Abstract
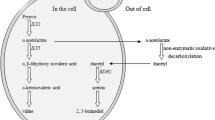
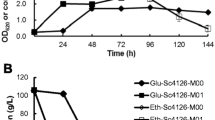
Mezcal is a traditional Mexican distilled beverage, known for its marked organoleptic profile, which is influenced by several factors, such as the fermentation process, where a wide variety of microorganisms are present. Kluyveromyces marxianus is one of the main yeasts isolated from mezcal fermentations and has been associated with ester synthesis, contributing to the flavors and aromas of the beverage. In this study, we employed CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) technology, using dCas9 fused to the Mxi1 repressor factor domain, to down-regulate the expression of the IAH1 gene, encoding for an isoamyl acetate-hydrolyzing esterase, in K. marxianus strain DU3. The constructed CRISPRi plasmid successfully targeted the IAH1 gene, allowing for specific gene expression modulation. Through gene expression analysis, we assessed the impact of IAH1 down-regulation on the metabolic profile of volatile compounds. We also measured the expression of other genes involved in volatile compound biosynthesis, including ATF1, EAT1, ADH1, and ZWF1 by RT-qPCR. Results demonstrated successful down-regulation of IAH1 expression in K. marxianus strain DU3 using the CRISPRi system. The modulation of IAH1 gene expression resulted in alterations in the production of volatile compounds, specifically ethyl acetate, which are important contributors to the beverage's aroma. Changes in the expression levels of other genes involved in ester biosynthesis, suggesting that the knockdown of IAH1 may generate intracellular alterations in the balance of these metabolites, triggering a regulatory response. The application of CRISPRi technology in K. marxianus opens the possibility of targeted modulation of gene expression, metabolic engineering strategies, and synthetic biology in this yeast strain.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The complete KmDU3 genome sequence has been deposited in the National Center of Biotechnology Information (NCBI) database with the accession number JAQIJY000000000. The raw reads obtained from the Oxford Nanopore Sequence and Illumina Sequences used to assemble the KmDU3 genome were deposited in the NCBI—Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under the BioProject ID PRJNA909832. RNA-Seq data supporting the genomic annotation of KmDU3 are not openly available for reasons of sensitivity of another publication and can be requested from the corresponding author.
References
Alcazar-Valle M, Gschaedler A, Gutierrez-Pulido H, Arana-Sanchez A, Arellano-Plaza M (2019) Fermentative capabilities of native yeast strains grown on juices from different Agave species used for tequila and mezcal production. Braz J Microbiol 50:379–388. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42770-019-00049-7
Alonge M, Lebeigle L, Kirsche M et al (2022) Automated assembly scaffolding using RagTag elevates a new tomato system for high-throughput genome editing. Genome Biol 23:258
Amaya-Delgado L, Herrera-López EJ, Arrizon J, Arellano-Plaza M, Gschaedler A (2013) Performance evaluation of Pichia kluyveri, Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in industrial tequila fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29(5):875–881
Andrews S. (2010). FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data [Online]. http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
Arellano-Plaza M, Noriega-Cisneros R, Clemente-Guerrero M, González-Hernández JC, Robles-Herrera PD, Manzo-Ávalos S, Saavedra-Molina A, Gschaedler-Mathis A (2017) Fermentative capacity of Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae after oxidative stress. J Inst Brew 123:519–526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1291-7
Azambuja SPH, Goldbeck R (2020) Butanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: perspectives, strategies and challenges. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36(3):48
Bilal M, Ji L, Xu Y, Xu S, Lin Y, Iqbal HMN, Cheng H (2022) Bioprospecting Kluyveromyces marxianus as a Robust Host for Industrial Biotechnology. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:851768. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.851768
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Burini JA, Eizaguirre JI, Loviso C, Libkind D (2021) Levaduras no convencionales como herramientas de innovación y diferenciación en la producción de cerveza. Rev Argent Microbiol 53:359–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ram.2021.01.003
