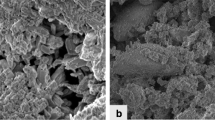
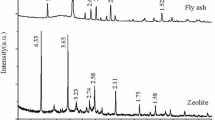
Abstract
The use of different types of zeolites (X, Na-P1, and 4A) synthesized by different methods and scales were tested in this work to adsorb nutrients present in synthetic solutions and industrial effluents for later application as fertilizer. Modifications with calcium chloride were performed on the zeolite with the best performance to increase its adsorption capacity. The best performing zeolite was type X (ZXH) produced on a pilot scale by the hydrothermal process. Its adsorption capacity without modification was 149 mg P-PO4/g zeolite and 349 mg K/g zeolite. With the change, there was a fourfold increase in these results, which were up to threefold higher than reported in the literature. The kinetic model that best characterized the adsorption process was the intraparticle diffusion model, and the equilibrium isotherm was that of Freundlich. The adsorption tests performed with industrial effluent showed high removal of the nutrients of interest (> 90% for PO43− and > 95% for K+). The desorption tests with zeolites nutrient-loaded from synthetic solutions showed 13 to 24% PO43− and 14 to 47% K+ release within 24 h, while for zeolite nutrient-loaded from effluent the release were 7 and 100% for PO43− and K+, respectively. The results we obtained in this work indicated the potential use of zeolites in the treatment of effluent and its application as a fertilizer.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abruzzi RC (2017) Aplicação de nanopartículas de SnO 2 e zeólitas em Porto Alegre Março , 2017 Porto Alegre Março, 2017. Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul
Aquino TF (2018) Síntese de zeólitas do tipo X a partir de cinzas volantes e de fundo de carvão mineral para a captura de CO2. Universidade Federal De Santa Catarina
Berkgaut V, Singer A (1996) High capacity cation exchanger by hydrothermal zeolitization of coal fly ash. Appl Clay Sci 10:369–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-1317(95)00033-X
Bernardi ACDC (2008) Potencial do uso de zeólitas na agropecuária. Embrapa Pecuária Sudeste 46. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0194
Bhardwaj D, Sharma P, Sharma M, Tomar R (2014) Removal and slow release studies of phosphate on surfactant loaded hydrothermally synthesized silicate nanoparticles. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 45:2649–2658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2014.07.010
Brassell JP, Ojumu TV, Petrik LF (2016) Upscaling of zeolite synthesis from coal fly ash waste: current status and future outlook. In: Zeolites - useful minerals
Bruulsema T (2018) Managing nutrients to mitigate soil pollution. Environ Pollut 243:1602–1605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.132
Canpolat F, Yilmaz K, Köse MM et al (2004) Use of zeolite, coal bottom ash and fly ash as replacement materials in cement production. Cem Concr Res 34:731–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(03)00063-2
Cardoso AM, Horn MB, Ferret LS, Azevedo CMN, Pires M (2015a) Integrated synthesis of zeolites 4A and Na-P1 using coal fly ash for application in the formulation of detergents and swine wastewater treatment. J Hazard Mater 287:69–77
Cardoso AM, Paprocki A, Ferret LS, Azevedo CMN, Pires M (2015b) Synthesis of zeolite Na-P1 under mild conditions using Brazilian coal fly ash and its application in wastewater treatment. Fuel 139:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.08.016
Cheng Q, Li H, Xu Y, Chen S, Liao Y, Deng F, Li J (2017) Study on the adsorption of nitrogen and phosphorus from biogas slurry by NaCl-modified zeolite. PLoS One 12:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0176109
Chmielewská E, Hodossyová R, Bujdoš M (2013) Kinetic and thermodynamic studies for phosphate removal using natural adsorption materials. Pol J Environ Stud 22:1307–1316
Choi J, Chung J, Lee W, Kim JO (2016) Phosphorous adsorption on synthesized magnetite in wastewater. J Ind Eng Chem 34:198–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.11.008
Collins F, Rozhkovskaya A, Outram JG, Millar GJ (2020) A critical review of waste resources, synthesis, and applications for Zeolite LTA. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 291:109667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109667
Dionisiou NS, Matsi T, Misopolinos ND (2013) Phosphorus adsorption-desorption on a surfactant-modified natural zeolite: A laboratory study. Water Air Soil Pollut 224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1362-7
