Abstract
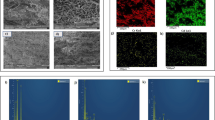
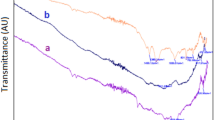
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic that is effective in vitro against Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms. Since the ciprofloxacin, along with other pharmaceuticals, can influence the environment, the goal of this study was to examine the possibility of ciprofloxacin removal from water using biosorbents, an unconventional and cheaper subclass of adsorbents. For this purpose, the effect of ionic strength, pH, temperature, different mass of the used biosorbent, and physical-chemical characteristics of biosorbents on ciprofloxacin sorption was investigated. Biosorbents, used in this study, are the various waste products like maple leaves (ML), tangerine peel (TP), and tomato waste (TW) (seeds and peel). Sorption parameters of ciprofloxacin were determined by linear, Freundlich, and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms. The highest value of the sorption coefficient, Kd, shows the maple leaves, while the minimum achieves a sample of tangerine peel. These values correspond to the analysis and distribution of pore size, where the tangerine peel sample has the lowest specific surface area. The obtained results indicated the potential of investigated biosorbents to sorption of ciprofloxacin, which ultimately can contribute to environmental protection and the disposal of waste products.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request
Code Availability
Not applicable
References
Ahmed, M. M., & Ahmed, S. S. (2008). A comparison study to determine the mean of particle size distribution for truthful characterization of environmental data (part 1). Journal of Engineering Sciences, 36, 147–166.
Ahsan, M. A., Islam, M. T., Imam, M. A., Golam Hyder, A. H. M., Jabbari, V., Dominguez, N., & Noveron, J. C. (2018). Biosorption of bisphenol A and sulfamethoxazole from water using sulfonated coffee waste: Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 6, 6602–6611.
Aksu, Z. (2005). Application of biosorption for the removal of organic pollutants: A review. Process Biochemistry, 40, 997–1026.
Alnajrani, M. N., & Alsager, O. A. (2020). Removal of antibiotics from water by polymer of intrinsic microporosity: Isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics, and adsorption mechanism. Nature Research, 10(1), 794.
Babić, S., Biošić, M., & Škorić, I. (2013). Photolytic degradation of norfloxacin, enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin in various aqueous media. Chemosphere, 91, 1635–1642.
Bajpai, S. K., Bajpai, M., & Rai, N. (2012). Sorptive removal of ciprofloxacin hydrochloride from simulated wastewater using sawdust: Kinetic study and effect of pH. Water SA, 38(5), 673–682.
Barišić, Z., Uropatogena Escherichia coli: Povezanost otpornosti na kinolone s prisutnošću činitelja virulencije, 2011., PhD disertation, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb.
Bekçi, Z., Seki, Y., & Yurdakoç, M. K. (2006). Equilibrium studies for trimethoprim adsorption on montmorillonite KSF. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 133(1-3), 233–242.
Brownawell, B. J., Chen, H., Collier, J. M., & Westall, J. C. (1990). Adsorption of organic cations to natural materials. Environmental Science & Technology, 24, 1234–1241.
Carabineiro, S. A. C., Thavorn-Amornsri, T., Pereira, M. F. R., & Figueiredo, J. L. (2011). Adsorption of ciprofloxacin on surface-modified carbon materials. Water Research, 45(15), 4583–4591.
Carmosini, N., & Lee, S. N. (2009). Ciprofloxacin sorption by dissolved organic carbon from reference and bio-waste material. Chemosphere, 77, 813–820.
Chen, H., Gao, B., Li, H., & Ma, L. Q. (2011). Effects of pH and ionic strength on sulfamethoxazole and ciprofloxacin transport in saturated porous media. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 126, 29–36.
Dada, A. O., Olalekan, A. P., Olatunya, A. M., & Dada, O. (2012). Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry, 3, 38–45.
Das, B., & Mondal, N. K. (2011). Calcareous soil as a new adsorbent to remove lead from aqueous solution: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study. Universal Journal of Environmental Research and Technology, 1, 515–530.
De Gisi, S., Lofrano, G., Grassi, M., & Notarnicola, M. (2016). Characteristics and adsorption capacities of low-cost sorbents for wastewater treatment: A review. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 9, 10–40.
Demirbas, A. (2008). Heavy metal adsorption onto agro-based waste materials: A review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 157(2-3), 220–229.
Doretto, K. M., & Rath, S. (2013). Sorption of sulfadiazine on Brazilian soils. Chemosphere, 90, 2027–2034.