Cebollero E, Gonzalez-Ramos D, Tabera L, Gonzalez R (2007) Transgenic wine yeast technology comes of age: is it time for transgenic wine? Biotech Lett 29(2):191–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9236-y
Cernak P, Estrela R, Poddar S, Skerker JM (2018) Engineering Kluyveromyces marxianus as a robust synthetic biology platform host. Mbio 9(5):e01410-e1418. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01410-18
Chomczynski P (1993) A reagent for the single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from cell and tissue samples. Biotechniques 15:532–537
Cordente AG, Curtin CD, Varela C, Pretorius IS (2012) Flavour active wine yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96(3):601–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4370-z
Dank A, Smid EJ, Notebaart RA (2018) CRISPR-Cas genome engineering of esterase activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae steers aroma formation. BMC Res Notes 11(1):4–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-018-3788-5
De Coster W, D’Hert S, Schultz DT, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C (2018) NanoPack: visualizing and processing long-read sequencing data. Bioinformatics (oxford, England) 34(15):2666–2669. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty149
De León-Rodríguez A, González-Hernández L, Barba de la Rosa AP, Escalante-Minakata P, López GM (2006) Characterization of volatile compounds of Mezcal, and ethnic alcoholic beverage obtained from Agave salmiana. J Agric Food Chem 54:1337–1341. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf052154+
De León-Rodríguez A, Escalante-Minakata P, Barba-De la Rosa AP, Blaschek HP (2008) Optimization of fermentation conditions for the production of the mezcal from Agave salmiana using response surface methodology. Chem Eng Process 47:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2007.08.010
De la Torre-González FJ, Narváez-Zapata JA, Larralde-Corona CP (2017) Microbial diversity and flavor quality of fermented beverages. In: Holban AM, Grumezescu AM (eds) Handbook of food bioengineering, microbial production of food ingredients and additives. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 125–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-811520-6.00005-2
Depardieu F, Bikard D (2020) Gene silencing with CRISPRi in bacteria and optimization of dCas9 expression levels. Methods 172:61–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.07.024
Duarte WF, Amorim JC, Schwan RF (2013) The effects of co-culturing non-Saccharomyces yeasts with S cerevisiae on the sugar cane spirit (cachaça) fermentation process. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 103(1):175–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9798-8
Escalante-Minakata P, Blaschek HP, Barba de la Rosa AP, Santos L, De León-Rodríguez A (2008) Identification of yeast and bacteria involved in the mezcal fermentation of Agave salmiana. Lett Appl Microbiol 46(6):626–630. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2008.02359.x
Flores JA, Gschaedler A, Amaya-Delgado L, Herrera-López EJ, Arellano M, Arrizon J (2013) Simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of Agave tequilana fructans by Kluyveromyces marxianus yeasts for bioethanol and tequila production. Bioresour Technol 146:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.078
Flores-Cosio G, Arellano-Plaza M, Gschaedler A, Amaya-Delgado L (2018) Physiological response to furan derivates stress by Kluyveromyces marxianus SLP1 in ethanol production. Rev Mex Ing Quim 17:189–202. https://doi.org/10.24275/uam/izt/dcbi/revmexingquim/2018v17n1/Flores
Fonseca GG, Gombert AK, Heinzle E, Wittmann C (2007) Physiology of the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus during batch and chemostat cultures with glucose as the sole carbon source. FEMS Yeast Res 7(3):422–435. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1567-1364.2006.00192.x
Fukuda K, Yamamoto N, Kiyokawa Y, Yanagiuchi T, Wakai Y, Kitamoto K et al (1998a) Brewing properties of sake yeast whose EST2 gene encoding isoamyl acetate-hydrolyzing esterase was disrupted. J Ferment Bioeng 85(1):101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0922-338X(97)80362-5
Fukuda K, Yamamoto N, Kiyokawa Y, Yanagiuchi T, Wakai Y, Kitamoto K, Inoue Y, Kimura A (1998b) Balance of activities of alcohol acetyltransferase and esterase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is important for production of isoamyl acetate. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4076–4078. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.64.10.4076-4078.1998
