Abstract
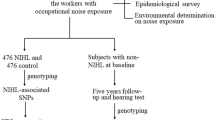
The purposes of the current study were to investigate the association of a few of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within the AKT2 gene and noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) susceptibility and explore the potential mechanism underlying NIHL. Three SNPs (rs2304186, rs41275750, and rs76524493) were genotyped in a Chinese population which consists of 690 NIHL patients and 650 normal hearing controls. Bioinformatic analysis was conducted to predict the potential miRNA-binding site of SNPs. Plasmid construction, cell transfection, and dual-luciferase reporter assay were performed to investigate the potential molecular mechanism of SNPs involving in NIHL. The results revealed that rs2304186 GT genotype (OR = 1.41; 95% CI = 1.09–1.83) and TT genotype (OR = 1.51; 95% CI = 1.08–2.10) imparted increased risk of NIHL, and the increased risk could also be found in a dominant model (OR = 1.44; 95% CI = 1.12–1.84). The stratification analysis showed that rs2304186 GT/TT conferred a higher risk for NIHL, especially in subgroups of male, age (35–45 and > 45 years), noise exposure time (> 16 years), and noise exposure level (≤ 85 and ≥ 92 dB), when GG genotype as a reference. Furthermore, the haplotype TCCTACT (rs2304186-rs41275750-rs76524493) was found to be significantly associated with a high risk of NIHL (OR = 1.19; 95% CI = 1.02–1.40). Functional experiments showed that rs2304186 G allele combined with hsa-miR-625-5p mimics could significantly decrease the luciferase activity compared with T allele, indicating that rs2304186 altered the binding affinity of hsa-miR-625-5p to SNP rs2304186 mutation region, thus directly targeting AKT2 gene. In conclusion, our study provides evidence for the first time that SNP rs2304186 of AKT2 3′UTR might affect NIHL susceptibility by altering the binding affinity of has-miR-625-5p to mutation region in an allele-specific manner and it may act as a potential biomarker of NIHL susceptibility.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Basner M, Babisch W, Davis A, Brink M, Clark C, Janssen S, Stansfeld S (2014) Auditory and non-auditory effects of noise on health. Lancet 383:1325–1332
Cargill M, Altshuler D, Ireland J, Sklar P, Ardlie K, Patil N, Shaw N, Lane CR, Lim EP, Kalyanaraman N, Nemesh J, Ziaugra L, Friedland L, Rolfe A, Warrington J, Lipshutz R, Daley GQ, Lander ES (1999) Characterization of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in coding regions of human genes. Nat Genet 22:231–238
Chen K, Zhou YX, Li K, Qi LX, Zhang QF, Wang MC, ** with next generation sequencing. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:4371–4377
Cheng JQ, Godwin AK, Bellacosa A, Taguchi T, Franke TF, Hamilton TC, Tsichlis PN, Testa JR (1992) AKT2, a putative oncogene encoding a member of a subfamily of protein-serine/threonine kinases, is amplified in human ovarian carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:9267–9271
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105
Genomes Project C, Auton A, Brooks LD, Durbin RM, Garrison EP, Kang HM, Korbel JO, Marchini JL, McCarthy S, McVean GA, Abecasis GR (2015) A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 526:68–74
George S, Rochford JJ, Wolfrum C, Gray SL, Schinner S, Wilson JC, Soos MA, Murgatroyd PR, Williams RM, Acerini CL, Dunger DB, Barford D, Umpleby AM, Wareham NJ, Davies HA, Schafer AJ, Stoffel M, O’Rahilly S, Barroso I (2004) A family with severe insulin resistance and diabetes due to a mutation in AKT2. Science 304:1325–1328
Gruber AR, Lorenz R, Bernhart SH, Neubock R, Hofacker IL (2008) The Vienna RNA websuite. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W70–W74
