Abstract
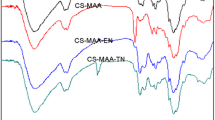
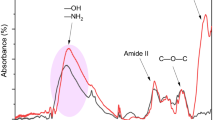
Ecotoxicity of diclofenac sodium (DS) even at low concentrations makes it urgent to remove DS from water. In this work, chitosan microspheres were prepared by one-step reversed-phase emulsion method, and then, polyethyleneimine (PEI) was successfully grafted to form CS/PEI composites. The CS/PEI was characterized by Fourier infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Effects of different influencing factors like material composition, dosage, pH, co-existing anions, and humic acid were investigated, and adsorption behavior of CS/PEI was explored by model simulation analysis. Results showed that adsorption process fits well with pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir adsorption isotherm model, indicating homogeneous and monolayer adsorption nature, and maximum Langmuir adsorption capacity was 364.12 mg/g at pH 6. The reusability of CS/PEI was confirmed by cyclic adsorption-desorption experiments, and electrostatic attraction and hydrogen bonding were the main mechanism for DS uptake by CS/PEI. Therefore, CS/PEI microspheres can be regarded as an efficient and convenient adsorbent for DS removal from aqueous media.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the results of this study are included in the paper.
References
Ahmad, Z., Li, Y., Huang, C., Gou, X., Fan, Y. & Chen, J. (2021). Underwater suspended bifunctionalized polyethyleneimine-based sponge for selective removal of anionic pollutants from aqueous solution. Journal of Hazardous Materials 412, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125284.
Araújo, C. S. T., Almeida, I. L. S., Rezende, H. C., Marcionilio, S., Léon, J. J. L., & de Matos, T. N. (2018). Elucidation of mechanism involved in adsorption of Pb(II) onto lobeira fruit (Solanum lycocarpum) using Langmuir. Freundlich and Temkin isotherms. Microchemical Journal, 137, 348–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2017.11.009
Azzaoui, K., Mejdoubi, E., Lamhamdi, A., Zaoui, S., Berrabah, M., Elidrissi, A., Hammouti, B., Fouda, M. M. G., & Al-Deyab, S. S. (2015). Structure and properties of hydroxyapatite/hydroxyethyl cellulose acetate composite films. Carbohydrate Polymers, 115, 170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.08.089
Brunel, F., Véron, L., Ladavière, C., David, L., Domard, A., & Delair, T. (2009). Synthesis and structural characterization of chitosan nanogels. Langmuir, 25, 8935–8943. https://doi.org/10.1021/la9002753
Cleuvers, M. (2004). Mixture toxicity of the anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen, and acetylsalicylic acid. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 59, 309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0147-6513(03)00141-6
dos Santos, J. M. N., Pereira, C. R., Foletto, E. L., & Dotto, G. L. (2019). Alternative synthesis for ZnFe2O4/chitosan magnetic particles to remove diclofenac from water by adsorption. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 131, 301–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.079
Eris, S., & Bashiri, H. (2016). Kinetic study of the adsorption of dyes onto activated carbon. Progress in Reaction Kinetics and Mechanism, 41, 109–119. https://doi.org/10.3184/146867816x14570175656394
Fan, H., Li, J., Zhang, L., & Feng, L. (2014). Contribution of sludge adsorption and biodegradation to the removal of five pharmaceuticals in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 88, 101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.04.008
Fan, L., Lu, Y., Yang, L-Y., Huang, F., Ouyang, X-K. (2019). Fabrication of polyethylenimine-functionalized sodium alginate/cellulose nanocrystal/polyvinyl alcohol core–shell microspheres ((PVA/SA/CNC)@PEI) for diclofenac sodium adsorption. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 554, 48-58,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.06.099
Fu, C.-C., Tran, H. N., Chen, X.-H., & Juang, R.-S. (2020). Preparation of polyaminated Fe3O4@chitosan core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for efficient adsorption of phosphate in aqueous solutions. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 83, 235–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.11.033
Funes, A., de Vicente, J., & de Vicente, I. (2017). Synthesis and characterization of magnetic chitosan microspheres as low-density and low-biotoxicity adsorbents for lake restoration. Chemosphere, 171, 571–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.101
Gao, P., Chen, D., Chen, W., Sun, J., Wang, G., & Zhou, L. (2021). Facile synthesis of amine-crosslinked starch as an efficient biosorbent for adsorptive removal of anionic organic pollutants from water. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 191, 1240–1248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.206
Ghiorghita, C.A., Bucatariu, F., Dragan, E.S. (2016). Sorption/release of diclofenac sodium in/from free‐standing poly(acrylic acid)/poly(ethyleneimine) multilayer films. Journal of Applied Polymer Science 133, https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43752.