Ehsan A, Bhatti HN, Iqbal M, Noreen S (2017) Native, acidic pre-treated and composite clay efficiency for the adsorption of dicationic dye in aqueous medium. Water Sci Technol 75:753–764
Fan Y, Li Y, Wu D, Li C, Kong H (2017) Application of zeolite/hydrous zirconia composite as a novel sediment cap** material to immobilize phosphorus. Water Res 123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.06.031
Ferrarini SFSF, Cardoso AMAMAM, Paprocki A, Pires M (2016) Integrated synthesis of zeolites using coal fly ash: Element distribution in the products, washing waters and effluent. J Braz Chem Soc 27:2034–2045. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20160093
Flores CG, Schneider H, Marcilio NR, Ferret L, Oliveira JCP (2017) Potassic zeolites from Brazilian coal ash for use as a fertilizer in agriculture. Waste Manag 70:263–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2017.08.039
Gollakota ARK, Volli V, Shu CM (2019) Progressive utilisation prospects of coal fly ash: a review. Sci Total Environ 672:951–989
Goscianska J, Ptaszkowska-Koniarz M, Frankowski M, Franus M, Panek R, Franus W (2018) Removal of phosphate from water by lanthanum-modified zeolites obtained from fly ash. J Colloid Interface Sci 513:72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.11.003
Guaya D, Valderrama C, Farran A, Armijos C, Cortina JL (2015) Simultaneous phosphate and ammonium removal from aqueous solution by a hydrated aluminum oxide modified natural zeolite. Chem Eng J 271:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.03.003
Guaya D, Valderrama C, Farran A, Cortina JL (2016) Modification of a natural zeolite with Fe (III) for simultaneous phosphate and ammonium removal from aqueous solutions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:1737–1746. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4763
Guo H, White JC, Wang Z, **ng B (2018) Nano-enabled fertilizers to control the release and use efficiency of nutrients. Curr Opin Environ Sci Health 6:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2018.07.009
Hamdi N, Srasra E (2012) Removal of phosphate ions from aqueous solution using Tunisian clays minerals and synthetic zeolite. J Environ Sci 24:617–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60791-2
Harikishore Kumar Reddy D, Vijayaraghavan K, Kim JA, Yun YS (2017) Valorisation of post-sorption materials: Opportunities, strategies, and challenges. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 242:35–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2016.12.002
He Y, Lin H, Dong Y, Liu Q, Wang L (2016) Simultaneous removal of ammonium and phosphate by alkaline-activated and lanthanum-impregnated zeolite. Chemosphere 164:387–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.110
He Y, Lin H, Dong Y, Wang L (2017) Preferable adsorption of phosphate using lanthanum-incorporated porous zeolite: Characteristics and mechanism. Appl Surf Sci 426:995–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.272
Hemalatha T, Ramaswamy A (2017) A review on fly ash characteristics – Towards promoting high volume utilization in develo** sustainable concrete. J Clean Prod 147:546–559
Hermassi M, Valderrama C, Moreno N, Font O, Querol X, Batis N, Cortina JL (2016) Powdered Ca-activated zeolite for phosphate removal from treated waste-water. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:1962–1971. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.4867
Hu T, Gao W, Liu X et al (2017) Synthesis of zeolites Na-A and Na-X from tablet compressed and calcinated coal fly ash. R Soc Open Sci 4. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.170921
Iqbal A, Sattar H, Haider R, Munir S (2019) Synthesis and characterization of pure phase zeolite 4A from coal fly ash. J Clean Prod 219:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.066
Izidoro J d C (2013) Cinzas volantes do carvão. USP
Jha B, Singh DN (2016) Fly Ash Zeolites. Adv Struct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-1404-8
Ji X, Zhang M, Wang Y, Song Y, Ke Y, Wang Y (2015) Immobilization of ammonium and phosphate in aqueous solution by zeolites synthesized from fly ashes with different compositions. J Ind Eng Chem 22:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.06.017
Jiang C, Jia L, He Y, Zhang B, Kirumba G, **e J (2013) Adsorptive removal of phosphorus from aqueous solution using sponge iron and zeolite. J Colloid Interface Sci 402:246–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.03.057
