Abstract
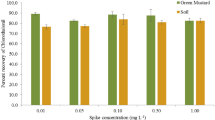
The single application of 0.5 % clothianidin granules, a novel formulation, was used to control pests in vegetables under a high dose. In this article, residues of clothianidin in cabbage and soil samples under field conditions from Guangzhou, Nanning, and Qianjiang were determined by HPLC. The terminal residues of clothianidin in cabbage were less than the limit of detection (<LOD) at pre-harvest intervals of 30 days, and these values were lower than the maximum residue limit of 0.2 mg kg−1 in cabbage set by the Codex Alimentarius Commission. To test on the influence of the pesticide fertilizers’ effect on clothianidin residual, clothianidin granules and fertilizers of chicken manure, urea, and organic fertilizer were mixed into different pesticide fertilizers through their normal field using dosage and evaluate residual influence of clothianidin in different formula. After analysis of variance of the effect factors, the effect of different pesticide types on half-life was not significant, but the effect of sample types was significant. Clothianidin granules and pesticide fertilizers could be safely applied in cabbage under a single high-dose administration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chauhan R, Monga S, Kumari B (2012) Dissipation and decontamination of bifenthrin residues in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum mill). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:181–186
Chen MF, Huang MF, Wong SS, Li GC (2005) Analysis of insecticide clothianidin and its metabolites in rice by liquid chromatography with a UV detector. J Food Drug Anal 13:279–283
Chen YJ, Wang Y, Gong ML, Li N, Zhao YX (2008) The dynamic of clothianidin (a new insecticide) in Brassica chinensis. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory 27:230–232
Chen YQ, Li XB, Tian YJ, Tan MH (2009a) Structural change of agricultural land use intensity and its regional disparity in China. Journal of Geography Science 19:545–556
Chen YJ, Wang Y, Li N, Gong ML (2009b) Methodological study on the determination of residual pesticide in Brassica chinensis by HPLC. China Tropical Medicine 9:361–362
European Commission (2010) Guidance document on pesticide residue analytical methods. DocumentNo.SANCO/825/00/rev.8.1/16/11/2010. http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/protection/resources/guide_doc_825-00_rev7_en.pdf. Accessed 25 May 2012
Hou RY, Cai HM, Zhang ZZ, Wan XC (2010) Determination of neonicotinoid pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits with high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory 29:59–63
Huang F, Guo ZY, Chen L, Xu Z, Liu Y, Yang CM (2010) Dissipation and evaluation of hexaflumuron residues in Chinese cabbage grown in open fields. J Agric Food Chem 58:4839–4843
Kim BM, Park JS, Choi JH, El-Aty AM, Na TW, Shim JH (2012) Residual determination of clothianidin and its metabolites in three minor crops via tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 131:1546–1551
Lambin EF, Rounsevell MDA, Geist HJ (2000) Are agricultural land-use models able to predict changes in land-use intensity? Agric Ecosyst Environ 82:321–331
Li XB (2002) Explanation of land use changes. Prog Geogr 21(3):195–203
Li L, Jiang GQ, Liu CY, Liang HW, Sun DL, Li W (2012) Clothianidin dissipation in tomato and soil, and distribution in tomato peel and flesh. Food Control 25:265–269
Mu KG, Zhang WJ, Ling JQ, Liu XL (2000) Study and practice on the interaction between pesticides and fertilizers [J]. World Agriculture 4:39–41
Ohkawara Y, Akayama A, Matsuda K, Andersch W (2002) Clothianidin: a novel broad-spectrum neonicotinoid insecticide. Br Crop Prot Council Conf-Pests Dis 1:51–58
Ramasubramanian T (2013) Persistence and dissipation kinetics of clothianidin in the soil of tropical sugarcane ecosystem. Water Air Soil Pollut 224:1468
Uneme H (2011) Chemistry of clothianidin and related compounds. J Agric Food Chem 59:2932–2937
Wu YJ, Wang DZ, Hong WY (2012) Bifenthrin and clothianidin to control the Phyllotreta striolata. Journal of Zhejiang Agriculture 2:194–197
**e W, Qian Y, Ding HY, Chen XM, ** JY, Jiang XY (2009) Determination of six neonicotinoid pesticides residues in tea samples using high performance chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Chin J Anal Chem 37:495–499
You XW, Jiang NW, Liu FM, Liu CY, Wang SL (2013) Dissipation and residue of bifenthrin in wheat under field conditions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90:238–241
Zhang ZY, Zhang CZ, Liu XJ, Hong XY (2006) Dynamics of pesticide residues in the autumn Chinese cabbage (Brassica chinensis L.) grown in open fields. Pest Manag Sci 62:350–355
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals, Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China, and Zhaoqing Zhenge Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Wang, S., Huang, C. et al. Dissipation and residue of clothianidin in granules and pesticide fertilizers used in cabbage and soil under field conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 27–33 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7736-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7736-4