Godiya, C.B., Kumar, S., **ao, Y. (2020). Amine functionalized egg albumin hydrogel with enhanced adsorption potential for diclofenac sodium in water. Journal of Hazardous Materials 393, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122417.
Gu, G., Yin, H., Zhu, Q., Shen, L., Zhang, K., Liu, M., & Wu, Q. (2018). Recognition of the prioritized types and individual of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in the drinking water of Shanghai and a health risk assessment. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, 25, 1207–1221. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1461009
Guo, H., Jiao, T., Zhang, Q., Guo, W., Peng, Q. & Yan, X. (2015). Preparation of graphene oxide-based hydrogels as efficient dye adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Nanoscale Research Letters 10, https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-015-0931-2.
Han, S., Zhou, X., **e, H., Wang, X., Yang, L., Wang, H. & Hao, C. (2022). Chitosan-based composite microspheres for treatment of hexavalent chromium and EBBR from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 305, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135486.
He, X., Zhang, T., Xue, Q., Zhou, Y., Wang, H., Bolan, N. S., Jiang, R. & Tsang, D. C. W. (2021). Enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Zn(II) from aqueous solution by polyethyleneimine modified straw hydrochar. Science of The Total Environment 778, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146116.
Hu, D., huang, H., Jiang, R., Wang, N., Xu, H., Wang, Y.-G. & Ouyang, X.-K. (2019). Adsorption of diclofenac sodium on bilayer amino-functionalized cellulose nanocrystals/chitosan composite. Journal of Hazardous Materials 369, 483-493,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.057
Jiang, X., An, Q.-D., **ao, Z.-Y., Zhai, S.-R., & Shi, Z. (2018). Mussel-inspired surface modification of untreated wasted husks with stable polydopamine/polyethylenimine for efficient continuous Cr(VI) removal. Materials Research Bulletin, 102, 218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2018.02.037
Jiang, X., Ding, W., Li, H., Zhang, Z., Zhong, Z., Liu, H. & Zheng, H. (2022) Facile synthesis of Poly(epichlorohydrin-diethylenetriamine) hydrogel for highly selective diclofenac sodium removal. Separation and Purification Technology 283, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120215.
Jiménez-Salcedo, M., Monge, M. Tena, M.T. (2021) The photocatalytic degradation of sodium diclofenac in different water matrices using g-C3N4 nanosheets: A study of the intermediate by-products and mechanism. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 9, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105827.
Kamaliya, B. P., Dave, P. N., & Chopda, L. V. (2023). Synthesis of GG-g-P(NIPAM-co-AA)/GO and evaluation of adsorption activity for the diclofenac and metformin. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 21, 403–416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-023-00867-w
Khawar, A., Aslam, Z., Javed, S., & Abbas, A. (2018). Pb(II) biosorption using DAP/EDTA-modified biopolymer (Chitosan). Chemical Engineering Communications, 205, 1555–1567. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2018.1460598
Khawar, A., Aslam, Z., Zahir, A., Akbar, I., & Abbas, A. (2019). Synthesis of Femur extracted hydroxyapatite reinforced nanocomposite and its application for Pb(II) ions abatement from aqueous phase. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 122, 667–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.223
Li, J., & Werth, C. J. (2009). Modeling sorption isotherms of volatile organic chemical mixtures in model and natural solids. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 21, 1377–1383. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620210707
Li, Y., Dong, X., & Zhao, L. (2021). Application of magnetic chitosan nanocomposites modified by graphene oxide and polyethyleneimine for removal of toxic heavy metals and dyes from water. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 192, 118–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.202
Liu, T., Aniagor, C.O., Ejimofor, M.I., Menkiti, M.C., Tang, K.H.D., Chin, B.L.F., Chan, Y.H., Yiin, C.L., Cheah, K.W., Ho Chai, Y., Lock, S.S.M., Yap, K.L., Wee, M.X.J., Yap, P.-S. (2023). Technologies for removing pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) from aqueous solutions: Recent advances, performances, challenges and recommendations for improvements. Journal of Molecular Liquids 374, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2022.121144.