DrugBank. (n.d.). http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00537#properties (December 2019)
Đurović-Pejčev, R. (2011). Procesi koji određuju sudbinu pesticida u zemljištu. Pesticides & Phytomedicine, 26(1), 9–22.
El-Sayed, H. E. M., & El-Sayed, M. M. H. (2014). Assessment of food processing and pharmaceutical industrial wastes as potential biosorbents: A review. BioMed Research International, 2014, 1–24.
El-Shafey, E. S. I., Al-Lawati, H., & Al-Sumri, A. S. (2012). Ciprofloxacin adsorption from aqueous solution onto chemically prepared carbon from date palm leaflets. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 24(9), 1579–1586.
Figueroa-Diva, R. A., Vasudevan, D., & MacKay, A. A. (2010). Trends in soil sorption coefficients within common antimicrobial families. Chemosphere, 79, 786–793.
Franco, A., & Trapp, S. (2008). Estimation of the soil-water partition coefficient normalized to organic carbon for ionisable organic chemicals. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 27, 1995–2004.
Fries, E., Crouzet, C., Michel, C., & Togola, A. (2016). Interactions of ciprofloxacin (CIP), titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles and natural organic matter (NOM) in aqueous suspensions. The Science of the Total Environment, 563-564, 971–976.
Golet, E. M., **fra, I., Siegrist, H., Alder, A. C., & Giger, W. (2003). Environmental exposure assessment of fluoroquinolone antibacterial agents from sewage to soil. Environmental Science & Technology, 37, 3243–3249.
group of authors, 2013. Environmental analytics, eds. Kaštelan-Macan, M. and Petrović, M., Faculty of Chemical Engineering and technology, Zagreb, Croatia, pp. 75.
Gu, C., & Karthikeyan, K. G. (2005). Sorption of the antimicrobial ciprofloxacin to aluminum and iron hydrous oxides. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 9166–9173.
Halling-Sørensen, B., Holten Lützhøft, H. C., Andersen, H. R., & Ingerslev, F. (2000). Environmental risk assessment of antibiotics: Comparison of mecillinam, trimethoprim and ciprofloxacin. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 46, 53–58.
Hamdaoui, O., Saoudi, F., Chiha, M., & Naffrechoux, E. (2008). Sorption of malachite green by a novel sorbent, dead leaves of plane tree: Equilibrium and kinetic modeling. Chemical Engineering Journal, 143, 73–84.
Hassan, S. A., & Ali, F. J. (2014). Determination of kinetics, thermodynamics and equilibrium parameters of ciprofloxacin adsorption from aqueous solution onto wastes of spent black tea leaves and pomegranate peel. International Journal of Advanced Scientific and Technical Research, 2(4), 237–253.
Hossain, A. (2013). Development of novel biosorbents in removing heavy metal from aqueous solution, disertation. Sydney: University of Technology.
Hossain, A., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W., Zhang, J., & Liang, S. (2014). A laboratory study using maple leaves as a biosorbent for lead removal from aqueous solutions. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 49(3), 195–209.
Houtman, C. J. (2010). Emerging contaminants in surface waters and their relevance for the production of drinking water in Europe. Journal of Integrative Environmental Sciences, 7(4), 271–295.
Kaewsarn, P. (2002). Biosorption of copper (II) from aqueous solutions by pre-treated biomass of marine algae Padina sp. Chemosphere, 47(10), 1081–1085.
Kostich, M. S., Batt, A. L., & Lazorchak, J. M. (2014). Concentrations of prioritized pharmaceuticals in effluents from 50 large wastewater treatment plants in the US and implications for risk estimation. Environmental Pollution, 184, 354–359.
Kumar, P. S., Ramalingam, S., Senthamarai, C., Niranjanaa, M., Vijayalakshmi, P., & Sivanesan, S. (2010). Adsorption of dye from aqueous solution by cashew nut shell: Studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics of interactions. Desalination, 261(1-2), 52–60.
Kümmerer, K., 2004. Pharmaceuticals in the environment: Sources, fate, effects and risks, Springer, Second edition. pp 3-11.
Leal, R. M. P., Alleoni, L. R. F., Tornisielo, V. L., & Regitano, J. B. (2013). Sorption of fluoroquinolones and sulfonamides in 13 Brazilian soils. Chemosphere, 92, 979–985.
Li, Y., Taggart, M. A., McKenzie, C., Zhang, Z., Lu, Y., Pap, S., & Gibb, S. (2019). Utilizing low-cost natural waste for the removal of pharmaceuticals from water: Mechanisms, isotherms and kinetics at low concentrations. Journal of Cleaner Production, 227, 88–97.
