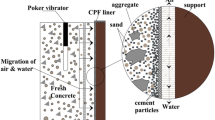
Abstract
At present, plastic concrete is widely used in anti-seepage engineering, and its strength and hydraulic conductivity are important indexes of plastic concrete cutoff walls. The pondus hydrogenii (pH) and electrical conductivity (EC) have an important effect on the strength and hydraulic conductivity of plastic concrete cutoff walls. However, it is not clear why the pH and EC are related to the strength and permeability of these walls. For this reason, plastic concrete composed of sand, cement, water, and bentonite was taken as the research object to study the influence of different mix ratios and curing ages on the unconfined compressive strength and permeability of plastic concrete. The pH and EC of the corresponding mix ratio and curing age were measured. The effects of the pH and EC on the strength and permeability of plastic concrete were studied, and the internal reason was explored from the product type and hydration reaction degree of plastic concrete. Furthermore, the quantitative relationship between pH and EC and the strength and hydraulic conductivity of plastic concrete was established. With increasing cement content, the strength, pH, and EC of plastic concrete increase continuously, while the hydraulic conductivity decreases. With increasing curing age, the strength increases, the hydraulic conductivity decreases, and both the pH and EC show a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. The pH value and electrical conductivity can reflect the product type and hydration reaction degree of plastic concrete, further affecting its strength and hydraulic conductivity. Under different dosage and curing age conditions, the pH showed three stages, namely, 11.7–12.27, 12.27–2.5, and 12.5–12.75, and there is a good power functional relationship among the EC and strength and hydraulic conductivity at each stage.









Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article and its additional files.
References
Abbaslou H, Ghanizadeh AR, Amlashi AT (2016) The compatibility of bentonite/sepiolite plastic concrete cut-off wall material. Constr Build Mater 124:1165–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.08.116
Au PI, Leong YK, Liu J (2014) Sequential yield stress and zeta potential measurements on the same suspensions for platelet and spherical alumina. Colloid Surface A 441:360–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.09.029
Aslani F (2013) Effects of specimen size and shape on compressive and tensile strengths of self-compacting concrete with or without fibres. Mag Concr Res 65(15-16):914–929. https://doi.org/10.1680/macr.13.00016
ASTM (2010) D5084 standard test method for measurement of hydraulic conductivity of saturated porous materials using a flexible wall permeameter. United States. https://doi.org/10.1520/D5084-10
ASTM (2011) D2487 standard practice for classification of soils for engineering purposes (unified soil classification system). United States. https://doi.org/10.1520/D2487
Babushnkin VI, Matveev GM, McHedlov-Petrosian O (1985) Thermodynamics of silicates. Berlin, Germany https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-69320-5
Ba M, Xue T, He Z, Wang H, Liu J (2019) Carbonation of magnesium oxysulfate cement and its influence on mechanical performance. Constr Build Mater 223:1030–1037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.341
Bindiganavile V, Mamun M, Dashtestani B, Banthia N (2018) Correlating the permeability of mortar under compression with connected porosity and tortuosity. Mag Concr Res 70(17-18):875–884. https://doi.org/10.1680/jmacr.17.00090
Chang J, Fang Y (2015) Quantitative analysis of accelerated carbonation products of the synthetic calcium silicate hydrate(C-S-H) by QXRD and TG/MS. J Therm Anal Calorim 119(1):57–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-014-4093-8
Che DR, Luo CY, Shen SL (2012) Relationship between pH value and electrical conductivity and strength characteristics of cement treated Shanghai clayey soil. Rock Soil Mech 33(12):3611–3615. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2012.12.006
Chrisp MCSM (2000) Electrical conductivity, diffusion, and permeability of Portland cement-based mortars. Cem Concr Res 30(9):1395–1400. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(00)00281-7
GB/T 20973-2007 (2007) Bentonite. China
GB/T 50123-2019 (2019) Standard for soil test method. China
Hasselman DPH, Penty RA (2010) Stress concentrations in polymer-impregnated porous brittle materials. J Am Ceram Soc 56(2):105–105. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1973.tb12370.x
Hinchberger S, Weck J, Newson T (2010) Mechanical and hydraulic characterization of plastic concrete for seepage cut-off walls. Can Geotech J 47(4):461–471. https://doi.org/10.1139/T09-103
Jefferis SA, Lam C (2012) Hydraulic characteristics of bentonite cake fabricated on cutoff walls. Clay Clay Miner 60(6):557–560. https://doi.org/10.1346/CCMN.2012.0600601
Jiang JY, Sun GW, Wang CH (2013) Numerical calculation on the porosity distribution and diffusion coefficient of interfacial transition zone in cement-based composite materials. Constr Build Mater 39:134–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.05.023
Liu SY, Du YJ, Han LH, Gu MF (2008) Experimental study on the electrical resistivity of soil-cement admixtures. Environ Geol 54(6):1227–1233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0905-5
Min F, Wang X, Li M, Ni Y, Al-qadhi E, Zhang J (2021) Preparation of high-porosity and high-strength ceramisites from municipal sludge using starch and CaCO3 as a combined pore-forming agent. J Mater Civ Eng 33(3):04020502
Taylor HFW (1997) Cement chemistry. Thomas Telford, London. https://doi.org/10.1680/cc.25929
Wang Y, Chen Y, **e H, Zhang C, Zhan L (2016) Lead adsorption and transport in loess-amended soil-bentonite cut-off wall. Environ Geol 215:69–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.002
Yang YL, Reddy KR, Du YJ, Fan RD (2018) Short-term hydraulic conductivity and consolidation properties of soil-bentonite backfills exposed to CCR-impacted groundwater. J Geothch Geoenviron 144(6):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001877
Wei X, **ao L (2011) Influence of the aggregate volume on the electrical resistivity and properties of Portland cement concretes. J Wuhan Univ Technol 26(5):965–971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-011-0346-6
Xu H, Zhu W, Qian X, Wang S, Fan X (2016) Studies on hydraulic conductivity and compressibility of backfills for soil-bentonite cutoff walls. Appl Clay Sci 132-133:326–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2016.06.025
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M640527), the science and technology innovation cultivation Foundation of Yangzhou University (2019CXJ062), the Qing Lan Project of Yangzhou University, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51778557) for supporting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shengwei Wang contributed to the conception of the study. Yijiang Wen performed the experiment and wrote the manuscript. Kang Fei performed the analysis with constructive discussions. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philipp Gariguess
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Wen, Y. & Fei, K. Effects of pH and EC on the strength and permeability of plastic concrete cutoff walls. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 42798–42806 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13776-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13776-y