Gethins L, Guneser O, Demirkol A, Rea MC, Stanton C, Ross RP et al (2014) Influence of carbon and nitrogen source on production of volatile fragrance and flavour metabolites by the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Yeast 32(1):67–76. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3047
Gibson DG, Young L, Chuang R-Y, Venter JG, Hutchinson CA III, Smith H (2009) Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat Methods 6(5):343–347. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1318
Gombert AK, Madeira JV Jr, Cerdán ME, González-Siso MI (2016) Kluyveromyces marxianus as a host for heterologous protein synthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(14):6193–6208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7645-y
Heinisch JJ, Knuesting J, Scheibe R (2020) Investigation of heterologously expressed glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase genes in a yeast zwf1 deletion. Microorganisms 8(4):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040546
Huerta-Cepas J, Forslund K, Coelho LP, Szklarczyk D, Jensen LJ, von Mering C, Bork P (2017) Fast genome-wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Mol Biol Evol 34(8):2115–2122. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx148
Jensen MK (2018) Design principles for nuclease-deficient CRISPR-based transcriptional regulators. FEMS Yeast Res 18(4):foy039. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/foy039
Jones P, Binns D, Chang HY, Fraser M, Li W, McAnulla C, McWilliam H, Maslen J, Mitchell A, Nuka G, Pesseat S, Quinn AF, Sangrador-Vegas A, Scheremetjew M, Yong SY, Lopez R, Hunter S (2014) InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics (oxford, England) 30(9):1236–1240. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu031
Kallel-Mhiri H, Miclo A (1993) Mechanism of ethyl acetate synthesis by Kluyveromyces fragilis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 111(2–3):207–212
Karim A, Gerliani N, Aïder M (2020) Kluyveromyces marxianus: An emerging yeast cell factory for applications in food and biotechnology. Int J Food Microbiol 333:108818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108818
Kirchmayr MR, Segura-García LE, Lappe-Oliveras P et al (2017) Impact of environmental conditions and process modifications on microbial diversity, fermentation efficiency and chemical profile during the fermentation of mezcal in Oaxaca. Food Sci Technol 79:160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.12.052
Kolmogorov M, Yuan J, Lin Y, Pevzner PA (2019) Assembly of long, error-prone reads using repeat graphs. Nat Biotechnol 37:540–546. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0072-8
Kruis AJ, Levisson M, Mars AE, van der Ploeg M, Garcés Daza F, Ellena V, Kengen SWM, van der Oost J, Weusthuis RA (2017) Ethyl acetate production by the elusive alcohol acetyltransferase from yeast. Metab Eng 41:92–101
Lahue C, Madden AA, Dunn RR, Smukowski HC (2020) History and Domestication of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in Bread Baking. Front Genet 11:584718. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.584718
Lane MM, Burke N, Karreman R, Wolfe KH, O’Byrne CP, Morrissey JP (2011) Physiological and metabolic diversity in the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100(4):507–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9606-x
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9(4):357–359. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1923
Lappe-Oliveras P, Moreno-Terrazas R, Arrizón-Gaviño J, Herrera-Suárez T, García-Mendoza A, Gschaedler-Mathis A (2008) Yeasts associated with the production of Mexican alcoholic nondistilled and distilled Agave beverages. FEMS Yeast Res 8:1037–1052. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1567-1364.2008.00430.x
Lee K-S, Kim J-S, Heo P, Yang T-J, Sung Y-J, Cheon Y, Koo HM, Yu BJ, Seo J-H, ** Y-S, Park JC, Kweon D-H (2013) Characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoters for heterologous gene expression in Kluyveromyces marxianus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:2029–2041. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4306-7
Lertwattanasakul N, Kosaka T, Hosoyama A, Suzuki Y, Rodrussamee N, Matsutani M, Murata M, Fujimoto N, Suprayogi TK, Limtong S, Fujita N, Yamada M (2015) Genetic basis of the highly efficient yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus: complete genome sequence and transcriptome analyses. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:47. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-015-0227-x
LEY DE BIOSEGURIDAD DE ORGANISMOS GENÉTICAMENTE MODIFICADOS (LBOGM). (2005). Available: https://www.gob.mx/profepa/documentos/ley-de-bioseguridad-de-organismos-geneticamente-modificados.
