajima F, Furumai H, Tomiyasu B, Owari M (2007) Identification of particles containing chromium and lead in road dust and soakaway sediment by electron probe microanalyzer. Chemosphere 67:2000–2010
Nemerow NL (1985) Stream, lake, estuary, and ocean pollution. Van Nostrand Reinhold Publishing Co, New York
Nouri M, ABDEM H (2016) Assessment of metals contamination and ecological risk in ait Ammar abandoned iron mine soil, Morocco. Ekológia (Bratislava) 35(1):32–49. https://doi.org/10.1515/eko-2016-0003
Pan L, Ma J, Hu Y, Su B, Fang G, Wang Y, Wang Z, Wang L, **ang B (2016) Assessments of levels, potential ecological risk, and human health risk of heavy metals in the soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:19330–19340
Pan H, Lu X, Lei K (2017) A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of **’an, China: contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Sci Total Environ 609:1361–1369
Prokofeva TV, Kiryushin AV, Shishkov VA, Ivannkov FA (2017) The importance of dust material in urban soil formation: the experience on study of two young Technosols on dust depositions. J Soils Sediments 17:515–524
Proshad R, Kormoker T, Islam MS (2019) Distribution, source identification, ecological and health risks of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Rupsa River, Bangladesh. Toxin Rev 40:77–101. https://doi.org/10.1080/15569543.2018.1564143
Qadeera A, Saqib ZA, Ajmal Z, **ng C, Khalil SK, Usman M, Huang Y, Bashir S, Ahmad Z, Ahmed J, Thebo KH, Liu M (2020) Concentrations, pollution indices and health risk assessment of heavy metals in road dust from two urbanized cities of Pakistan: Comparing two sampling methods for heavy metals concentration. Sustain Cities Soc 53:101959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2019.101959
Rabbi AM, Hasan MM, Akhter A (2016) Heavy metals content in inlet water, treated and untreated waste water of garments industries at Gazipur, Bangladesh. ESAIJ 12(4):133–136
Rahman MS, Khan MDH, Jolly YN, Kabir J, Akter S, Salam A (2019) Assessing risk to human health for heavy metal contamination through street dust in the Southeast Asian Megacity: Dhaka, Bangladesh. Sci Total Environ 660:1610–1622
Rakib MA, Ali M, Akter MS, Bhuiyan, Mohammad AH (2014) Assessment of heavy metal (Pb, Zn, Cr and Cu) content in roadside dust of Dhaka Metropolitan City, Bangladesh. Int Res J Environ Sci 3(1):1–5
Rasmussen PE, Subramanian KS, Jessiman BJ (2001) A multielement profile of house dust in relation to exterior dust and soil in the city of Ottawa, Canada. Sci Total Environ 267:125–140
Razanica A, Huremovic J, Zero S, Gojak-Salimovic S, Memic M (2014) Heavy metals in street dust in Sarajevo area, Bosnia and Herzegovina. Curr World Environ 9(1):43–47. https://doi.org/10.12944/CWE.9.1.06
Robertson DJ, Taylor KG, Hoon SR (2003) Geochemical and mineral magnetic characterization of urban sediment particulates, Manchester, UK. Appl Geochem 18:269–282
Roy S, Gupta SK, Prakash J, Habib G, Baudh K, Nasr M (2019) Ecological and human health risk assessment of heavy metal contamination in road dust in the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:30413–30425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06216-5
Sezgin N, Ozcan HK, Demir G, Nemlioglu S, Bayat C (2003) Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environ Int 29:979–985
Shah ME, Hoque MM, Roy S (2016) Assessment of physicochemical characteristics of industrial effluents and water body at Tongi Region, Gazipur, Bangladesh. J Sci Technol 6(1 & 2):1–10
Sheijany MSP, ShariatiF MNY, Karimzadegan H (2020) Evaluation of heavy metal contamination and ecological risk of soil adjacent to Saravan municipal solid waste disposal site, Rasht, Iran. Environ Monit Assess 192:757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08716-1