Guo H, Ding E, Bai Y, Zhang H, Shen H, Wang J, Song X, Cai W, Guo J, Zhu B (2017) Association of genetic variations in FOXO3 gene with susceptibility to noise induced hearing loss in a Chinese population. PLoS One 12:e0189186
Hers I, Vincent EE, Tavare JM (2011) Akt signalling in health and disease. Cell Signal 23:1515–1527
Hildebrandt MA, Yang H, Hung MC, Izzo JG, Huang M, Lin J, Ajani JA, Wu X (2009) Genetic variations in the PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway are associated with clinical outcomes in esophageal cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy. J Clin Oncol 27:857–871
Honkura Y, Matsuo H, Murakami S, Sakiyama M, Mizutari K, Shiotani A, Yamamoto M, Morita I, Shinomiya N, Kawase T, Katori Y, Motohashi H (2016) NRF2 is a key target for prevention of noise-induced hearing loss by reducing oxidative damage of cochlea. Sci Rep 6:19329
Jamesdaniel S, Hu B, Kermany MH, Jiang H, Ding D, Coling D, Salvi R (2011) Noise induced changes in the expression of p38/MAPK signaling proteins in the sensory epithelium of the inner ear. J Proteomics 75:410–424
Knox B, Wang Y, Rogers LJ, Xuan J, Yu D, Guan H, Chen J, Shi T, Ning B, Kadlubar SA (2018) A functional SNP in the 3′-UTR of TAP2 gene interacts with microRNA hsa-miR-1270 to suppress the gene expression. Environ Mol Mutagen 59:134–143
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, Wolf R, Rosenberg L, Epstein EJ, MacMenamin P, da Piedade I, Gunsalus KC, Stoffel M, Rajewsky N (2005) Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet 37:495–500
Kurabi A, Keithley EM, Housley GD, Ryan AF, Wong AC (2017) Cellular mechanisms of noise-induced hearing loss. Hear Res 349:129–137
Liu C, Zhang F, Li T, Lu M, Wang L, Yue W, Zhang D (2012) MirSNP, a database of polymorphisms altering miRNA target sites, identifies miRNA-related SNPs in GWAS SNPs and eQTLs. BMC Genomics 13:661
Liu YM, Li XD, Guo X, Liu B, Lin AH, Ding YL, Rao SQ (2010) SOD2 V16A SNP in the mitochondrial targeting sequence is associated with noise induced hearing loss in Chinese workers. Dis Markers 28:137–147
Lou X, Qi X, Zhang Y, Long H, Yang J (2013) Decreased expression of microRNA-625 is associated with tumor metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol 108:230–235
Mahen EM, Watson PY, Cottrell JW, Fedor MJ (2010) mRNA secondary structures fold sequentially but exchange rapidly in vivo. PLoS Biol 8:e1000307
Miao L, Ji J, Wan L, Zhang J, Yin L, Pu Y (2019) An overview of research trends and genetic polymorphisms for noise-induced hearing loss from 2009 to 2018. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 26:34754–34774
Miller JM, Brown JN, Schacht J (2003) 8-iso-prostaglandin F(2alpha), a product of noise exposure, reduces inner ear blood flow. Audiol Neurootol 8:207–221
Murai N, Kirkegaard M, Jarlebark L, Risling M, Suneson A, Ulfendahl M (2008) Activation of JNK in the inner ear following impulse noise exposure. J Neurotrauma 25:72–77
Nelson DI, Nelson RY, Concha-Barrientos M, Fingerhut M (2005) The global burden of occupational noise-induced hearing loss. Am J Ind Med 48:446–458
Patel M, Hu Z, Bard J, Jamison J, Cai Q, Hu BH (2013) Transcriptome characterization by RNA-Seq reveals the involvement of the complement components in noise-traumatized rat cochleae. Neuroscience 248:1–16
Pereira L, Horta S, Mateus R, Videira MA (2015) Implications of Akt2/Twist crosstalk on breast cancer metastatic outcome. Drug Discov Today 20:1152–1158
Pirooz HJ, Jafari N, Rastegari M, Fathi-Roudsari M, Tasharrofi N, Shokri G, Tamadon M, Sazegar H, Kouhkan F (2018) Functional SNP in microRNA-491-5p binding site of MMP9 3′-UTR affects cancer susceptibility. J Cell Biochem 119:5126–5134
Roth C, Stuckrath I, Pantel K, Izbicki JR, Tachezy M, Schwarzenbach H (2012) Low levels of cell-free circulating miR-361-3p and miR-625* as blood-based markers for discriminating malignant from benign lung tumors. PLoS One 7:e38248
