Abstract
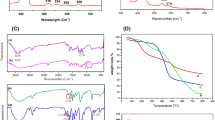
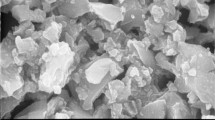
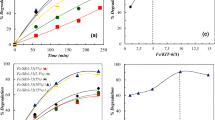
Iron (II) phthalocyanine (FePc) supported on electrospun polyester/poly-4-vinylpyridine nanofibers (PET/P4VP NFs) was prepared by stirring in tetrahydrofuran. The resulting product was confirmed and characterized by ultraviolet-visible diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectra, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, gas chromatography/mass spectrometry, and ultra-performance liquid chromatography. More than 95% of sulfaquinoxalinum (SQX) could be removed by the activation of hydrogen peroxide in the presence of FePc-P4VP/PET with a PET and P4VP mass ratio of 1:1. This system exhibited a high catalytic activity across a wide pH and temperature range. The degradation rates of SQX achieved 100, 95, and 78% at a pH of 3, 7, and 9, respectively, and the degradation rates of SQX are more than 80% at the temperature ranging from 35 to 65 °C. DMSO2 could be detected by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry after the addition of DMSO, suggesting the formation of the high-valent iron intermediates in this catalytic system. In addition, the electron paramagnetic resonance experiments proved that free radicals did not dominate the reaction in our system. Therefore, the high-valent iron intermediates were proposed to the main active species in the FePc-P4VP/PET/hydrogen peroxide system. In summary, the heterogeneous catalytic processes with non-radical catalytic mechanism might have better catalytic performance for the removal of organic pollutants, which can potentially be used in wastewater treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afanasiev P, Sorokin AB (2016) μ-Nitrido diiron macrocyclic platform: particular structure for particular catalysis. Acc Chem Res 49(4):583–593. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00458
Agboola BO, Ozoemena KI (2008) Self-assembly and heterogeneous electron transfer properties of metallo-octacarboxyphthalocyanine complexes on gold electrode. Phys Chem Chem Phys 10(17):2399–2408. https://doi.org/10.1039/b800611c
Baran W, Adamek E, Ziemiańska J, Sobczak A (2011) Effects of the presence of sulfonamides in the environment and their influence on human health. J Hazard Mater 196:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.08.082
Ben W, Shi Y, Li W, Zhang Y, Qiang Z (2017) Oxidation of sulfonamide antibiotics by chlorine dioxide in water: kinetics and reaction pathways. Chem Eng J 327:743–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.157
Bialk-Bielińska A, Stolte S, Arning J, Uebers U, Böschen A, Stepnowski P, Matzke M (2011) Ecotoxicity evaluation of selected sulfonamides. Chemosphere 85(6):928–933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.06.058
Biošić M, Mitrevski M, Babic S (2017) Environmental behavior of sulfadiazine, sulfamethazine, and their metabolites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(10):9802–9812. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8639-8
Bloem E, Albihn A, Elving J, Hermann L, Lehmann L, Sarvi M, Schaaf T, Schick J, Turtola E, Ylivainio K (2017) Contamination of organic nutrient sources with potentially toxic elements, antibiotics and pathogen microorganisms in relation to P fertilizer potential and treatment options for the production of sustainable fertilizers: a review. Sci Total Environ 607:225–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.06.274
Boreen AL, Arnold WA, Mcneill K (2005) Triplet-sensitized photodegradation of sulfa drugs containing six-membered heterocyclic groups : identification of an SO2 extrusion photoproduct. Environ Sci Technol 39(10):3630–3638. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048331p
Carmona E, Andreu V, Pico Y (2014) Occurrence of acidic pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Turia River Basin: from waste to drinking water. Sci Total Environ 484:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.02.085
Cetecioglu Z (2014) Aerobic inhibition assessment for anaerobic treatment effluent of antibiotic production wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(4):2856–2864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2243-3
Dewil R, Mantzavinos D, Poulios I, Rodrigo MA (2017) New perspectives for advanced oxidation processes. J Environ Manag 195(Pt 2):93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.04.010
Gao Y-Q, Gao N-Y, Deng Y, Yang Y-Q, Ma Y (2012) Ultraviolet (UV) light-activated persulfate oxidation of sulfamethazine in water. Chem Eng J 195-196:248–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.04.084
Gashti MP, Ebrahimi I, Pousti M (2015) New insights into corona discharge surface ionization of polyethylene terephthalate via a combined computational and experimental assessment. Curr Appl Phys 15(9):1075–1083. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2015.06.009
Gehling W, Khachatryan L, Dellinger B (2014) Hydroxyl radical generation from environmentally persistent free radicals (EPFRs) in PM2.5. Environ Sci Technol 48(8):4266–4272. https://doi.org/10.1021/es401770y
González O, Justo A, Bacardit J, Ferrero E, Malfeito JJ, Sans C (2013) Characterization and fate of effluent organic matter treated with UV/H2O2 and ozonation. Chem Eng J 226:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.04.066
Guo Z, Zhou F, Zhao Y, Zhang C, Liu F, Bao C (2012a) Gamma irradiation-induced sulfadiazine degradation and its removal mechanisms. Chem Eng J 191:256–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.03.012