Shi G, Chen Z, Xu S, Zhang J, Wang L, Bi C, Teng J (2008) Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environ Pollut 156(2):251–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.02.027
Shifaw E (2018) Review of heavy metals pollution in China in agricultural and urban soils. J Health Pollut 18:180607
Sun C, Liu J, Wang Y, Sun L, Yu H (2013) Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, Northeast China. Chemosphere 92:517–523
Suryawanshi PV, Rajaram BS, Bhanarkar AD, Rao CVC (2016) Determining heavy metal contamination of road dust in Delhi, India. Atmósfera 29(3):221–234
Sutherland RA, Tolosa CA (2000) Multi-element analysis of road-deposited sediment in an urban drainage basin, Honolulu, Hawaii. Environ Pollut 110:483–495
Tamim U, Khan R, Jolly YN, Fatema K, Das S, Naher K, Islam MA, Islam SMA, Hossain SM (2016) Elemental distribution of metals in urban river sediments near an industrial effluent source. Chemosphere 155:509–518
Tan SY, Praveena SM, Abidin EZ, Cheema MS (2018) Heavy metal quantification of classroom dust in school environment and its impacts on children health from Rawang (Malaysia). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(34):34623–34635
Tang R, Ma K, Zhang Y, Mao Q (2013) The spatial characteristics and pollution levels of metals in urban street dust of Bei**g, China. Appl Geochem 35:88–98
Taşpınar F, Bozkurt Z (2018) Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of road dust on selected highways in Düzce, Turkey. Environ Forensic 19:298–314. https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2018.1519736
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgoländer Meeresun 33(1–4):566–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414780
Tong R, Fang Y, Zhang B, Wang Y, Yang X (2020) Monitoring and evaluating the control effect of dust suppressant on heavy metals based on ecological and health risks: a case study of Bei**g. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:14750–14763. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11648-5
Trojanowska M, Świetlik R (2019) Investigations of the chemical distribution of heavy metals in street dust and its impact on risk assessment for human health, case study of Radom (Poland). Hum Ecol Risk Assess Int J 26:1907–1926. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1619070
Urrutia-Goyes R, Hernandez N, Carrillo-Gamboa O, Nigam KDP, Ornelas-Sato N (2018) Street dust from a heavily-populated and industrialized city: Evaluation of spatial distribution, origins, pollution, ecological risks and human health repercussions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 159:198–204
USDOE (2011) The risk assessment information system (RAIS). Cass Avenue Argonne, IL: U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge Operations Office (ORO).
USEPA (1986) Superfund Public Health Evaluation Manual EPA/540/1-86.
USEPA (1989) Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Vol. I, Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A), EPA/540/1-89/002. Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, Washington, DC
USEPA (1997) Exposure factors handbook. EPA/600/P-95/002F. Ishington.D.C: Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Developmentl; 1997.
USEPA (1999) Screening level ecological risk assessment protocol for hazardous waste combustion facilities, Appendix E: Toxicity reference values. Washington DC, USA. p. 340-357.
USEPA (2001) Methods for collection, storage and manipulation of sediments for chemical and toxicological analyses. Technical Manual, EPA-823-B-01-002, Office of Water, Washington, DC.
USEPA (2011) Exposure factors handbook: 2011 Edition. Washington, DC: National Center for Environmental Assessment, Office of Research and Development, EPA/600/R-09/052F.