Lu, M., Guan, X.-H., Xu, X.-H., & Wei, D.-Z. (2013). Characteristic and mechanism of Cr(VI) adsorption by ammonium sulfamate-bacterial cellulose in aqueous solutions. Chinese Chemical Letters, 24, 253–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2013.01.034
Lu, X., Shao, Y., Gao, N., Chen, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, Q., & Lu, Y. (2016). Adsorption and removal of clofibric acid and diclofenac from water with MIEX resin. Chemosphere, 161, 400–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.07.025
Lu, Y., Fan, L., Yang, L.-Y., Huang, F., Ouyang, X.-K. (2020a). PEI-modified core-shell/bead-like amino silica enhanced poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan for diclofenac sodium efficient adsorption. Carbohydrate Polymers 229, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115459.
Lu, Y., Wang, Z., Ouyang, X.-K., Ji, C., Liu, Y., Huang, F., & Yang, L.-Y. (2020b). Fabrication of cross-linked chitosan beads grafted by polyethylenimine for efficient adsorption of diclofenac sodium from water. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 145, 1180–1188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.044
Mao, N., Huang, L., & Shuai, Q. (2019). Facile synthesis of porous carbon for the removal of diclofenac sodium from water. ACS Omega, 4, 15051–15060. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b01838
Nguyen, L. N., Nghiem, L. D., Pramanik, B. K., & Oh, S. (2019). Cometabolic biotransformation and impacts of the anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac on activated sludge microbial communities. Science of The Total Environment, 657, 739–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.094
Oaks, J. L., Gilbert, M., Virani, M. Z., Watson, R. T., Meteyer, C. U., Rideout, B. A., Shivaprasad, H. L., Ahmed, S., Chaudhry, M. J. I., Arshad, M., Mahmood, S., Ali, A., & Khan, A. A. (2004). Diclofenac residues as the cause of vulture population decline in Pakistan. Nature, 427, 630–633. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02317
Peng, Z.e., Wu, F., Deng, N. (2006). Photodegradation of bisphenol A in simulated lake water containing algae, humic acid and ferric ions. Environmental Pollution 144, 840-846.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.02.006
Shao, H., Zhao, X., Wang, Y., Mao, R., Wang, Y., Qiao, M., Zhao, S., & Zhu, Y. (2017). Synergetic activation of peroxymonosulfate by Co3O4 modified g-C3N4 for enhanced degradation of diclofenac sodium under visible light irradiation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 218, 810–818. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.07.016
Sharma, S., Setia, H., Toor, A.P. (2021). Assessing the bioremediation potential of indigenously isolated Klebsiella sp. WAH1 for diclofenac sodium: optimization, toxicity and metabolic pathway studies. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 37, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-021-02998-4.
Sim, W.-J., Lee, J.-W., Lee, E.-S., Shin, S.-K., Hwang, S.-R., & Oh, J.-E. (2011). Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater from households, livestock farms, hospitals and pharmaceutical manufactures. Chemosphere, 82, 179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.10.026
Soares, S. F., Fernandes, T., Sacramento, M., Trindade, T., & Daniel-da-Silva, A. L. (2019). Magnetic quaternary chitosan hybrid nanoparticles for the efficient uptake of diclofenac from water. Carbohydrate Polymers, 203, 35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.09.030
Sousa, M.U., Rodrigues, A.M., Araujo, M.E.B., Menezes, R.R., Neves, G.A., Lira, H.L. (2022). Adsorption of sodium diclofenac in functionalized palygoskite clays. Materials 15, https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15082708.
Sui, Q., Huang, J., Deng, S., Chen, W., & Yu, G. (2011). Seasonal variation in the occurrence and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in different biological wastewater treatment processes. Environmental Science & Technology, 45, 3341–3348. https://doi.org/10.1021/es200248d
Tahira, I., Aslam, Z., Abbas, A., Monim-ul-Mehboob, M., Ali, S., & Asghar, A. (2019). Adsorptive removal of acidic dye onto grafted chitosan: A plausible grafting and adsorption mechanism. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 136, 1209–1218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.173
Triebskorn, R., Casper, H., Heyd, A., Eikemper, R., Köhler, H. R., & Schwaiger, J. (2004). Toxic effects of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac. Aquatic Toxicology, 68, 151–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.03.015
Wang, S., Lu, Y., Ouyang, X.-K., Liang, X. X., Yu, D., Yang, L.-Y., & Huang, F. (2019). Fabrication of chitosan-based MCS/ZnO@Alg gel microspheres for efficient adsorption of As(V). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 139, 886–895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.08.070
Wang, B., Hu, X., Li, L., Wang, H., Huang, H., Wang, R., Zhou, D., Yuan, J. & Chen, L. (2023a). Application and functionalization of toxic waste sludge-derived biochar for efficient phosphate separation from aqueous media: Toxicity diminution, robust adsorption, and inner mechanism. Chemical Engineering Journal 468, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.143745.