Mac Kay, A. A., & Vasudevan, D. (2012). Polyfunctional ionogenic compound sorption: Challenges and new approaches to advance predictive models. Environmental Science & Technology, 46, 9209–9223.
Malakootian, M., Nasiri, A., & Gharaghani, M. A. (2019). Photocatalytic degradation of ciprofloxacin antibiotic by TiO2 nanoparticles immobilized on a glass plate. Chemical Engineering Communications, 207, 56–72.
Mckay, G. (1983). The adsorption of dyestuffs from aqueous solutions using activated carbon, III. Intraparticle diffusion process. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 33, 196–204.
Menk, J. D. J., do Nascimento, A. I. S., Leite, F. G., de Oliveira, R. A., Jozala, A. F., de Oliveira Junior, J. M., Chaud, M. V., & Grotto, D. (2019). Biosorption of pharmaceutical products by mushroom stem waste. Chemosphere, 237, 124515.
Mukaka, M. M. (2012). Statistics Corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Medical Journal, 24(3), 69–71.
Mutavdžić Pavlović, D., Pinušić, T., Periša, M., & Babić, S. (2012). Optimization of matrix solid-phase dispersion for liquid chromatography tandem mass chromatography analysis of 12 pharmaceuticals in sediments. Journal of Chromatography A, 1258, 1–15.
Mutavdžić Pavlović, D., Ćurković, L., Grčić, I., Šimić, I., & Župan, J. (2017a). Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic study of ciprofloxacin sorption on sediments. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24, 10091–10106.
Mutavdžić Pavlović, D., Ćurković, L., Macan, J., & Žižek, K. (2017b). Eggshell as a new biosorbent for the removal of pharmaceuticals from aqueous solutions. CLEAN – Soil, Air, Water, 45(12), 1–14.
Mutavdžić Pavlović, D., Glavač, A., Gluhak, M., & Runje, M. (2018). Sorption of albendazole in sediments and soils: Isotherms and kinetics. Chemosphere, 193, 635–644.
Najafi, H., Pajootan, E., Ebrahimi, A., & Mokhtar, A. (2016). The potential application of tomato seeds as low-cost industrial waste in the adsorption of organic dye molecules from colored effluents. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57, 15026–15036.
Ötker, H. M., & Akmehmet-Balcioǧlu, I. (2005). Adsorption and degradation of enrofloxacin, a veterinary antibiotic on natural zeolite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 122, 251–258.
Panday, K. K., Prasad, G., & Singh, V. N. (1986). Use of wollastonite for the treatment of Cu (II) rich effluents. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 27(3), 287–296.
Pascual-Reguera, M. I., Perez Parras, G., & Molina Dıaz, A. (2004). Solid-phase UV spectrophotometric method for determination of ciprofloxacin. Microchemical Journal, 77, 79–84.
Peigney, A., Laurent, C., Flahaut, E., Bacsa, R., & Rousset, A. (2001). Specific surface area of carbon nanotubes and bundles of carbon nanotubes. Carbon, 39(4), 507–514.
Pham, T. D., Vu, T. N., Nguyen, H. L., Le, P. H. P., & Hoang, T. S. (2020). Adsorptive removal of antibiotic ciprofloxacin from aqueous solution using protein-modified danosilica. Polymers, 12(1), 57.
Polesel, F., Lehnberg, K., Dott, W., Trapp, S., Thomas, K. V., & Plósz, B. G. (2015). Factors influencing sorption of ciprofloxacin onto activated sludge: Experimental assessment and modelling implications. Chemosphere, 119, 105–111.
Rakshit, S., Sarkar, D., Elzinga, E. J., Punamiya, P., & Datta, R. (2013). Mechanisms of ciprofloxacin removal by nano-sized magnetite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 246–247, 221–226.
Ramachandran, P., Vairamuthu, R., & Ponnusamy, S. (2011). Adsorption isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamics and desorption studies of reactive orange 16 on activated carbon derived from Ananas comosus (L.) carbon. ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, 6, 15–26.
Ren, Y. M., Wei, X. Z., & Zhang, M. L. (2008). Adsorption character for removal Cu(II) by magnetic Cu(II) ion imprinted composite adsorbent. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 158(1), 14–22.
Ribeiro, G. C., Coelho, L. M., Oliviera, E., & Coelho, N. M. M. (2013). Removal of Cu (II) from ethanol fuel using mandarin peel as biosorbent. BioResources, 8(3), 3309–3321.
