Abstract
Purpose
Amide proton transfer (APT) imaging is able to extend the achievable magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast to the protein level. In this study, we demonstrate the feasibility of applying a turbo-spin-echo (TSE)-based, three-dimensional (3D) APT sequence into routine clinical practice for patients with brain tumors.
Procedures
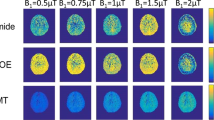
Experiments were performed on a Philips 3-Tesla (3-T) MRI scanner using an eight-channel phased-array coil for reception. A fast 3D APT sequence with a TSE acquisition was proposed (saturation power, 2 μT; saturation time, 500 ms; 8 slices). The gradient echo (GRE)-based field-map** technique or water-saturation-shift-referencing (WASSR) technique was used to acquire B0 maps to correct for B0-induced artifacts in APT images. The test was performed on a box of homogenous protein solution, four healthy volunteers, and eight patients with high-grade gliomas.
Results
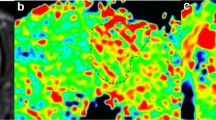
The experimental data from a homogenous, protein-containing phantom and healthy volunteers show that the sequence produced a uniform contrast across all slices. The average MTRasym(3.5 ppm) values with GRE B0-corrected 3D APT imaging and WASSR-corrected 3D APT imaging were both comparable to the values obtained using the undemanding single-slice acquisition. The average APT image intensity was consistently higher in the tumor core than in the peripheral edema and in the contralateral normal-appearing white matter (both P < 0.001).
Conclusion
3D APT imaging of brain tumors can be performed in about 5 min at 3-T using a routine, commercial eight-channel SENSE coil.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wuthrich K (1986) NMR of proteins and nucleic acids, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Zhou J, Payen J, Wilson DA, Traystman RJ, van Zijl PCM (2003) Using the amide proton signals of intracellular proteins and peptides to detect pH effects in MRI. Nature Med 9:1085–1090
Ward KM, Aletras AH, Balaban RS (2000) A new class of contrast agents for MRI based on proton chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST). J Magn Reson 143:79–87
Zhou J, van Zijl PC (2006) Chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging and spectroscopy. Progr NMR Spectr 48:109–136
Aime S, Crich SG, Gianolio E, Giovenzana GB, Tei L, Terreno E (2006) High sensitivity lanthanide(III) based probes for MR-medical imaging. Coord Chem Rev 250:1562–1579
Sherry AD, Woods M (2008) Chemical exchange saturation transfer contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 10:391–411
Hancu I, Dixon WT, Woods M, Vinogradov E, Sherry AD, Lenkinski RE (2010) CEST and PARACEST MR contrast agents. Acta Radiol 51:910–923
Wolff SD, Balaban RS (1989) Magnetization transfer contrast (MTC) and tissue water proton relaxation in vivo. Magn Reson Med 10:135–144
Zhou JY, Yan K, Zhu H (2012) A simple model for understanding the origin of the amide proton transfer MRI signal in tissue. Appl Magn Reson 42(3):393–402
Zhou J, Lal B, Wilson DA, Laterra J, van Zijl PCM (2003) Amide proton transfer (APT) contrast for imaging of brain tumors. Magn Reson Med 50:1120–1126
Zhou J, Tryggestad E, Wen Z et al (2011) Differentiation between glioma and radiation necrosis using molecular magnetic resonance imaging of endogenous proteins and peptides. Nat Med 17:130–134
Jones CK, Schlosser MJ, van Zijl PC, Pomper MG, Golay X, Zhou J (2006) Amide proton transfer imaging of human brain tumors at 3T. Magn Reson Med 56:585–592
Zhou J, Blakeley JO, Hua J et al (2008) Practical data acquisition method for human brain tumor amide proton transfer (APT) imaging. Magn Reson Med 60:842–849
Wen Z, Hu S, Huang F et al (2010) MR imaging of high-grade brain tumors using endogenous protein and peptide-based contrast. NeuroImage 51:616–622
Zhao X, Wen Z, Huang F et al (2011) Saturation power dependence of amide proton transfer image contrasts in human brain tumors and strokes at 3T. Magn Reson Med 66:1033–1041
Sun PZ, Murata Y, Lu J, Wang X, Lo EH, Sorensen AG (2008) Relaxation-compensated fast multislice amide proton transfer (APT) imaging of acute ischemic stroke. Magn Reson Med 59:1175–1182
Dixon WT, Hancu I, Ratnakar SJ, Sherry AD, Lenkinski RE, Alsop DC (2009) A multislice gradient echo pulse sequence for CEST imaging. Magn Reson Med 63:253–256
Zhu H, Jones CK, van Zijl PCM, Barker PB, Zhou J (2010) Fast 3D chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) imaging of the human brain. Magn Reson Med 64:638–644
Sun PZ, Cheung JS, Wang E, Berner T, Sorensen AG (2011) Fast multislice pH-weighted chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) MRI with unevenly segmented RF irradiation. Magn Reson Med 65:588–594
Park SH, Duong TQ (2011) Alternate ascending/descending directional navigation approach for imaging magnetization transfer asymmetry. Magn Reson Med 65(6):1702–1710
Jones CK, Polders D, Hua J, et al. (2012) In vivo 3D whole-brain pulsed steady state chemical exchange saturation transfer at 7T. Magn Reson Med 67:1579–1589
Kim M, Gillen J, Landman BA, Zhou J, van Zijl PCM (2009) Water saturation shift referencing (WASSR) for chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) experiments. Magn Reson Med 61:1441–1450
Hua J, Jones CK, Blakeley J, Smith SA, van Zijl PCM, Zhou J (2007) Quantitative description of the asymmetry in magnetization transfer effects around the water resonance in the human brain. Magn Reson Med 58:786–793
Sun PZ, Zhou J, Sun W, Huang J, van Zijl PCM (2007) Detection of the ischemic penumbra using pH-weighted MRI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27:1129–1136
Jokivarsi KT, Grohn HI, Grohn OH, Kauppinen RA (2007) Proton transfer ratio, lactate, and intracellular pH in acute cerebral ischemia. Magn Reson Med 57:647–653
Mougin OE, Coxon RC, Pitiot A, Gowland PA (2010) Magnetization transfer phenomenon in the human brain at 7T. NeuroImage 49:272–281
Jia G, Abaza R, Williams JD et al (2011) Amide proton transfer MR imaging of prostate cancer: a preliminary study. J Magn Reson Imaging 33(3):647–654
Dula AN, Asche EM, Landman BA et al (2011) Development of chemical exchange saturation transfer at 7T. Magn Reson Med 66(3):831–838
Scheidegger R, Vinogradov E, Alsop DC (2011) Amide proton transfer imaging with improved robustness to magnetic field inhomogeneity and magnetization transfer asymmetry using saturation with frequency alternating RF irradiation. Magn Reson Med 66(5):1275–1285
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01EB009731, R01EB015032, R21EB009112, R21EB015555, and P41EB015909), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81128006 and 81171322), and Dana Foundation. We thank Ms. Mary McAllister for editorial assistance.
Conflict of Interest
J.Z. is a co-inventor on a patent at the US Patent and Trademark Office for the APT-MRI technology. This patent is owned and managed by Johns Hopkins University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Wen, Z., Zhang, G. et al. Three-Dimensional Turbo-Spin-Echo Amide Proton Transfer MR Imaging at 3-Tesla and Its Application to High-Grade Human Brain Tumors. Mol Imaging Biol 15, 114–122 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-012-0563-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-012-0563-1