Abstract
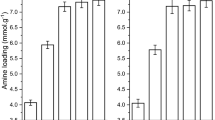
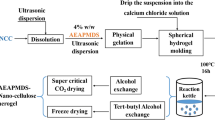
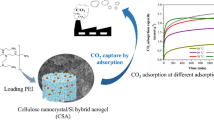
In this study, the cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) obtained by acid hydrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) are customized by suspension to obtain a spherical CNC hydrogel. The N-(2-aminoethyl) (3-amino-propyl) methyldimethoxyansile (AEAPMDS) preparation was grafted to spherical CNC hydrogel using a water phase heat treatment. Finally, aerogel samples were obtained by tert-butanol replacement and freeze-drying. The test results confirmed that the aminosilane was grafted on CNC. Electron micrographs and N2 sorption isotherms showed that the pores of the aerogel were partially blocked due to the introduction of AEAPMDS, and the specific surface area was decreased. Due to the presence of chemisorption, the amount of CO2 adsorbed at a pressure of 3 bar by the modified aerogel (2.63 mmol/g) was greatly improved compared with the unmodified aerogel (0.26 mmol/g), and the adsorption results were fit well by the Langmuir model. Thus, our experiments provided the opportunity to develop a new CO2 absorbent material.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmouleha M, Boufia S, Belgacemb MN, Duartec AP, Salaha AB, Gandinib A (2004) Modification of cellulosic fibres with functionalised silanes: development of surface properties. Int J Adhes Adhes 24:43–54
Bhanja P, Chatterjee S, Bhaumik A (2016) Triazine-based porous organic polymer with good CO2 gas adsorption properties and an efficient organocatalyst for the one-pot multicomponent condensation. Chemcatchem 8:3089–3098. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201600840
Cervin NT, Aulin C, Larsson PT, Wågberg L (2012) Ultra porous nanocellulose aerogels as separation medium for mixtures of oil/water liquids. Cellulose 19:401–410
Chen W, Yu H, Li Q, Liu Y, Li J (2011) Ultralight and highly flexible aerogels with long cellulose I nanofibers. Soft Matter 7:10360–10368
Darunte LA, Walton KS, Sholl DS, Jones CW (2016) CO2 capture via adsorption in amine-functionalized sorbents. Curr Opin Chem Eng 12:82–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2016.03.002
De France KJ, Hoare T, Cranston ED (2017) Review of hydrogels and aerogels containing nanocellulose. Chem Mater 29:4609–4631. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b00531
Fu J, Wang S, He C, Lu Z, Huang J, Chen Z (2016) Facilitated fabrication of high strength silica aerogels using cellulose nanofibrils as scaffold. Carbohydr Polym 147:89–96
Gao Z, Ma M, Zhai X, Zhang M, Zang D, Wang C (2015) Improvement of chemical stability and durability of superhydrophobic wood surface via a film of TiO2 coated CaCO3 micro-/nano-composite particles. RSC Adv 5:63978–63984
García-González CA, Alnaief M, Smirnova I (2011) Polysaccharide-based aerogels—promising biodegradable carriers for drug delivery systems. Carbohydr Polym 86:1425–1438
García-González CA, ** M, Gerth J, Alvarez-Lorenzo C, Smirnova I (2015) Polysaccharide-based aerogel microspheres for oral drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym 117:797–806
Gebald C, Wurzbacher JA, Tingaut P, Zimmermann T, Steinfeld A (2011) Amine-based nanofibrillated cellulose as adsorbent for CO2 capture from air. Environ Sci Technol 45:9101–9108. https://doi.org/10.1021/es202223p
He Y-L, **e T (2015) Advances of thermal conductivity models of nanoscale silica aerogel insulation material. Appl Therm Eng 81:28–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.02.013
Jadhav PD, Chatti RV, Biniwale RB, Labhsetwar NK, Devotta S, Rayalu SS (2007) Monoethanol amine modified zeolite 13X for CO2 adsorption at different temperatures. Energy Fuel 21:3555–3559
Jiao Y, Wan C, Qiang T, Li J (2016) Synthesis of superhydrophobic ultralight aerogels from nanofibrillated cellulose isolated from natural reed for high-performance adsorbents. Appl Phys A 122:686
Kim J, Rubino I, Lee J-Y, Choi H-J (2016) Application of halloysite nanotubes for carbon dioxide capture. Mater Res Express 3. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/3/4/045019
Kyohyun S, Nakwon L, Joonseok K, Eun-Bum C, Chamila G, Mietek J (2015) CO2 adsorption on amine-functionalized periodic mesoporous benzenesilicas. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:6792–6802
Lamy-Mendes A, Silva RF, Duraes L (2018) Advances in carbon nanostructure-silica aerogel composites: a review. J Mater Chem A 6:1340–1369. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta08959g
Le Y, Guo D, Cheng B, Yu J (2013) Amine-functionalized monodispersed porous silica microspheres with enhanced CO2 adsorption performance and good cyclic stability. J Colloid Interface Sci 408:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.07.014
Lee KY, Tammelin T, Schulfter K, Kiiskinen H, Samela J, Bismarck A (2012) High performance cellulose nanocomposites: comparing the reinforcing ability of bacterial cellulose and nanofibrillated cellulose. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:4078
Li N, Chen W, Chen G, Wan X, Tian J (2018) Low-cost, sustainable, and environmentally sound cellulose absorbent with high efficiency for collecting methane bubbles from seawater. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6: 6370–6377
Li D et al (2019) Effects of activation temperature on densities and volumetric CO2 adsorption performance of alkali-activated carbons. Fuel 238:232–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.10.122
Long L-Y, Weng Y-X, Wang Y-Z (2018) Cellulose Aerogels: Synthesis, Applications, and Prospects. Polymers (Basel) 10:623. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10060623
Lu J, Askeland P, Drzal LT (2008) Surface modification of microfibrillated cellulose for epoxy composite applications. Polymer (Guildf) 49:1285–1296