Juan R, Hernández S, Andrés JM, Ruiz C (2007) Synthesis of granular zeolitic materials with high cation exchange capacity from agglomerated coal fly ash. Fuel 86:1811–1821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2007.01.011
Kanwal A, Bhatti HN, Iqbal M, et al (2017) Basic dye adsorption onto clay/MnFe 2 O 4 composite : a mechanistic study. 2. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143017X14839994522984
Kausar A, Iqbal M, Javed A, Aftab K, Nazli ZIH, Bhatti HN, Nouren S (2018) Dyes adsorption using clay and modi fi ed clay: a review. J Mol Liq 256:395–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.034
Kim JH, Kim SB, Lee SH, Choi JW (2018) Laboratory and pilot-scale field experiments for application of iron oxide nanoparticle-loaded chitosan composites to phosphate removal from natural water. Environ Technol (UK) 39:770–779. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2017.1310937
Lateef A, Nazir R, Jamil N, Alam S, Shah R, Khan MN, Saleem M (2016) Synthesis and characterization of zeolite based nano-composite: an environment friendly slow release fertilizer. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 232:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.06.020
Liu C, Ma H, Gao Y (2019) Hydrothermal processing on potassic syenite powder: zeolite synthesis and potassium release kinetics. Adv Powder Technol 30:2483–2491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2019.07.024
Lopes TR (2017) Utilização de RMN no estado sólido em uma abordagem multinuclear para estudo de materiais carbonosos porosos Utilização de RMN no estado sólido em uma abordagem multinuclear para estudo de materiais carbonosos porosos. UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DO ESPÍRITO SANTO
Manto MJ, **e P, Keller MA, Liano WE, Pu T, Wang C (2017) Recovery of inorganic phosphorus using copper-substituted ZSM-5. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:6192–6200. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b01127
Melo CR, Riella HG (2010) Síntese de zeólita tipo NaA a partir de caulim para obtenção de zeólita 5A através de troca iônica. Cerâmica 56:340–346. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0366-69132010000400005
Mitrogiannis D, Psychoyou M, Baziotis I, Inglezakis VJ, Koukouzas N, Tsoukalas N, Palles D, Kamitsos E, Oikonomou G, Markou G (2017) Removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto Ca (OH)2treated natural clinoptilolite. Chem Eng J 320:510–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.03.063
Nausheen S, Bhatti HN, Hanif MA (2017) Enhanced removal of golden XGL dye by clay composites : batch and column studies. Pol J Environ Stud 26:2113–2123. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/68535
Onyango MS, Kuchar D, Kubota M, Matsuda H (2007) Adsorptive removal of phosphate ions from aqueous solution using synthetic zeolite. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:894–900. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie060742m
Pearce HA (1975) Zeolite molecular sieves—Structure, chemistry and use. J Chromatogr A 106:499. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9673(00)93871-8
Pengthamkeerati P, Satapanajaru T, Chularuengoaksorn P (2008) Chemical modification of coal fly ash for the removal of phosphate from aqueous solution. Fuel 87:2469–2476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2008.03.013
Petrov I, Michalev T (2012) Synthesis of Zeolite A: A Review. НАУЧНИ ТРУДОВЕ НА РУСЕНСКИЯ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ. Proc Chem Technol 30–35
Philippi M, dos Santos HS, Martins AO, Azevedo CMN, Pires M (2007) Alternative spectrophotometric method for standardization of chlorite aqueous solutions. Anal Chim Acta 585:361–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2006.12.053
Querol X, Moreno N, Umaa JC et al (2002) Synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash: an overview. Int J Coal Geol 50:413–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-5162(02)00124-6
Reddy DHK, Vijayaraghavan K, Kim JA, Yun YS (2017) Valorisation of post-sorption materials: opportunities, strategies, and challenges. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2016.12.002
Rhodes CJ (2010) Properties and applications of zeolites. Sci Prog 93:223–284. https://doi.org/10.3184/003685010X12800828155007
da Rocha Junior PR, Andrade FV, Mendonça E d S et al (2017) Soil, water, and nutrient losses from management alternatives for degraded pasture in Brazilian Atlantic Rainforest biome. Sci Total Environ 583:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.187
