Abstract
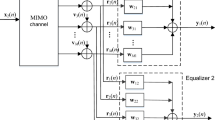
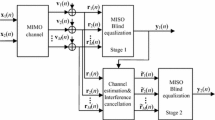
Blind equalization can effectively reduce the intersymbol interference introduced by the frequency selective channel in the absence of the training sequence. The Shalvi-Weinstein Algorithm (SWA) performs better under most channels, especially for highly distorted ones compared with constant modulus algorithm (CMA) or its modified versions. The disadvantage of the SWA is the high complexity resulting from the computation of the inverse matrix. A low complexity SWA based on dichotomous coordinate descent algorithm is proposed in the paper, whose computation complexity is on the same order of magnitude as the CMA. Besides the low complexity, the proposed algorithm also avoids the possible numerical error resulting from the computation of the matrix inversion. Moreover, a low complexity of decision directed algorithm based on RLS is presented for a dual mode blind equalization. Simulations verify the effectiveness of the algorithm.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shalvi, O., & Weinstein, E. (1990). New criteria for blind deconvolution of nonminimum phase systems(channels). IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 42, 1145–1156.
Ahmed, S., Khan, Y., & Wahab, A. (2019). A review on training and blind equalization algorithms for wireless communications. Wireless Personal Communications, 108, 1759–1783.
Johnson, R., Jr., Schniter, P., et al. (1998). Blind equalization using the constant modulus criterion: A review. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(10), 1927–1950.
Miranda, M. D., Silva, M., & Nascimento, V. H. (2008). Avoiding divergence in the Shalvi-Weinstein algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(11), 5403–5413.
Pavan, F. R. M., Silva, M. T. M., & Maria, D. (2019). Miranda, performance analysis of the multiuser Shalvi-Weinstein algorithm. Signal Processing, 163, 153–165.
Abrar, S., & Nandi, A. K. (2010). Blind equalization of square-QAM signals: A multimodulus approach. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 58(6), 1674–1685.
Filho, J. M., Miranda, M. D., et al. (2012). A regional multimodulus algorithm for blind equalizationof QAM signals: Introduction and steady-state analysis. Signal Processing, 92, 2643–2656.
Zakharov, Y. V., & Tozer, T. C. (2004). Multiplication-free iterative algorithm for LS problem. Electronics Letters, 40(9), 567–569.
Zakharov, Y. V., White, G. P., & Liu, J. (2008). Low-complexity RLS algorithms using dichotomous coordinate descent iterations. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 56(7), 3150–3161.
Liu, J., Zakharov, Y. V., & Weaver, B. (2009). Architecture and FPGA design of dichotomous coordinate descent algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 56(11), 2425–2438.
Chen, T., & Wang, S. (2020). An efficient nonlinear dichotomous coordinate descent adaptive algorithm based on random Fourier features. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 27, 1804–1808.
Silva, M., & Arenas-Garcia, J. (2013). A soft-switching blind equalization scheme via convex combination of adaptive filters. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 61(5), 1171–1182.
Jianqiu, S., **ngguang, L., Kang, C., Wei, C., & Ming, C. (2020). A novel CMA+DD_LMS blind equalization algorithm for underwater acoustic communication. The Computer Journal, 63(6), 974–981.
Azim, A. W., Abrar, S., et al. (2015). Steady-state performance of multimodulus blind equalizers. Signal Processing, 108, 509–520.
Simon, H. (2013). Adaptive filter theory (5th ed.). Pearson Publisher.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Substituting the above equation into the following equation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Zhang, L., Jia, C. et al. Low Complexity Shalvi-Weinstein Algorithm. Wireless Pers Commun 120, 3265–3275 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08612-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08612-y