Guo C, Xu J, Zhang Y, He Y (2012b) Hierarchical mesoporous TiO2 microspheres for the enhanced photocatalytic oxidation of sulfonamides and their mechanism. RSC Adv 2(11):4720–4727. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra01164f
Hoff RB, Barreto F, Kist TBL (2009) Use of capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection to screen and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to confirm sulfonamide residues: validation according to European Union 2002/657/EC. J Chromatogr A 1216(46):8254–8261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2009.07.074
Hoff RB, Barreto F, Melo J, Jank L, Peralba MDCR, Pizzolato TM (2012) Characterization and estimation of sulfaquinoxaline metabolites in animal tissues using liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Methods 4(9):2822. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2AY25197C
Hoff RB, Meneghini L, Pizzolato TM, Peralba MDCR, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barcelό D (2014) Structural elucidation of sulfaquinoxaline metabolism products and their occurrence in biological samples using high-resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 86(11):5579–5586. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac501132r
Hou J, Wang C, Mao D, Luo Y (2016) The occurrence and fate of tetracyclines in two pharmaceutical wastewater treatment plants of Northern China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):1722–1731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5431-5
Ikhlaq A, Brown DR, Kasprzyk-Hordern B (2013) Mechanisms of catalytic ozonation: an investigation into superoxide ion radical and hydrogen peroxide formation during catalytic ozonation on alumina and zeolites in water. Appl Catal B Environ 129:437–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.09.038
Kay P, Blackwell PA, Boxall ABA (2005) A lysimeter experiment to investigate the leaching of veterinary antibiotics through a clay soil and comparison with field data. Environ Pollut 134(2):333–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.07.021
Kovacic M, Perisic DJ, Biosic M, Kusic H, Babic S, Bozic AL (2016) UV photolysis of diclofenac in water; kinetics, degradation pathway and environmental aspects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(15):14908–14917. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6580-x
Lekunberri I, Villagrasa M, Luis Balcázar J, Borrego CM (2017) Contribution of bacteriophage and plasmid DNA to the mobilization of antibiotic resistance genes in a river receiving treated wastewater discharges. Sci Total Environ 601:206–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.05.174
Liao Q-N, Ji F, Li J-C, Zhan X, Hu Z-H (2016) Decomposition and mineralization of sulfaquinoxaline sodium during UV/H2O2 oxidation processes. Chem Eng J 284:494–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.08.150
Lin H, Zhang J, Chen H, Wang J, Sun W, Zhang X, Yang Y, Wang Q, Ma J (2017) Effect of temperature on sulfonamide antibiotics degradation, and on antibiotic resistance determinants and hosts in animal manures. Sci Total Environ 607:725–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.057
Liu Y, Wang J (2013) Degradation of sulfamethazine by gamma irradiation in the presence of hydrogen peroxide. J Hazard Mater 250-251:99–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.01.050
Liu J, Huang J-W, Shen H, Wang H, Yu H-C, Ji L-N (2008) The synthesis of two novel hybrids containing a zinc(II) porphyrin unit and a polypyridyl ruthenium(II) complex unit and their photoinduced intramolecular electron and energy transfer. Dyes Pigments 77(2):374–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.06.008
Mano T, Nishimoto S, Kameshima Y, Miyake M (2015) Water treatment efficacy of various metal oxide semiconductors for photocatalytic ozonation under UV and visible light irradiation. Chem Eng J 264:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.088
Mantzavinos D, Poulios I, Fernández-Ibañez P, Malato S (2014) Advanced oxidation processes for environmental protection. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(21):12109–12111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3359-9
Mantzavinos D, Poulios I, Pintar A (2017) Advances and trends in advanced oxidation processes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(2):1061–1062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8021-2
Nawrot TS, Kuenzli N, Sunyer J, Shi T, Moreno T, Viana M, Heinrich J, Forsberg B, Kelly FJ, Sughis M, Nemery B, Borm P (2009) Oxidative properties of ambient PM2.5 and elemental composition: heterogeneous associations in 19 European cities. Atmos Environ 43(30):4595–4602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.06.010
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimathi R (2014a) Comparative removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution by electro-Fenton and electro-Fenton-like processes. Clean Soil Air Water 42(6):779–784. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201300093
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimathi R (2014b) Electrolytic removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution by peroxicoagulation process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(14):8585–8594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2775-1
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimathi R, Ramesh ST (2013) Degradation of dyes from aqueous solution by Fenton processes: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(4):2099–2132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1385-z