Sandomierski M, Buchwald Z, Koczorowski W, Voelkel A (2019) Calcium forms of zeolites A and X as fillers in dental restorative materials with remineralizing potential. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 294:109899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.109899
Sharma P, Song JS, Han MH, Cho CH (2016) GIS-NaP1 zeolite microspheres as potential water adsorption material: Influence of initial silica concentration on adsorptive and physical/topological properties. Sci Rep 6:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22734
Shi J, Yang Z, Dai H, Lu X, Peng L, Tan X, Shi L, Fahim R (2017) Preparation and application of modified zeolites as adsorbents in wastewater treatment. Water Sci Technol 2017:621–635. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.249
Tran DNH, Kabiri S, Wang L, Losic D (2015) Engineered graphene-nanoparticle aerogel composites for efficient removal of phosphate from water. J Mater Chem A 3:6844–6852. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta06308b
Van Raij B (2011) Melhorando o ambiente radicular em subsuperfície. Int Plant Nutr Inst
Vilar CC, Costa ACS, Hoepers A, Junior IGS (2010) Capacidade máxima de adsorção de fósforo relacionada a formas de ferro e alumínio em solos subtropicais. R Bras Ci Solo 34:1059–1068
Wan C, Ding S, Zhang C, Tan X, Zou W, Liu X, Yang X (2017) Simultaneous recovery of nitrogen and phosphorus from sludge fermentation liquid by zeolite adsorption: Mechanism and application. Sep Purif Technol 180:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2017.02.031
Wang S, Peng Y (2010) Natural zeolites as effective adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Chem Eng J
Wu D, Sui Y, Chen X, He S, Wang X, Kong H (2008) Changes of mineralogical-chemical composition, cation exchange capacity, and phosphate immobilization capacity during the hydrothermal conversion process of coal fly ash into zeolite. Fuel 87:2194–2200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2007.10.028
**e J, Wang Z, Fang D, Li C, Wu D (2014) Green synthesis of a novel hybrid sorbent of zeolite/lanthanum hydroxide and its application in the removal and recovery of phosphate from water. J Colloid Interface Sci 423:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.02.020
Yang L, Qian X, Yuan P, Bai H, Miki T, Men F, Li H, Nagasaka T (2019) Green synthesis of zeolite 4A using fly ash fused with synergism of NaOH and Na2CO3. J Clean Prod 212:250–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.259
Yang M, Lin J, Zhan Y, Zhang H (2014) Adsorption of phosphate from water on lake sediments amended with zirconium-modified zeolites in batch mode. Ecol Eng 71:223–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2014.07.035
Yoldi M, Fuentes-Ordoñez EG, Korili SA, Gil A (2019) Zeolite synthesis from industrial wastes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 287:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2019.06.009
Zhan Y, Zhang H, Lin J, Zhang Z, Gao J (2017) Role of zeolite’s exchangeable cations in phosphate adsorption onto zirconium-modified zeolite Yanhui. J Mol Liq 243:624–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.08.091
Zhang M, Gao B, Yao Y, Xue Y, Inyang M (2012) Synthesis of porous MgO-biochar nanocomposites for removal of phosphate and nitrate from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 210:26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.052
Zou H, Wang Y (2016) Phosphorus removal and recovery from domestic wastewater in a novel process of enhanced biological phosphorus removal coupled with crystallization. Bioresour Technol 211:87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.03.073
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the CNPq (312489/2018-8) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal Nível Superior – Brasil (CAPES, Código de Financiamento 001).
Availability of data and materials
Data and material access are not available.
Funding
Students Beatriz Bonetti and Etienne C. Waldown receive a scholarship from CNPq (312489 / 2018-8) and Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel - Brazil (CAPES, Financing Code 001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 4833 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonetti, B., Waldow, E.C., Trapp, G. et al. Production of zeolitic materials in pilot scale based on coal ash for phosphate and potassium adsorption in order to obtain fertilizer. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28, 2638–2654 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11447-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11447-y