Wang, B., Hu, X., Li, L., **e, Y., Chen, R., Guo, W., Wang, H., Wang, M., Shi, J., Chen, L. & Zhou, D. (2023b). Enhanced phosphate removal by filler encapsulation and surface engineering using SA/PVA matrix: Fabrication optimization, adsorption behaviors and inner removal mechanism. Chemical Engineering Journal 472, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.145073.
Wei, H., Deng, S., Huang, Q., Nie, Y., Wang, B., Huang, J., & Yu, G. (2013). Regenerable granular carbon nanotubes/alumina hybrid adsorbents for diclofenac sodium and carbamazepine removal from aqueous solution. Water Research, 47, 4139–4147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.11.062
Yan, H., Yang, L., Yang, Z., Yang, H., Li, A., & Cheng, R. (2012). Preparation of chitosan/poly(acrylic acid) magnetic composite microspheres and applications in the removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 229–230, 371–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.06.014
Yao, C. C. (2000). Extended and improved Langmuir equation for correlating adsorption equilibrium data. Separation and Purification Technology, 19, 237–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1383-5866(00)00060-5
Yu, X., **g, Y., & Gao, H. (2018). Enhanced adsorption of xylenol orange from aqueous solutions by polyethylenimine-grafted chitosan microspheres. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 96, 2007–2013. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.23118
Yu, S., Yang, Y., Kuroda, K., Pu, J., Guo, R. & Hou, L.-a. (2023). Selective removal of Cr(VI) using polyvinylpyrrolidone and polyacrylamide co-modified MoS2 composites by adsorption combined with reduction. Chinese Chemical Letters. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2023.109130.
Zahir, A., Aslam, Z., Kamal, M. S., Ahmad, W., Abbas, A., & Shawabkeh, R. A. (2017). Development of novel cross-linked chitosan for the removal of anionic Congo red dye. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 244, 211–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.09.006
Zhang, S., Dong, Y., Yang, Z., Yang, W., Wu, J., & Dong, C. (2016). Adsorption of pharmaceuticals on chitosan-based magnetic composite particles with core-brush topology. Chemical Engineering Journal, 304, 325–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.087
Zhang, W., Deng, Q., He, Q., Song, J., Zhang, S., Wang, H., Zhou, J., & Zhang, H. (2018). A facile synthesis of core-shell/bead-like poly (vinyl alcohol)/alginate@PAM with good adsorption capacity, high adaptability and stability towards Cu(II) removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 351, 462–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.129
Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Li, Y., Shi, Y., Pan, S., Nie, G., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Simultaneous adsorption of phosphate and diclofenac by Li/Al layered double hydroxides loaded on modified wheat straw. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 7, 2381–2389. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ew00578b
Zhao, X., Wang, X. & Lou, T. (2021). Preparation of fibrous chitosan/sodium alginate composite foams for the adsorption of cationic and anionic dyes. Journal of Hazardous Materials 403, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124054.
Zhou, X., Maimaitiniyazi, R. & Wang, Y. (2022). Some consideration triggered by misquotation of Temkin model and the derivation of its correct form. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 15, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.104267.
Funding
This work was financially supported by Open Project Funding of Key Laboratory of Health Intelligent Perception and Ecological Restoration of River and Lake, Ministry of Education, Hubei University of Technology (No. HGKFZ03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Hongyu Wang and Henglin **ao; funding acquisition and resources: Hongyu Wang; data curation, formal analysis, and writing—original draft: Yi **e; methodology: Yi **e, Bin Wang, and **aoling Hu; supervision: Lu Li and Shujia Zhang; visualization: Shujia Zhang, Dao Zhou, and Can Jiang; writing—review and editing: Hongyu Wang and Dongyun Nan. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., **e, Y., **ao, H. et al. Fabrication of Polyethyleneimine-Functionalized Chitosan Composite Microspheres for Efficient Removal of Diclofenac Sodium from Water: Behavior and Mechanism Study. Water Air Soil Pollut 235, 242 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07063-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-024-07063-y