Ustaoğlu F, Islam MS (2020) Potential toxic elements in sediment of some rivers at Giresun, Northeast Turkey: a preliminary assessment for ecotoxicological status and health risk. Ecol Indic 113:106237
Ustaoğlu F, Tepe Y (2019) Water quality and sediment contamination assessment of Pazarsuyu Stream, Turkey using multivariate statistical methods and pollution indicators. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 7(1):47–56
Varrica D, Dongarra G, Sabatino G, Monna F (2003) Inorganic geochemistry of roadway dust from the metropolitan area of Palermo, Italy. Environ Geol 44:222–230
Victoria AG, CobbinaSJ DSB, Duwiejuah AB (2014) Heavy metals concentration in road dust in the Bolgatanga Municipality, Ghana. J Environ Poll Hum Health 2(4):74–80
Wahab MIA, AbdRazak WMA, Sahani M, Khna MF (2020) Characteristics and health effect of heavy metals on non-exhaust road dusts in Kuala Lumpur. Sci Total Environ 703:135535
Wang Q, Lu X, Pan H (2016) Analysis of heavy metals in the re-suspended road dusts from different functional areas in **’an, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:19838–19846
Wei B, Jiang F, Mu S (2009) Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in urban road dusts from Urumqi, NW China. Microchem J 93:147–152
Weissmannová HD, Pavlovský J (2017) Indices of soil contamination by heavy metals—methodology of calculation for pollution assessment (minireview). Environ Monit Assess 189:616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6340-5
Wu Y, Xu Y, Zhang G, Hu S (2010) Evaluation of ecological risk and primary empirical research on heavy metals in polluted soil over **aoqinling gold mining region, Shaanxi, China. Trans Nonferrous Metals Soc China 20(4):688–694
Xu S, Zheng N, Liu J, Wang Y, Chang S (2013) Geochemistry and health risk assessment of arsenic exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, Northeast China. Environ Geochem Health 35:89–99
Yang Z, Lu W, Long Y, BaoX YQ (2011) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun City, China. J Geochem Explor 108:27–38
Yeung ZLL, Kwok RCW, Yu KN (2003) Determination of multi-element profiles of streeent dust using energy dispersive X-ray flurescence (EDXRF). Appl Radiat Isot 58:339–346
Yu L, Zhang B, Zhang SQ (2004) Heavy metal elements pollution evaluation on the ecological environment of the Sanjiang Plain based on GIS. Chin J Soil Sci 35(5):529–532
Zakir HM, Sumi SA, Sharmin S, MohiuddinKM KS (2015) Heavy metal contamination in surface soils of some industrial areas of Gazipur, Bangladesh. J Chem Biol Phys Sci 5(2):2191–2206
Zeb B, ** Z, Mahmood Q. Lin Q, Parvez A, Irshad M, Bilal M, Bhatti ZA, Shaheen S (2017) Assessment of combined toxicity of heavy metals from industrial wastewaters on Photobacteriumphosphoreum T3S. Appl Water Sci 7:2043–2050.
Zglobicki W, Telecka M, Skupiński S, Pasierbińska A, Koziel M (2018) Assessment of heavy metal contamination levels of street dust in the city of Lublin, E Poland. Environ Earth Sci 77:774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7969-2
Zhao L, Xu Y, Hou H, Shangguan Y, Li F (2014) Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tian**, China. Sci Total Environ 468–469:654–662
Zhao L, Hu G, Yan Y, Yu R, Cui J, Wang X, Yan Y (2019) Source apportionment of heavy metals in urban road dust in a continental city of eastern China: using Pb and Sr isotopes combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Atmos Environ 201:201–211
Zheng N, Wang Q, Liang Z, Zheng D (2008) Characterization of heavy metal concentrations in the sediments of three freshwater rivers in Huludao City, Northeast China. Environ Pollut 154(1):135–142
Zheng N, Liu J, Wang Q, Liang Z (2010a) Heavy metals exposure of children from stair way and sidewalk dust in the smelting district, northeast of China. Atmos Environ 44:3239–3245
Zheng N, Liu J, Wang Q, Liang Z (2010b) Health risk assessment of heavy metal exposure to street dust in the zinc smelting district, Northeast of China. Sci Total Environ 408:726–733
Acknowledgements
The author is thankful to the authority of Mawlana Bhashani Science and Technology University (MBSTU) and Patuakhali Science and Technology University (PSTU) for sample processing and analysis.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Khalid University for funding this work through Group Research Project under grant number (R.G.P2/114/41).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KMH, KT, IMS, SRS, KR, TTR, PR, IAM: methodology and investigation and sample analysis; KMH, KT, and SRS writing—original draft preparation; KT, IMS, and IAM: funding acquisition. All authors read, revised, and improved the manuscript and attested to the validity and legitimacy of the data and its interpretation, and agreed to its submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 131 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabir, M.H., Kormoker, T., Islam, M.S. et al. Potentially toxic elements in street dust from an urban city of a develo** country: ecological and probabilistic health risks assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 57126–57148 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14581-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-14581-3