Abstract
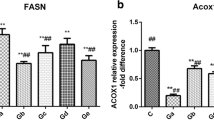
Cr (chromium, with common valence states of III and VI) is one of the common broiler feed additives. Liver injury and metabolic disorders could be caused by Cr(VI) (hexavalent chromium) poisoning in broilers. Oxidative damage and metabolic disorders of organisms caused by heavy metals could be antagonized by nano-Se (nano-selenium). Nano-Se was chosen to study the antagonism of Cr(VI) poisoning in broilers. AMPK (Adenosine 5,-monophosphate-activated protein kinase) is known as a “cell energy regulator” and plays a key regulatory role in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. AMPK pathway and ACACA/CPT1A two genes were selected to study the prevention and treatment of nano-Se on Cr(VI) poisoning in broilers and its molecular mechanism. For this purpose, 180 1-day-old AA (Arbor Acres) broilers were selected and randomly divided into 6 groups (n = 30) for further testing. After feeding as planned for 35 days, the livers of such broilers were taken for further examination including histopathological examination, differential gene expression analysis, and further validation on both mRNA and protein levels using related techniques like RT-qPCR, western blot, and immunohistochemistry (IHC). The histopathological examination suggested that the liver cells of the Cr(VI) poisoning group were more severely injured than the nano-Se addition group. RT-qPCR results showed that the relative expression of ACACA gene in the Cr(VI) poisoning group was significantly increased (P < 0.05), while the CPT1A gene’s expression was significantly decreased (P < 0.01). Those results were reversed in the nano-Se addition group. Western blot results were consistent with RT-qPCR and both suggested antagonism of nano-Se on Cr(VI). Through morphological and histopathological observation, as well as the measurement of the mRNA and protein expression levels of ACACA and CPT1A genes in AMPK pathway, it was confirmed that nano-Se has certain preventive and protective effects on Cr(VI) poisoning in broiler chickens. Furthermore, the adverse effects of Cr(VI) on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in broilers can be antagonized by nano-Se through AMPK pathway. A new method and experimental basis were provided to the future study of Cr(VI) poisoning in broilers.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alehagen U, Alexander J, Aaseth J (2016) Supplementation with selenium and coenzyme Q10 reduces cardiovascular mortality in elderly with low selenium status. A Secondary Analysis of a Randomised Clinical Trial. Plos One 11:e0157541
Al-Quraishy S, Dkhil MA, Moneim AEA (2015) Anti-hyperglycemic activity of selenium nanoparticles in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Nanomedicine 10:6741–6756
Ates B, Orun I, Talas ZS, Durmaz G, Yilmaz I (2008) Effects of sodium selenite on some biochemical and hematological parameters of rainbow trout ( Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1792) exposed to Pb 2+ and cu 2+. Fish Physiol Biochem 34:53–59
Chen P, Zhu Y, Wan H, Wang Y, Hao P, Cheng Z, Liu Y, Liu J (2017) Effects of the oral administration of K 2 Cr 2 O 7 and Na 2 SeO 3 on Ca, mg, Mn, Fe, cu, and Zn contents in the heart, liver, spleen, and kidney of chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 180:285–296
Chinese National feed hygiene standard (2001) NY5037-2001
De Flora S, Camoirano A, Bagnasco M, Bennicelli C, Corbett GE, Kerger BD (1997) Estimates of the chromium(VI) reducing capacity in human body compartments as a mechanism for attenuating its potential toxicity and carcinogenicity. Carcinogenesis 18:531
Fan W-T, Zhao X-N, Cheng J, Liu Y-H, Liu J-Z (2015) Oxidative stress and hepatocellular injury induced by oral administration of Cr3+ in chicken. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 29:280–287
Hardie DG (2014) AMP-activated protein kinase: maintaining energy homeostasis at the cellular and whole-body levels. Annu Rev Nutr 34:31
Hardie DG (2015) AMP-activated protein kinase: a key regulator of energy balance with many roles in human disease. J Intern Med 276:543–559
Hatfield DL, Tsuji PA, Carlson BA, Gladyshev VN (2014) Selenium and selenocysteine: roles in cancer, health, and development. Trends Biochem Sci 39:112–120
Iqbal ZM, Akbar H, Hosseini A, Forteguerri EBR, Osorio JS, Loor JJ (2016) Digital cushion fatty acid composition and lipid metabolism gene network expression in Holstein dairy cows fed a high-energy diet. PLoS One 11:e0159536
Jafari Dehkordi A, Mohebbi AN, Aslani MR, Ghoreyshi SM (2017) Evaluation of nanoselenium (Nano-Se) effect on hematological and serum biochemical parameters of rat in experimentally lead poisoning. Hum Exp Toxicol 36(4):421–427
Jaroslav R, Sindberg CD, Moesgaard S, Josef M, Jaroslav F, Luděk M, Katarína R (2013) Effect of chromium-enriched yeast on fasting plasma glucose, glycated haemoglobin and serum lipid levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with insulin. Biol Trace Elem Res 155:1–4
Jeyasingh J, Philip L (2005) Bioremediation of chromium contaminated soil: optimization of operating parameters under laboratory conditions. J Hazard Mater 118:113–120
Khorsandi K, Rabbani-Chadegani A (2013) Studies on the genotoxic effect of chromium oxide (Cr VI): interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid in solution. Mutat Res 750:105–110
Król E, Michalak S, Wójciak RW, Bogdański P (2012) Effects of combined dietary chromium(III) propionate complex and thiamine supplementation on insulin sensitivity, blood biochemical indices, and mineral levels in high-fructose-fed rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 150:350–359
Lau FC, Bagchi M, Sen CK, Bagchi D (2008) Nutrigenomic basis of beneficial effects of chromium(III) on obesity and diabetes. Mol Cell Biochem 317:1–10
