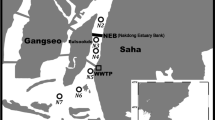
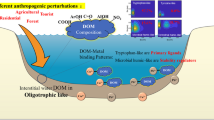
Abstract
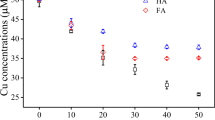
There is widespread concern about pollution of freshwater ecosystems caused by heavy metals. The aim of this study was to determine how humic acid affected the bioavailability of Cu at a range of Cu concentrations in water. The concentrations of selected Cu species were characterized by spectroscopic methods and multiple regression models. The results showed that the dissolved Cu concentration decreased by an average of 13.4% for every 5-mg/l increase in the humic acid concentration in the Cu-treated water, indicating that humic acid could reduce the Cu bioavailability. Tests to show how DOM fluorescent components affected the Cu species concentrations showed that the Cu species were significantly correlated with five fluorescent components of DOM (P<0.01, linear goodness of fit: R2min=0.8374). We then examined how the pH and DOM fluorescent components together affected the concentrations of the Cu forms. When 3≤pH≤7, both tryptophan and fulvic acid promoted the transformation of dissolved Cu forms to suspended Cu forms. The Cu forms were significantly correlated with the pH and DOM fluorescence (P<0.01, linear regression goodness of fit: R2min=0.8898). However, tryptophan and fulvic acid had contrasting effects when the pH was less than, or greater than, 7. The influences on the migration ability and bioavailability of Cu therefore varied, depending on the water conditions. We conclude that it may be possible to identify the substances that have most effect on the bioavailability of Cu in water environments from the pH range of the water body, and that the bioavailability of heavy metals in water environments may be controlled by adding substances with specific properties.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Chen, Y. R., Chen, Y. N., Li, Y. P., Li, H., Jiang, H. J., Luo, X. L., Tang, P., Chen, L., & Yan, H. Q. (2021). Evolution of humic substances and the forms of heavy metals during co-composting of rice straw and sediment with the aid of Fenton-like process. Bioresource Technology, 333, 0960–8524.
Dan, Z. C., Li, X., & Sun, H. (2023). Characteristics and influencing factors of metals release from water-quenched slag of lead smelting. Environmental Pollution and Control, 45(02), 163–170+218 (in Chinese).
Fan, C. H., Zhang, Y. C., & Wang, J. H. (2015). Influence Mechanism of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) from Straw Humification on Chemical Speciation of Lead in Loess Region. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 35(11), 3146–3150 (in Chinese).
He, X. S., **, B. D., Cui, D. Y., Liu, Y., Tan, W. B., Pan, H. W., & Li, D. (2014). Influence of chemical and structural evolution of dissolved organic matter on electron transfer capacity during composting. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 268, 256–263.
He, X. S., **, B. D., Zhang, Z. Y., Gao, R. T., Tan, W. B., & Cui, D. Y. (2014). Insight into the evolution, redox, and metal binding properties of dissolved organic matter from municipal solid wastes using two–dimensional correlation spectroscopy. Chemosphere, 117, 701–707.
He, X. S., **, B. D., **, B. D., Gao, R. T., Zhang, H., Dang, Q. L., Li, D., & Huang, C. H. (2016). Insight into the composition and degradation potential of dissolved organic matter with different hydrophobicity in landfill leachates. Chemosphere, 144, 75–80.
Huang, J. X. (2008). Research on the separation law of the UF membrane on the complex of humic acid-Cu and the characteristics of the membrane fouling. Sun Yat-sen University (in Chinese).
Huang, W. J., Gong, X. Z., Gao, F., & Liu, Y. (2023). Copper products environmental footprint assessment and comprehensive supply risk evaluation for China. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 1–18 (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.11817/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2022-43646. (on line)
Jiang, Y. F., Yuan, J. M., Lu, Z. Y., Wang, A. P., & Chen, H. (2005). The effect of humic acid on species of Cu, Cd, Pb, Zn in sewage farm. Journal of Northwest Normal University, 41(6), 42–46 (in Chinese).
Kungolos, A., Samaras, P., Tsiridis, V., Petala, M., & Sakellaropoulos, G. (2006). Bioavail-ability and toxicity of heavy metals in the presence of natu-ral organic matter. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A, 41(8), 1509–1517.
Li, J. W., Zhao, L. Y., Li, M., Min, Y. E., Zhan, F. S., Wang, Y., Sheng, L. X., & Bian, H. F. (2022). Changes in soil dissolved organic matter optical properties during peatland succession. Ecological Indicators, 143, 109386.
Li, L. (2009). Study on the complexation of Cu2+ metal ions with dissolved humic acid and influencing factors. **'an University of Architecture and Technology (in Chinese).
Li, N., **a, Y., He, X. W., Yuan, L. H., Li, W. J., He, X. J., & **a, K. Y. (2021). Research progress of Cd Form transformation and the effective environmental factors in soil based on tessier analysis. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 52(06), 1505–1512 (in Chinese).