Li H (2018) Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics (oxford, England) 34(18):3094–3100. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty191
Li M, Lang X, Moran Cabrera M, De Keyser S, Sun X, Da Silva N, Wheeldon I (2021) CRISPR-mediated multigene integration enables Shikimate pathway refactoring for enhanced 2-phenylethanol biosynthesis in Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biotechnol Biofuels 14(1):3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-020-01852-3
Lilly M, Bauer FF, Lambrechts MG, Swiegers JH, Coz-zolino D, Pretorius IS (2006) The effect of increased yeast alcohol acetyltransferase and esterase activity on the flavour profiles of wine and distillates. Yeast 23(9):641–659. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1382
Liu N, Qin L, Hu L, Miao S (2023) Formation mechanisms of ethyl acetate and organic acids in Kluyveromyces marxianus L1–1 in Chinese acid rice soup. Food Sci Human Wellness 12(1):45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2022.07.017
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T) (-Delta DeltaC) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Löbs A-K, Engel R, Schwartz C, Flores A, Wheeldon I (2017) CRISPR-Cas9-enabled genetic disruptions for understanding ethanol and ethyl acetate biosynthesis in Kluyveromyces marxianus. Biotechnol Biofuels 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-0854-5
Löbs AK, Schwartz C, Thorwall S, Wheeldon I (2018) Highly multiplexed CRISPRi repression of respiratory functions enhances mitochondrial localized ethyl acetate biosynthesis in Kluyveromyces marxianus. ACS Synth Biol 7(11):2647–2655. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.8b00331
Lopez CL, Beaufort S, Brandam C, Taillandier P (2014) Interactions between Kluyveromyces marxianus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae in tequila must type medium fermentation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30(8):2223–2229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-014-1643-y
Lopez-Alvarez A, Diaz-Perez AL, Sosa-Aguirre C, Macias-Rodriguez L, Campos-Garcia J (2012) Ethanol yield and volatile compound content in fermentation of agave must by Kluyveromyces marxianus UMPe-1 comparing with Saccharomyces cerevisiae baker’s yeast used in tequila production. J Biosci Bioeng 113(5):614–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.12.015
Lorenz R, Bernhart SH, Siederdissen CH, Tafer H, Flamm C, Stadler PP, Hofacker IL (2011) ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol Biol 6:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-7188-6-26
Löser C, Urit T, Bley T (2014) Perspectives for the biotechnological production of ethyl acetate by yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:5397–5415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5765-9
Löser C, Urit T, Keil P, Bley T (2015) Studies on the mechanism of synthesis of ethyl acetate in Kluyveromyces marxianus DSM 5422. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(3):1131–1144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6098-4
Ma Y, Deng Q, Du Y, Ren J, Chen Y, Liu X, Guo X, **ao D (2020) Biosynthetic pathway for ethyl butyrate production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Agric Food Chem 68(14):4252–4260
Mannaa M, Han G, Seo YS, Park I (2021) Evolution of food fermentation processes and the use of multi-omics in deciphering the roles of the microbiota. Foods 10(11):2861. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10112861
Martell-Nevárez MA, Córdova-Gurrola EE, López-Miranda J, Soto-Cruz NO, López-Perez MG, Rutiaga-Quiñones OM (2011) Effect of fermentation temperature on chemical composition of mescals made from Agave duranguensis juice with different native yeast genera. African J Microbiol Res 5:3669–3676. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR11.467
McMillan J, Lu Z, Rodriguez JS, Ahn TH, Lin Z (2019) YeasTSS: an integrative web database of yeast transcription start sites. Database (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/database/baz048
McMillan D (2019) Optimizing a transformation protocol for Kluyveromyces marxianus. The California Digital Library. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/3p5717k9.
Medaka: Sequence correction provided by ONT Research. https://github.com/nanoporetech/medaka. Accessed 22 Nov 2023
Méndez-Zamora A, Gutiérrez-Avendaño DO, Arellano-Plaza M, De la Torre González FJ, Barrera-Martínez I, Gschaedler Mathis A, Casas-Godoy L (2021) The non-Saccharomyces yeast Pichia kluyveri for the production of aromatic volatile compounds in alcoholic fermentation. FEMS Yeast Res 20(8):067. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/foaa067
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Mitri S, Koubaa M, Maroun RG, Rossignol T, Nicaud JM, Louka N (2022) Bioproduction of 2-phenylethanol through yeast fermentation on synthetic media and on agro-industrial waste and by-products: a review. Foods (basel, Switzerland) 11(1):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11010109
Morrissey JP, Etschmann MMW, Schrader J, de Billerbeck GM (2015) Cell factory applications of the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus for the biotechnological production of natural flavour and fragrance molecules. Yeast 32(1):3–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3054
Naito Y, Hino K, Bono H, Ui-Tei K (2015) CRISPRdirect: software for designing CRISPR/Cas guide RNA with reduced off-target sites. Bioinformatics 31:1120–1123. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu743
Nambu-Nishida Y, Nishida K, Hasunuma T, Kondo A (2018) Genetic and physiological basis for antibody production by Kluyveromyces marxianus. AMB Express 8(1):56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-018-0588-1
Nolasco-Cancino H, Santiago-Urbina JA, Wacher C, Ruíz-Terán F (2018) Predominant yeasts during artisanal mezcal fermentation and their capacity to ferment maguey juice. Front Microbiol 9:2900. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02900
Nonklang S, Babiker MA, Abdel-Banat BM, Cha-aim K, Nareerat M, Hoshida H, Limtong S, Yamada M, Akada R (2008) High-Temperature ethanol and transformation with linear DNA in thermotolerant yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus DMKU3-1042. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(24):7514–7521. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01854-08
Notebaart RA, Szappanos B, Kintses B, Pál F, Györkei Á, Bogos B, Lázár V, Spohn R, Csörgő B, Wagner A, Ruppin E, Pál C, Papp B (2014) Network-level architecture and the evolutionary potential of underground metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(32):11762–11767
Nuñez-Guerrero ME, Páez-Lerma JB, Rutiaga-Quiñones OM, González-Herrera SM, Soto-Cruz NO (2016) Performance of mixtures of Saccharomyces and non-Saccharomyces native yeasts during alcoholic fermentation of Agave duranguensis juice. Food Microbiol 54:72–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fm.2015.10.011
Palmer JM, Stajich JE (2022) Funannotate (Version 1.8.13) [Computer software]. https://github.com/nextgenusfs/funannotate.