Ou D, Chen B, Bai R, Song P, Lin H (2015) Contamination of sulfonamide antibiotics and sulfamethazine-resistant bacteria in the downstream and estuarine areas of Jiulong River in Southeast China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(16):12104–12113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4473-z
Sahiner N, Yasar AO (2013) The generation of desired functional groups on poly(4-vinyl pyridine) particles by post-modification technique for antimicrobial and environmental applications. J Colloid Interface Sci 402:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.03.032
Sahiner N, Yildiz S (2014) Preparation of superporous poly(4-vinyl pyridine) cryogel and their templated metal nanoparticle composites for H2 production via hydrolysis reactions. Fuel Process Technol 126:324–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.05.025
Sahiner N, Atta AM, Yasar AO, Al-Lohedan HA, Ezzat AO (2015) Surface activity of amphiphilic cationic pH-responsive poly(4-vinylpyridine) microgel at air/water interface. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 482:647–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.07.035
Sakai N, Sakai M, Haron DEM, Yoneda M, Mohd MA (2016) Beta-agonist residues in cattle, chicken and swine livers at the wet market and the environmental impacts of wastewater from livestock farms in Selangor State, Malaysia. Chemosphere 165:183–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.09.022
Salaeh S, Perisic DJ, Biosic M, Kusic H, Babic S, Stangar UL, Dionysiou DD, Bozic AL (2016) Diclofenac removal by simulated solar assisted photocatalysis using TiO2-based zeolite catalyst; mechanisms, pathways and environmental aspects. Chem Eng J 304:289–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.083
Sorokin AB (2013) Phthalocyanine metal complexes in catalysis. Chem Rev 113(10):8152–8191. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr4000072
Sorokin AB, Kudrik EV (2011) Phthalocyanine metal complexes: versatile catalysts for selective oxidation and bleaching. Catal Today 159(1):37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2010.06.020
Tai C, Peng J-F, Liu J-F, Jiang G-B, Zou H (2004) Determination of hydroxyl radicals in advanced oxidation processes with dimethyl sulfoxide trap** and liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 527(1):73–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.08.019
van Doorslaer X, Heynderickx PM, Demeestere K, Debevere K, Van Langenhove H, Dewulf J (2012) TiO2 mediated heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of moxifloxacin: operational variables and scavenger study. Appl Catal B Environ 111-112:150–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.09.029
Vasiliadou IA, Molina R, Martínez F, Melero JA (2013) Biological removal of pharmaceutical and personal care products by a mixed microbial culture: sorption, desorption and biodegradation. Biochem Eng J 81:108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.10.010
Wang L, Wu J, Wang Q, He C, Zhou L, Wang J, Pu Q (2012) Rapid and sensitive determination of sulfonamide residues in milk and chicken muscle by microfluidic chip electrophoresis. J Agric Food Chem 60(7):1613–1618. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf2036577
Wang M, Liu X, Pan B, Zhang S (2013) Photodegradation of Acid Orange 7 in a UV/acetylacetone process. Chemosphere 93(11):2877–2882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.08.082
Wang A-Q, Lin Y-L, Xu B, Hu C-Y, **a S-J, Zhang T-Y, Chu W-H, Gao N-Y (2017) Kinetics and modeling of iodoform degradation during UV/chlorine advanced oxidation process. Chem Eng J 323:312–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.061
Wols BA, Harmsen DJH, Beerendonk EF, Hofman-Caris CHM (2015) Predicting pharmaceutical degradation by UV (MP)/H2O2 processes: a kinetic model. Chem Eng J 263:336–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.10.101
Yu Y, Liu Y, Wu L (2013) Sorption and degradation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(6):4261–4267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1442-7
Zhang Y, Xu J, Zhong Z, Guo C, Li L, He Y, Fan W, Chen Y (2013) Degradation of sulfonamides antibiotics in lake water and sediment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(4):2372–2380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1121-8
Zhao X, Wang J, Zhu L, Ge W, Wang J (2017) Environmental analysis of typical antibiotic-resistant bacteria and ARGs in farmland soil chronically fertilized with chicken manure. Sci Total Environ 593:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.062
Zhu Z, Chen Y, Gu Y, Wu F, Lu W, Xu T, Chen W (2016) Catalytic degradation of recalcitrant pollutants by Fenton-like process using polyacrylonitrile-supported iron (II) phthalocyanine nanofibers: intermediates and pathway. Water Res 93:296–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.02.035
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51703201) and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LQ17E030003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Suresh Pillai
Electronic supplementary material
Details regarding the Experimental Section; Fig. S1–S6: Determination of iron phthalocyanine content in FePc-P4VP/PET, TG, XPS spectra, the effect of H2O2 concentration, pH and experimental temperature; Table S1: Degradation of other sulfonamides. The Supplementary Material is available free of charge on.
ESM 1
(DOCX 267 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, N., Lu, P., He, C. et al. Catalytic degradation of sulfaquinoxalinum by polyester/poly-4-vinylpyridine nanofibers-supported iron phthalocyanine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 5902–5910 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0943-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0943-9