Li, S. D., Lu, L. F., Wu, Y. F., Zhao, Z. L., Huang, C. C., Huang, T., Yang, H., Ma, X. H., & Jiang, Q. L. (2021). Investigation on depth-dependent properties and benthic effluxes of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in pore water from plateau lake sediments. Ecological Indicators, 125, 1–11.
Li, Y. H., Gong, X. F., **ong, J. Q., Sun, Y. H., Shu, Y., Niu, D. N., Lin, Y., Wu, L., & Zhang, R. (2021). Different dissolved organic matters regulate the bioavailability of heavy metals and rhizosphere microbial activity in a plant-wetland soil system. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 9(6), 106823.
Liang, Y. H., Deng, R. R., Huang, J. L., **ong, L. H., Qin, Y., & Liu, Z. T. (2019). The Spectral Characteristic Analysis of Typical Heavy Metal Polluted Water-a Case Study of Mine Drainage in Dabaoshan Mountain, Guangdong Province. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 39(10), 3237–3244.
Lin, Q., & Xu, S. H. (2008). A review of competitive adsorption of heavy metal in soils. Soils, 40(5), 706–711 (in Chinese).
Liu, W. Y., Meng, Y., **g, B. C., Jiang, M. Y., Lin, Z. H., Hu, L. Y., & Zhang, T. T. (2020). ICP-OES research on the spatial distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the North Canal. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 40(12), 3912–3918.
Ma, C., Liu, F. Y., Wei, M. B., Zhao, J. H., & Zhang, H. Z. (2020). Synthesis of novel core-shell magnetic Fe3O4@C nanoparticles with carboxyl function for use as an immobilisation agent to remediate lead-contaminated soils. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 29, 2273–2283.
Mao, M. Y., Wei, J. X., & Liu, Z. H. (1981). Preliminary study on the existence forms of heavy metals in natural water. Environmental Science, 04, 25–29 (in Chinese).
Meng, F. D., Yuan, G. D., Wei, J., Bi, D. X., Yong, S. O., Wang, H. L. (2017). Humic substances as a washing agent for Cd-contaminated soils. Chemosphere, 181, 461-467.
Qin, X. Q., Yao, B., **, L., Zheng, X. Z., Ma, J., & Marc, F. (2020). Characterizing Soil Dissolved Organic Matter in Typical Soils from China Using Fluorescence EEM-PARAFAC and UV-Visible Absorption. Aquatic Geochemistry, 26(1), 71–88.
Qiu, J. W., Tang, X., Zheng, C. B., Li, Y., & Huang, Y. L. (2007). Copper complexation by fulvic acid affects copper toxicity to the larvae of the polychaete Hydroides elegans. Marine Environmental Research, 64(5), 563–573.
Ren, W., **ong, L. L., Yuan, X. H., Yu, Z. W., Zhang, H., Duan, X. G., & Wang, S. B. (2020). Activation of Peroxydisulfate on Carbon Nanotubes: Electron-Transfer Mechanism. Environmental Science and Technology, 53(24), 14595–14603.
Shi, J., Jiang, G. H., Sun, Z. Y., Guo, F., Wang, Q. G., Liu, F., et al. (2022). Dissolved organic matter tracers reveal contrasting characteristics in the concentrated flow zone and matrix-with-fractures zone of a sulfate-contaminated karst aquifer in South China. Applied Geochemistry, 146, 105431.
Wang, Q., Wen, J. Y., Zheng, J. X., Zhao, J. Q., Qiu, C. S., **ao, D., Mu, L., & Liu, X. W. (2021). Arsenate phytotoxicity regulation by humic acid and related metabolic mechanisms. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 207, 111379.
Wang, X. Y., Zhang, X., Ding, J. T., Shen, Y. J., Meng, H. B., Zhou, H. B., Chen, H. S., Wang, J., & Li, R. (2021). Effect of biochar on the aerobic fermentation of dissolved organic matter and on heavy metal forms. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 40(11), 2372–2382 (in Chinese).
Wang, Y. G., Huang, Z. B., Sheng, L. L., & Ma, Y. (2023). Effect of modified humic acid residue on the adsorption and passivation of Hg2+/Pb2+ in solution and soil. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2023(377), 121581.
Wang, Z., Han, R. X., Muhammad, A., Guan, D. X., Zama, E., & Li, G. (2022). Correlative distribution of DOM and heavy metals in the soils of the Zhangxi watershed in Ningbo City. East of China. Environmental pollution, 299, 118811.
Wei, Z. M., Zhang, X., Wei, Y. Q., Wen, X., Shi, J. H., Wu, J. Q., Zhao, Y., **, B. D., et al. (2014). Fractions and biodegradability of dissolved organic matter derived from different composts. Bioresource Technology, 161, 179–185.
Wei, Z., Zhao, X. Y., Zhu, C. W., **, B. D., Zhao, Y., & Yu, X. (2014). Assessment of humification degree of dissolved organic matter from different composts using fluorescence spectroscopy technology. Chemosphere, 95, 261–267.
