Abstract
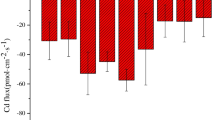
The purpose of the study was to investigate the effects of salinity and pH variations on cadmium uptake by Bidens tripartita L. roots using non-invasive micro-test technology (NMT). The results indicated that Cd2+ influx at 300 µm from the root apexes decreased in treatments with Cd and 5 mM or 10 mM NaCl compared to Cd stress alone. However, treatments with Cd and 2.5 mM NaCl had little effect on net Cd2+ influx compared to Cd treatments alone. Importantly, Cd treatments at pH = 4.0 markedly increased Cd2+ influx to the roots. While it was significantly decreased when pH was adjusted to 7.0 compared to those at pH = 5.5. The results also showed that treatments with Cd in combination with 5 mM or 10 mM NaCl significantly decreased chlorophyll (Chl) a and b concentrations in leaves and root vigor of B. tripartita relative to Cd treatments alone, while there were no significant differences between Cd treatments with 2.5 mM NaCl and Cd treatments alone. A significant increase in root vigor was observed in Cd treatments at pH = 4.0 in comparison to pH = 5.5.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Dai, H., Wei, S., & Skuza, L. (2020). Effects of different soil pH and nitrogen fertilizers on Bidens pilosa L. Cd Accumulation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 27(9), 9403–9409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07579-5
Dai, H., Wei, S., Twardowska, I., Hou, N., & Zhang, Q. (2022). Cosmopolitan cadmium hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum: Exploring cadmium uptake, transport and physiological mechanisms of accumulation in different ecotypes as a way of enhancing its hyperaccumulative capacity. Journal of Environmental Management, 320, 115878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115878
Fan, Y. G., Zhang, S. L., Meng, Y. Y., & Huang, Z. J. (2016). Increase in salt tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana by TaDi19. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 35(1), 163–171. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-015-9513-x
Guo, S. H., Jiang, L. Y., Xu, Z. M., Li, Q. S., Wang, J. F., Ye, H. J., Wang, L. L., He, B. Y., Zhou, C., & Zeng, E. Y. (2020). Biological mechanisms of cadmium accumulation in edible Amaranth (Amaranthus mangostanus L) cultivars promoted by salinity: A transcriptome analysis. Environmental Pollution, 262, 114304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114304
Hamid, Y., Tang, L., Yaseen, M., Hussain, B., Zehra, A., Aziz, M. Z., He, Z., & Yang, X. (2019). Comparative efficacy of organic and inorganic amendments for cadmium and lead immobilization in contaminated soil under rice-wheat crop** system. Chemosphere, 214, 259–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.113
Han, M., Yang, H., Yu, G., Jiang, P., You, S., Zhang, L., Lin, H., Liu, J., & Shu, Y. (2022). Application of non-invasive micro-test technology (NMT) in environmental fields: A comprehensive review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 240, 113706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113706
Hao, L., Chen, L., Zhu, P., Zhang, J., Zhang, D., **ao, J., Xu, Z., Zhang, L., Liu, Y., Li, H., Yang, H., & Cao, G. (2020). Sex-specific responses of Populus deltoides to interaction of cadmium and salinity in root systems. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 195, 110437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110437
He, J., Li, H., Ma, C., Zhang, Y., Polle, A., Rennenberg, H., Cheng, X., & Luo, Z. B. (2015). Overexpression of bacterial γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase mediates changes in cadmium influx, allocation and detoxification in poplar. New Phytologist, 205(1), 240–254. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13013
Lan, X. Y., He, Q. S., Yang, B., Yan, Y. Y., Li, X. Y., & Xu, F. L. (2020). Influence of Cd exposure on H+ and Cd2+ fluxes in the leaf, stem and root of a novel aquatic hyperaccumulator-Microsorum pteropus. Chemosphere, 249, 126552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126552
Li, L., Liu, X., Peijnenburg, W. J., Zhao, J., Chen, X., Yu, J., & Wu, H. (2012). Pathways of cadmium fluxes in the root of the halophyte Suaeda salsa. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 75, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.09.007
Li, L. Z., Tu, C., Wu, L. H., Peijnenburg, W. J., Ebbs, S., & Luo, Y. M. (2017). Pathways of root uptake and membrane transport of Cd2+ in the zinc/cadmium hyperaccumulating plant Sedum plumbizincicola. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 36(4), 1038–1046. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3625