Shi YY, He L (2005) SHEsis, a powerful software platform for analyses of linkage disequilibrium, haplotype construction, and genetic association at polymorphism loci. Cell Res 15:97–98
Sliwinska-Kowalska M, Pawelczyk M (2013) Contribution of genetic factors to noise-induced hearing loss: a human studies review. Mutat Res 752:61–65
Sun X, Chen L, He Z (2019) PI3K/Akt-Nrf2 and anti-inflammation effect of macrolides in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Curr Drug Metab 20:301–304
Wang B, Ding E, Shen H, Wang J, Sun K, Chen S, Han L, Zhang H, Zhu B, Xu M (2017) Association of TagSNP in lncRNA HOTAIR with susceptibility to noise-induced hearing loss in a Chinese population. Hear Res 347:41–46
Wang N, Wang B, Guo J, Zhang S, Han L, Zhang J, Zhu B (2020) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in XPO5 are associated with noise-induced hearing loss in a Chinese population. Biochem Res Int 2020:9589310
Wang Z, Qiao Q, Chen M, Li X, Wang Z, Liu C, **e Z (2014) miR-625 down-regulation promotes proliferation and invasion in esophageal cancer by targeting Sox2. FEBS Lett 588:915–921
Yang S, Cai Q, Vethanayagam RR, Wang J, Yang W, Hu BH (2016) Immune defense is the primary function associated with the differentially expressed genes in the cochlea following acoustic trauma. Hear Res 333:283–294
Yu SF (2016) Strengthen the research for the prevention and control of occupational noise-induced hearing loss in our country. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi 34:881–883
Zdychova J, Komers R (2005) Emerging role of Akt kinase/protein kinase B signaling in pathophysiology of diabetes and its complications. Physiol Res 54:1–16
Zhang QY, Cheng WX, Li WM, Au W, Lu YY (2014) Occurrence of low frequency PIK3CA and AKT2 mutations in gastric cancer. Mutat Res 769:108–112
Zheng H, Ma R, Wang Q, Zhang P, Li D, Wang Q, Wang J, Li H, Liu H, Wang Z (2015) MiR-625-3p promotes cell migration and invasion via inhibition of SCAI in colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 6:27805–27815
Zhu DL, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Dong SS, Xu W, Hao RH, Chen XF, Yan H, Yang SY, Yang TL (2017) A functional SNP regulated by miR-196a-3p in the 3′UTR of FGF2 is associated with bone mineral density in the Chinese population. Hum Mutat 38:725–735
Zhu J, Wang M, He J, Zhu M, Wang JC, ** L, Wang XF, Yang YJ, **ang JQ, Wei Q (2016) Polymorphisms in the AKT1 and AKT2 genes and oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk in an Eastern Chinese population. J Cell Mol Med 20:666–677
Acknowledgements
The authors thank every worker for their participations in this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the Open Research Fund of State Key Laboratory of Bioelectronics, Southeast University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YP designed the research study. LM and BW performed the research and analyzed the data. LM drafted the manuscript. JZ and LY critically reviewed and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhongda Hospital, Affiliated Hospital of Southeast University.
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
The participant has consented to the submission of the case report to the journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Lotfi Aleya
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 4945 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, L., Wang, B., Zhang, J. et al. A functional SNP in miR-625-5p binding site of AKT2 3′UTR is associated with noise-induced hearing loss susceptibility in the Chinese population. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 40782–40792 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13649-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13649-4