Williams, J., Hill, R. R., Pignatiello, J. J. J., & Chicken, E. (2021). Wavelet analysis of variance box plot. Journal of Applied Statistics, 49(14), 3536–3563.
Wu, M., Dan, Y. T., Miao, J., Wang, X. X., Liu, F. H., & Sang, W. J. (2023). Interactions of Moisture Content, pH, and HA on the Immobilization of Pb and Zn in Paddy Soil Using Magnetic-chitosan Hydrochar. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 234(2), 104.
**ang, M. T., Ma, J. Y., Cheng, J. L., Lei, K. G., Li, F., Shi, Z., & Li, Y. (2022). Collaborative evaluation of heavy metal pollution of soil-crop system in the southeast of Yangtze River Delta. China. Ecological Indicators, 143, 109412.
**ao, Y. G., Chen, H. G., Wei, Z. Q., Chen, S. B., Shangguan, H. D., Lin, H., Li, Z. S., Lin, Z. Y., & Fan, G. D. (2021). Three-Dimensional Fluorescence Characteristics Analysis of DOM in the Process of Treatment of Brackish Water by Ultrafiltration-Nanofiltration Double Membrane Process. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 41(8), 2518–2523.
Xu, L. J., & Yuan, Z. (2009). Effect of Exogenous Cadmium Pollution and Dissolved Organic Matter on Forms of Cd in Soil. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 40(06), 1442–1445 (in Chinese).
Xu, M. Y., Zhang, C., Shan, B. Q., & Liu, C. (2022). Speciation and Risk of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediments of Different Types of Water Bodies in Baiyangdian Lake. Environmental Science, 43(09), 4532–4542.
Xu, R. Z., Cao, J. S., Feng, G. Y., Luo, J. Y., Feng, Q., Ni, B. J., & Fang, F. (2022). Fast identification of fluorescent components in three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectra via deep learning. Chemical Engineering Journal, 430(2), 132893.
Xu, X. T., Kang, J., Shen, J. M., Zhao, S. X., Wang, B. Y., Zhang, X. X., & Chen, Z. L. (2021). EEM–PARAFAC characterization of dissolved organic matter and its relationship with disinfection by-products formation potential in drinking water sources of northeastern China. Science of the Total Environment, 774, 145297.
Yan, K., Wang, H. Z., Lan, Z., Zhou, J. H., Fu, H. Z., Wu, L. S., & Xu, J. M. (2022). Heavy metal pollution in the soil of contaminated sites in China: Research status and pollution assessment over the past two decades. Journal of Cleaner Production, 373, 1–11.
Yang, T., Huang, H. J., & Lai, F. Y. (2017). Pollution hazards of heavy metals in sewage sludge from four wastewater treatment plants in Nanchang. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 27(10), 2249–2259.
Zhang, W., Li, T., & Dong, B. (2022). Characterizing dissolved organic matter in Taihu Lake with PARAFAC and SOM method. Water Science and Technology, 85(2), 706–718.
Zhang, Y. H., Liu, G. H., Gao, S. Q., Zhang, Z. B., & Huang, L. L. (2023). Effect of humic acid on phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated sediment. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 9, 100235.
Zhang, X. L., Wang, H. B., Yang, F., Wang, S. Y., Guo, X. Y., & Feng, H. J. (2022). Parallel factor analysis with three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy on dissolved organic matter of rural black and odorous water bodies in **du City of Shandong Province. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 12(03), 651–659 (in Chinese).
Zhu, P. F., Knoop, O., & Helmreich, B. (2021). Interaction of heavy metals and biocide/herbicide from stormwater runoff of buildings with dissolved organic matter. Science of the Total Environment, 814, 152599.
Zuo, H., Ma, X. L., Chen, Y. Z., & Liu, Y. (2016). Studied on Distribution and Heavy Metal Pollution Index of Heavy Metals in Water from Upper Reaches of the Yellow River. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 36(9), 3047–3052.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51809095), the Scientific and Technological Project in Henan Province (No. 172102110101) and the Fund of the Innovative Education Program for Graduate Students at North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, China (No. YK-2021-35, YK-2021-53). We thank Liwen Bianji (Edanz) (www.liwenbianji.cn) for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed the conception and design of this study. The empirical work and the manuscript’s first draft were performed by Hongwei Pan and Lili Shi; the conceptualization and funding acquisition were provided by Hongwei Pan; the data collection were provided by Lili Shi, **n Liu, Hongjun Lei, Guang Yang, and Huiru Chen; and the project administration and funding acquisition were provided by Hongwei Pan, Lili Shi, and Guang Yang. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no any actual or potential conflict of interest to this work, including any financial, personal or other relationships with other people or organizations.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, H., Shi, L., Liu, X. et al. Interactions Between Humic Acid and the Forms and Bioavailability of Copper in Water. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 312 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06326-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06326-4