Shang, J. G., Kong, X. R., He, L. L., Li, W. H., & Liao, Q. J. H. (2016). Low-cost biochar derived from herbal residue: Characterization and application for ciprofloxacin adsorption. International journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 13, 2449–2458.
Souza, J. V. M. T., Diniz, K. M., Massocatto, C. L., Tarley, C. R. T., Caetano, J., & Dragunski, D. C. (2012). Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution with orange sub-products chemically modified as biosorbent. BioResources, 7(2), 2300–2318.
Ter Laak, T. I., Gebbink, W. A., & Tolls, J. (2006). Estimation of soil sorption coefficients of veterinary pharmaceuticals from soil properties. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25(4), 933–941.
Theivarasu, C., & Mylsamy, S. (2010). Equilibrium and kinetic adsorption studies of rhodamine-B from aqueous solutions using cocoa (Theobroma cacao) shell as a new adsorbent. International Journal of Engineering, Science and Technology, 2, 6284–6292.
Tolić, K., Mutavdžić Pavlović, D., Židanić, D., & Runje, M. (2019). Nitrofurantoin in sediments and soils: Sorption, isotherms and kinetics. Science of the Total Environment, 681, 9–17.
Tor, A., & Cengeloglu, Y. (2006). Removal of congo red from aqueous solution by adsorption onto acid activated red mud. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 138(2), 409–415.
Tóth, J. (2000). Calculation of the BET-compatible surface area from any type I isotherms measured above the critical temperature. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 225(2), 378–383.
Tsezos, M., Remoudaki, E., & Angelatou, V. (1995). A systematic study on equilibrium and kinetics of biosorptive accumulation. The case of Ag and Ni. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 35(1), 129–153.
Turku, I., Sainio, T., & Paatero, E. (2007). Thermodynamics of tetracycline adsorption on silica. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 5, 225–228.
Udovičić, M., Baždarić, K., Bilić-Zulle, L., & Petrovečki, M. (2007). What we need to know when calculating the coefficient of correlation? Biochemia Medica, 17, 10–15.
Urase, T., & Kikuta, T. (2005). Separate estimation of adsorption and degradation of pharmaceutical substances and estrogens in the activated sludge process. Water Research, 39, 1289–1300.
Van Doorslaer, X., Demeestere, K., & Heynderickx, P. M. (2011). UV-A and UV-C induced photolytic and photocatalytic degradation of aqueous ciprofloxacin and moxifloxacin: Reaction kinetics and role of adsorption. Applied Catalysts B: Environmental, 10, 540–547.
Vasudevan, D., Bruland, G. L., Torrance, B. S., Upchurch, V. G., & MacKay, A. A. (2009). pH-dependent ciprofloxacin sorption to soils: Interaction mechanisms and soil factors influencing sorption. Geoderma, 151, 68–76.
Vilar, V. J., Botelho, C., & Boaventura, R. A. (2007). Methylene blue adsorption by algal biomass based materials: Biosorbents characterization and process behaviour. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 147(1), 120–132.
Wang, C. J., Li, Z., Jiang, W. T., Jean, J. S., & Liu, C. C. (2010). Cation exchange interaction between antibiotic ciprofloxacin and montmorillonite. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 183, 309–314.
Yu, F., Wu, Y., Li, X., & Ma, J. (2012). Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of toluene, ethylbenzene, and m-xylene adsorption from aqueous solutions onto KOH-activated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Agric. Food Chem, 60, 12245–12253.
Zhang, H., **ong, C., Liu, F., Zheng, X., Jiang, J., Zheng, Q., & Yao, C. (2014). Optimization of conditions for Cu (II) adsorption on D151 resin from aqueous solutions using response surface methodology and its mechanism study. Water Science and Technology, 69, 2446–2451.
Zhuang, Y., Yu, F., & Ma, J. (2015). Enhanced adsorption and removal of ciprofloxacin on regenerable long TiO2 nanotube/graphene oxide hydrogel adsorbents. Journal of Nanomaterials, 2015, 1–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KTexperimental work in laboratory; writing the manuscript
DMPwriting the manuscript
NSexperimental work in laboratory
MRanalysis on LC-MS/MS
All authors read and approved the final manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tolić, K., Mutavdžić Pavlović, D., Stankir, N. et al. Biosorbents from Tomato, Tangerine, and Maple Leaves for the Removal of Ciprofloxacin from Aqueous Media. Water Air Soil Pollut 232, 218 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05153-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05153-9