Lipinski B (2017) Sodium selenite as an anticancer agent. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem 17:658–661
Liu X, Rehman MU, Mehmood K, Huang S, Tian X, Wu X, Zhou D (2018) Ameliorative effects of nano-elemental selenium against hexavalent chromium-induced apoptosis in broiler liver. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:15609
Loeschner K, Hadrup N, Hansen M, Pereira SA, Gammelgaard B, Møller LH, Mortensen A, Lam HR, Larsen EH (2014) Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of selenium following oral administration of elemental selenium nanoparticles or selenite in rats. Metallomics 6:330–337
Malhotra S, Welling MN, Mantri SB, Desai K (2015) In vitro and in vivo antioxidant, cytotoxic, and anti-chronic inflammatory arthritic effect of selenium nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 104:993–1003
Munehiro Y (2012) Is chromium an essential trace element in human nutrition? Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi 67:485
Nejla S, Mediha S, Ibtissem BA, Tahia B, Najiba Z (2010) Protective effects of selenium (se) on chromium (VI) induced nephrotoxicity in adult rats. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:671–678
Passerieux E, Hayot M, Jaussent A, Carnac G, Gouzi F, Pillard F, Picot MC, Böcker K, Hugon G, Pincemail J (2015) Effects of vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc gluconate, and selenomethionine supplementation on muscle function and oxidative stress biomarkers in patients with facioscapulohumeral dystrophy: a double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Free Radic Biol Med 81:158–169
Pati A, Chaudhary R, Subramani S (2014) A review on management of chrome-tanned leather shavings: a holistic paradigm to combat the environmental issues. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:11266–11282
Ray RR (2016) Adverse hematological effects of hexavalent chromium: an overview. Interdiscip Toxicol 9:55–65
Saeed AA, Sandhu MA, Khilji MS, Yousaf MS, Rehman HU, Tanvir ZI, Ahmad T (2017) Effects of dietary chromium supplementation on muscle and bone mineral interaction in broiler chicken. J Trace Elem Med Biol 42:25
Saez G, Davail S, Gentès G, Hocquette JF, Jourdan T, Degrace P, Baéza E (2009) Gene expression and protein content in relation to intramuscular fat content in Muscovy and Pekin ducks. Poult Sci 88:2382–2391
Sahin N, Hayirli A, Orhan C, Tuzcu M, Akdemir F, Komorowski JR, Sahin K (2017) Effects of the supplemental chromium form on performance and oxidative stress in broilers exposed to heat stress. Poult Sci:96
Siddiqui MA, Alhadlaq HA, Javed A, Al-Khedhairy AA, Javed M, Maqusood A (2013) Copper oxide nanoparticles induced mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human hepatocarcinoma cells. PLoS One 8:e69534
State G, Popescu IV, Radulescu C, Macris C, Stihi C, Gheboianu A, Dulama I, Niţescu O (2012) Comparative studies of metal air pollution by atomic spectrometry techniques and biomonitoring with moss and lichens. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:580–586
Suzuki K, Nagara H (1981) Brindled mottled mouse: morphological changes of brain and visceral organs in hemizygous males following copper supplementation. Acta Neuropathol 55:251
Tian X, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Mehmood K, Wu X, Chang Z, Luo M, Liu X, Ijaz M, Javed MT (2018) Transcriptome analysis reveals the molecular mechanism of hepatic metabolism disorder caused by chromium poisoning in chickens. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:1–11
Wan H, Zhu Y, Chen P, Wang Y, Hao P, Cheng Z, Liu Y, Liu J (2017) Effect of various selenium doses on chromium(IV)-induced nephrotoxicity in a male chicken model. Chemosphere 174:306
Wang Y, Tang JW, Ma WQ, Feng J, Feng J (2010) Dietary zinc glycine chelate on growth performance, tissue mineral concentrations, and serum enzyme activity in weanling piglets. Biol Trace Elem Res 133:325–334
Whanger PD (2002) Selenocompounds in plants and animals and their biological significance. J Am Coll Nutr 21:223–232
Xu X, Yekeen TA, Liu J, Zhuang B, Li W, Huo X (2015) Chromium exposure among children from an electronic waste recycling town of China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1778–1785
Zhao Y, Zhang H, Wu X et al (2019) Metabonomic analysis of the hepatic injury suffer from hexavalent chromium poisoning in broilers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:18181
Zheng-Jiang Z, Schultz AW, Junhua W, Johnson CH, Yannone SM, Patti GJ, Gary S (2013) Liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry characterization of metabolites guided by the METLIN database. Nat Protoc 8:451–460
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFD0501208) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31972748).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Z.T., Z.Y., and Z.D. were responsible for study conception and design; L.L. was involved in the drafting of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mohamed M. Abdel-Daim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Tg., Zhao, Yl., Li, L. et al. Antagonistic effects of nano-selenium on broilers hepatic injury induced by Cr(VI) poisoning in AMPK pathway. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 41585–41595 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08501-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08501-0
Keywords
- AMPK pathway
- ACACA gene
- CPT1A gene
- Cr(VI) poisoning
- High-throughput sequencing
- Nano-selenium
- Abbreviations
- Nano-SeNano-selenium
- CrChromium
- Cr (III)Trivalent chromium
- Cr (VI)Hexavalent chromium
- AMPKAdenosine 5,-monophosphate-activated protein kinase
- K2Cr2O7Potassium dichromate
- LD50Median lethal dose
- ACACAAcetyl CoA carboxylase
- CPT1ACarnitine palmitoyl transferase 1 A
- GTFGlucose tolerance factor
- AA broilersArbor Acres broilers
- PSEPale soft exudative meat