Liu, Z., He, X., Chen, W., Yuan, F., Yan, K., & Tao, D. (2009). Accumulation and tolerance characteristics of cadmium in a potential hyperaccumulator-Lonicera japonica Thunb. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 169(1–3), 170–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.03.090
Liu, Q., Liu, R., Ma, Y., & Song, J. (2018). Physiological and molecular evidence for Na+ and Cl− exclusion in the roots of two Suaeda salsa populations. Aquatic Botany, 146, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2018.01.001
Lu, H., Dong, Y., Feng, Y., Bai, Y., Tang, X., Li, Y., Yang, L., & Liu, J. (2020). Paddy periphyton reduced cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa) by removing and immobilizing cadmium from the water–soil interface. Environmental Pollution, 261, 114103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114103
Ma, W., Xu, W., Xu, H., Chen, Y., He, Z., & Ma, M. (2010). Nitric oxide modulates cadmium influx during cadmium-induced programmed cell death in tobacco BY-2 cells. Planta, 232(2), 325–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1177-y
Meychik, N., Nikolaeva, Y., & Kushunina, M. (2021). The significance of ion-exchange properties of plant root cell walls for nutrient and water uptake by plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 166, 140–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.05.048
Nawrot, N., Wojciechowska, E., Pazdro, K., Szmagliński, J., & Pempkowiak, J. (2021). Uptake, accumulation, and translocation of Zn, Cu, Pb, Cd, Ni, and Cr by P australis seedlings in an urban dredged sediment mesocosm: Impact of seedling origin and initial trace metal content. Science of the Total Environment, 768, 144983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.144983
Ni, L., Wang, S., Shen, T., Wang, Q.W., Chen, C., **a, J.X., Jiang, M.Y. (2020) Alcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase OsDMI3 positively regulates saline-alkaline tolerance in rice roots. Plant Sig Behavior, e1813999. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2020.1813999
Pan, F., Meng, Q., Wang, Q., Luo, S., Chen, B., Khan, K. Y., Yang, X., & Feng, Y. (2016). Endophytic bacterium Sphingomonas SaMR12 promotes cadmium accumulation by increasing glutathione biosynthesis in Sedum alfredii Hance. Chemosphere, 154, 358–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.03.120
Rehman, S., Abbas, G., Shahid, M., Saqib, M., Farooq, A. B. U., Hussain, M., Murtaza, B., Amjad, M., Naeem, M. A., & Farooq, A. (2019). Effect of salinity on cadmium tolerance, ionic homeostasis and oxidative stress responses in conocarpus exposed to cadmium stress: Implications for phytoremediation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 171, 146–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.077
Sun, J., Wang, M. J., Ding, M. Q., Deng, S. R., Liu, M. Q., Lu, C. F., Zhou, X. Y., Shen, X., Zheng, X. J., Zhang, Z. K., Song, J., Hu, Z. M., Xu, Y., & Chen, S. L. (2010). H2O2 and cytosolic Ca2+ signals triggered by the PM H+-coupled transport system mediate K+/Na+ homeostasis in NaCl-stressed Populus euphratica cells. Plant, Cell and Environment, 33(6), 943–958. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02118.x
Uysal, S., Ugurlu, A., Zengin, G., Baloglu, M. C., Altunoglu, Y. C., Mollica, A., Custodio, L., Neng, N. R., Nogueira, J. M. F., & Mahomoodally, M. F. (2018). Novel in vitro and in silico insights of the multi-biological activities and chemical composition of Bidens tripartita L. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 111, 525–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.11.058
Wang, Q., Ma, L., Zhou, Q., Chen, B., Zhang, X., Wu, Y., Pan, F., Huang, L., Yang, X., & Feng, Y. (2019). Inoculation of plant growth promoting bacteria from hyperaccumulator facilitated non-host root development and provided promising agents for elevated phytoremediation efficiency. Chemosphere, 234, 769–776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.132
Wang, Q., Chen, L., Xu, H., Ren, K., Xu, Z., Tang, Y., & **ao, J. (2021). The effects of warming on root exudation and associated soil N transformation depend on soil nutrient availability. Rhizosphere, 17, 100263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2020.100263
Wang, S., Dai, H., Skuza, L., Chen, Y., & Wei, S. (2022). Difference in Cd2+ flux around the root tips of different soybean (Glycine max L) cultivars and physiological response under mild cadmium stress. Chemosphere, 297, 134120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134120
Wei, S., Niu, R., Srivastava, M., Zhou, Q., Wu, Z., Sun, T., Hu, Y., & Li, Y. (2009). Bidens tripartite L.: A Cd-accumulator confirmed by pot culture and site sampling experiment. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 170(2–3), 1269–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.05.078