Mishra AK, Ramaprabhu S (2012) Polyaniline/multiwalled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite-an excellent reversible CO2 capture candidate. RSC Adv 2:1746–1750
Nie S, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Zhang K, Zhang Y, Tao P, Wang S (2018) Enzymatic and cold alkaline pretreatments of sugarcane bagasse pulp to produce cellulose nanofibrils using a mechanical method. Ind Crop Prod 124:435–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.08.033
Niu M, Yang H, Zhang X, Wang Y, Tang A (2016) Amine-impregnated mesoporous silica nanotube as an emerging nanocomposite for CO2 capture. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:17312–17320
Ouyang J, Gu W, Zhang Y, Yang H, ** Y, Chen J, Jiang J (2018a) CO2 capturing performances of millimeter scale beads made by tetraethylenepentamine loaded ultra-fine palygorskite powders from jet pulverization. Chem Eng J 341:432–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.02.040
Ouyang J et al (2018b) Polyethyleneimine (PEI) loaded MgO-SiO2 nanofibers from sepiolite minerals for reusable CO2 capture/release applications. Appl Clay Sci 152:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2017.11.023
Ouyang J, Zheng C, Gu W, Zhang Y, Yang H, Suib SL (2018c) Textural properties determined CO2 capture of tetraethylenepentamine loaded SiO2 nanowires from alpha-sepiolite. Chem Eng J 337:342–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.109
Perera F (2018) Pollution from fossil-fuel combustion is the leading environmental threat to global pediatric health and equity: solutions exist. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15010016
Razmkhah M, Mosavian MTH, Moosavi F, Ahmadpour A (2018) CO2 gas adsorption into graphene oxide framework: effect of electric and magnetic field. Appl Surf Sci 456:318–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.075
Sharma P, Baek I-H, Park Y-W, Sung-Chan N, Park J-H, Park S-D, Park SY (2012) Adsorptive separation of carbon dioxide by polyethyleneimine modified adsorbents. Korean J Chem Eng 29:249–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-011-0158-6
Shen X, Du H, Mullins RH, Kommalapati RR (2017) Polyethylenimine applications in carbon dioxide capture and separation: from theoretical study to experimental work. Energ Technol 5:822–833. https://doi.org/10.1002/ente.201600694
Shi J, Lu L, Guo W, Zhang J, Cao Y (2013) Heat insulation performance, mechanics and hydrophobic modification of cellulose-SiO2 composite aerogels. Carbohydr Polym 98:282–289
Sing KSW (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems-with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619
Tiwari D, Bhunia H, Bajpai PK (2018) Adsorption of CO2 on KOH activated, N-enriched carbon derived from urea formaldehyde resin: kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Appl Surf Sci 439:760–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.203
Vilarrasa-Garcia E, Ortigosa-Moya EM, Cecilia JA, Cavalcante CL Jr, Jimenez-Jimenez J, Azevedo DCS, Rodriguez-Castellon E (2015) CO2 adsorption on amine modified mesoporous silicas: effect of the progressive disorder of the honeycomb arrangement. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 209:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.08.032
Wan C, Lu Y, Jiao Y, ** C, Sun Q, Li J (2015) Ultralight and hydrophobic nanofibrillated cellulose aerogels from coconut shell with ultrastrong adsorption properties. J Appl Polym Sci 132:42037
Wang Z, Han NM, Wu Y, Liu X, Shen X, Zheng Q, Kim JK (2017) Ultrahigh dielectric constant and low loss of highly-aligned graphene aerogel/poly(vinyl alcohol) composites with insulating barriers. Carbon N Y 123:385–394
Wang X et al (2018) Synthesis and characterization of amine-modified spherical nanocellulose aerogels. J Mater Sci 53:13304–13315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2595-7
Yang Y, Li H, Chen S, Zhao Y, Li Q (2010) Preparation and characterization of a solid amine adsorbent for capturing CO2 by grafting allylamine onto PAN fiber. Langmuir 26:13897–13902
Yin F, Zhuang L, Luo X, Chen S (2018) Simple synthesis of nitrogen-rich polymer network and its further amination with PEI for CO2 adsorption. Appl Surf Sci 434:514–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.198
Yin F, Wu Z, Luo X, Zhuang L, Ou H, Chen S (2019) Synthesis of nitrogen-rich hollow microspheres for CO2 adsorption. J Mater Sci 54:3805–3816. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-3107-5
Yu J, Le Y, Cheng B (2012) Fabrication and CO2 adsorption performance of bimodal porous silica hollow spheres with amine-modified surfaces. RSC Adv 2:6784–6791
Zettlemoyer AC (1958) Colloid and surface Chemistry.
Zhang F, Ren H, Tong G, Deng Y (2016) Ultra-lightweight poly (sodium acrylate) modified TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibril aerogel spheres and their superabsorbent properties. Cellulose 23:1–12
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Wang X, Liu S, Yao Y (2018) Characterization of the nano-cellulose aerogel from mixing CNF and CNC with different ratio. Mater Lett 229:103–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.06.101
Zhao S, Malfait WJ, Guerrero-Alburquerque N, Koebel MM, Nystroem G (2018) Biopolymer aerogels and foams: chemistry, properties, and applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 57:7580–7608. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201709014
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Special Fund for Forest Scientific Research in the Public Welfare (201504603).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 812 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Zhang, Y., Jiang, H. et al. Aminosilane-grafted spherical cellulose nanocrystal aerogel with high CO2 adsorption capacity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 16716–16726 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05068-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05068-3