Prado-Jaramillo N, Estarrón-Espinosa M, Escalona-Buendía H, Cosío-Ramírez R, Martín-del-Campo ST (2015) Volatile compounds generation during different stages of the Tequila production process. a preliminary study. LWT Food Sci Technol 61:471–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.11.042
Pretorius IS, Boeke JD (2018) Yeast 2.0-connecting the dots in the construction of the world’s first functional synthetic eukaryotic genome. FEMS Yeast Res 18(4):032. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsyr/foy032
R Core Team (2017) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. https://www.R-project.org/.
Rossouw D, Naes T, Bauer FF (2008) Linking gene regulation and the exo-metabolome: a comparative transcriptomics approach to identify genes that impact on the production of volatile aroma compounds in yeast. BMC Genomics 9:530. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-530
Saerens SM, Verstrepen KJ, Van Laere SD, Voet AR, Van Dijck P, Delvaux FR (2006) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae EHT1 and EEB1 genes encode novel enzymes with medium-chain fatty acid ethyl ester synthesis and hydrolysis capacity. J Biol Chem 281(7):4446–4456. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M512028200
Saerens SMG, Delvaux F, Verstrepen KJ, Van Dijck P, Thevelein JM, Delvaux FR (2008) Parameters affecting ethyl ester production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae during fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(2):454–461. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01616-07
Saerens SMG, Delvaux FR, Verstrepen KJ, Thevelein JM (2010) Production and biological function of volatile esters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Biotechnol 3(2):165–177. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-7915.2009.00106.x
Segura-García LE, Taillandier P, Brandam C, Gschaedler A (2015) Fermentative capacity of Saccharomyces and non-Saccharomyces in agave juice and semi-synthetic medium. LWT Food Sci Technol 60:284–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2014.08.005
Shi S, Si T, Liu Z, Zhang H, Ang EL, Zhao H (2016) Metabolic engineering of a synergistic pathway for n-butanol production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Sci Rep 6:25675. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25675
Sievers F, Higgins DG (2014) Clustal Omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. Methods Mol Biol 1079:105–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-646-7_6
Smith JD, Suresh S, Schlecht U, Wu M, Wagih O, Peltz G, Davis RW, Steinmetz LM, Parts L, St Onge RP (2016) Quantitative CRISPR interference screens in yeast identify chemical-genetic interactions and new rules for guide RNA design. Genome Biol 17:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-0900-9
Stewart GG (2017) The production of secondary metabolites with flavour potential during brewing and distilling wort fermentations. Fermentation 3(4):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation3040063
Swiegers JH, Pretorius IS (2005) Yeast modulation of wine flavor. Adv Appl Microbiol 57:131–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2164(05)57005-9
van Rijswijck IMH, Kruis AJ, Wolkers-Rooijackers JCM, Abee T, Smid EJ (2019) Acetate-ester hydrolase activity for screening of the variation in acetate ester yield of Cyberlindnera fabianii, Pichia kudriavzevii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. LWT 104:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.01.019
Varela C (2016) The impact of non-Saccharomyces yeasts in the production of alcoholic beverages. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(23):9861–9874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7941-6
Varela C, Kutyna DR, Solomon MR, Black CA, Borneman A, Henschke PA, Pretorius IS, Chambers PJ (2012) Evaluation of gene modification strategies for the development of low-alcohol-wine yeasts. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(17):6068–6077
Vaser R, Sović I, Nagarajan N, Šikić M (2017) Fast and accurate de novo genome assembly from long uncorrected reads. Genome Res 27(5):737–746. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.214270.116
Vera-Guzmán AM, Santiago-García PA, López MG (2009) Compuestos Volátiles Aromáticos Generados durante la Elaboración de Mezcal de Agave angustifolia y Agave potatorum. Rev Fitotec Mex 32:273–279. https://doi.org/10.35196/rfm.2009.4.273-279