Wei, S., Zhou, Q., Zhan, J., Wu, Z., Sun, T., Lyubu, Y., & Prasad, M. N. V. (2010). Poultry manured Bidens tripartite L. extracting Cd from soil-potential for phytoremediating Cd contaminated soil. Bioresource Technology, 101(22), 8907–8910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.090
Wu, M., Luo, Q., Liu, S., Zhao, Y., Long, Y., & Pan, Y. (2018). Screening ornamental plants to identify potential Cd hyperaccumulators for bioremediation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 162, 35–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.06.049
Wu, S., Shi, K., Hu, C., Guo, J., Tan, Q., & Sun, X. (2019a). Non-invasive microelectrode cadmium flux measurements reveal the decrease of cadmium uptake by zinc supply in pakchoi root (Brassica chinensis L.). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 168, 363–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.10.081
Wu, H. H., Shabala, L., Zhou, M. X., Su, N., Wu, Q., Ui-haq, T., Zhu, J., Mancuso, S., Azzarello, E., & Shabala, S. (2019b). Root vacuolar Na+ sequestration but not exclusion from uptake correlates with barley salt tolerance. The Plant Journal, 100(1), 55–67. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14424
Yu, H., Wu, Y., Huang, H., Zhan, J., Wang, K., & Li, T. (2020). The predominant role of pectin in binding Cd in the root cell wall of a high Cd accumulating rice line (Oryza sativa L ). Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 206, 111210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111210
Zeng, H. Y., Chen, L. H., Yang, Y., Deng, X., Zhou, X. H., & Zeng, Q. R. (2019). Basal and foliar treatment using an organic fertilizer amendment lowers cadmium availability in soil and cadmium uptake by rice on field micro-plot experiment planted in contaminated acidic paddy soil. Soil Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 28(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2018.1525336
Zhang, X. K., Zhou, Q. H., Cao, J. H., & Yu, B. J. (2011). Differential Cl− /salt tolerance and NaCl-induced alternations of tissue and cellular ion fluxes in Glycine max, Glycine soja and their hybrid seedlings. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, 197, 329–339. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-037X.2011.00467.x
Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Sa, G., Zhang, Y., Deng, J., Deng, S., Wang, M., Zhang, H., Yao, J., Ma, X., Zhao, R., Zhou, X., Lu, C., Lin, S., Chen, S., & Chen, S. (2017). Populus euphratica J3 mediates root K+/Na+ homeostasis by activating plasma membrane H+-ATPase in transgenic Arabidopsis under NaCl salinity. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ, 131(1), 75–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-017-1263-y
Zhang, S., Ni, X., Arif, M., Yuan, Z., Li, L., & Li, C. (2020). Salinity influences Cd accumulation and distribution characteristics in two contrasting halophytes, Suaeda glauca and Limonium aureum. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 191, 110230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110230
Zheljazkov, V. D., Jeliazkova, E. A., Kovacheva, N., & Dzhurmanski, A. (2008). Metal uptake by medicinal plant species grown in soils contaminated by a smelter. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 64(3), 207–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2008.07.003
Zhou, C., Huang, M., Ren, H., Yu, J., Wu, J., & Ma, X. (2017). Bioaccumulation and detoxification mechanisms for lead uptake identified in Rhus chinensis Mill. seedlings. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 142, 59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.03.052
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific research project of City-University co-construction of Shaanxi Province, China (SXJ-2101; SXZJ-2301). Open Fund of Cultivation State Key Laboratory of Qinba Biological Resources and Ecological Environment of Shaanxi University of Technology, China (SLGPT2019KF04-02), Qinba Bioremediation and Resource Development Research and Innovation Base (2022-ZC-GXYZ-0029), Innovation Capability Support Program of Shaanxi (2022WGZJ-20), the project of Foreign Experts Bureau of Shaanxi province of China, China (2023WGZJ-YB-05, G2022040018L, G2021041011L, G20200241015). The General Program from the Education Department of Liaoning Province (LJKMZ20220595). The Scientific Research Funds for the Innovation Team Construction Plan of Shenyang Ligong University (SYLUTD202103). The Shenyang Scientific Plan Project (21-109-3-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Dai, H., Ji, D. et al. Characteristics of Cd Uptake by the Roots of Bidens tripartita L. Under Salinity and pH Variations Assessed by Applying Non-invasive Micro-test Technology. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 335 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06286-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06286-9