Vera-Guzmán AM, López MG, Chávez-Servia JL (2012) Chemical composition and volatile compounds in the artisanal fermentation of mezcal in Oaxaca. Mexico Afr J Biotechnol 11:14344–14353. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.1963
Vera-Guzmán AM, Guzmán-Gerónimo RI, López MG, Chávez-Servia JL (2018) Volatile compound profiles in mezcal spirits as influenced by Agave species and production processes. Beverages 4(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages4010009
Verdugo Valdez A, Segura Garcia L, Kirchmayr M, Ramírez Rodríguez P, González Esquinca A, Coria R, Gschaedler A (2011) Yeast communities associated with artisanal mezcal fermentations from Agave salmiana. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100(4):497–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9605-y
Vickers CE, Bydder SF, Zhou Y, Nielsen LK (2013) Dual gene expression cassete vectors with antibiotic selection markers for engineering in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 12(96):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-12-96
Vidal EE, de Billerbeck GM, Simões DA, Schuler A, François JM, de Morais MA (2013) Influence of nitrogen supply on the production of higher alcohols/esters and expression of flavour-related genes in cachaça fermentation. Food Chem 138(1):701–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.10.147
Vigentini I, Gonzalez R, Tronchoni J (2019) Genetic improvement of wine yeasts. In: Romano P, Ciani M, Fleet G (eds) Yeasts in the Production of Wine. Springer, New York, pp 315–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-9782-4_10
Walker ME, Gardner JM, Vystavelova A, McBryde C, de Barros LM, Jiranek V (2003) Application of the reuseable, KanMX selectable marker to industrial yeast: construction and evaluation of heterothallic wine strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, possessing minimal foreign DNA sequences. FEMS Yeast Res 4(3):339–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1567-1356(03)00161-2
Walker BJ, Abeel T, Shea T, Priest M, Abouelliel A, Sakthikumar S, Cuomo CA, Zeng Q, Wortman J, Young SK, Earl AM (2014) Pilon: an integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 9(11):e112963. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112963
Wensing L, Sharma J, Uthayakumar D, Proteau Y, Chavez A, Shapiro RS (2019) A CRISPR Interference Platform for Efficient Genetic Repression in Candida albicans. mSphere 4(1):e00002-19. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSphere.00002-19
Wick RR (2017) Filtlong. https://github.com/rrwick/Filtlong.
Wickham H (2016) ggplot2: elegant graphics for data analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York
Yu A, Zhao Y, Pang Y, Hu Z, Zhang C, **ao D, Chang MW, Leong SSJ (2018) An oleaginous yeast platform for renewable 1-butanol synthesis based on a heterologous CoA-dependent pathway and an endogenous pathway. Microb Cell Fact 17(1):166. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-1014-8
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Cesar Arturo Nava Valdivia and M. en C. Martin Zermeño Ruíz (Centro Universitario de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad de Guadalajara) for the space and technical assistance during the RT-qPCR experiments
Funding
The present work was financed by the CONAHCYT Basic Science fund with project number 252465, with the title "Study of ester production by non-Saccharomyces yeasts with a multidisciplinary approach".
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: [LJFY], Methodology: [LAMM, ACZP, ACGM, AMZ, APS, LCG, ICBM], Formal analysis [APS, LAMM, AMZ, LJFY], Data curation [APS, LAMM], Investigation: [LAMM, ACZP, ACGM, AMZ], Funding acquisition: [ACGM], Resources: [ACGM, LJFY, LCG, ICBM, LAMM, APS], Supervision: [ACGM, LJFY], Software [APS, LAMM], Validation [LAMM, LJFY], Visualization [LAMM], Project administration [LJFY, ACGM], Writing—original draft preparation: [LAMM], Writing—review and editing: [LAMM, ACZP, ACGM, AMZ, APS, LCG, ICBM, LCRZ].
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Muñoz-Miranda, L.A., Zepeda-Peña, A.C., Casas-Godoy, L. et al. CRISPRi-induced transcriptional regulation of IAH1 gene and its influence on volatile compounds profile in Kluyveromyces marxianus DU3. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 121 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03811-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-023-03811-0