Abstract
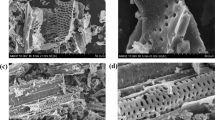
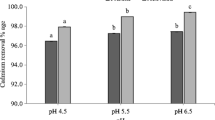
Biochar is a promising material for removing metal ions from water and soil through adsorption. In this study, rice straw was pyrolyzed to prepare biochars at 300 °C (RSBC300), 500 °C (RSBC500), and 700 °C (RSBC700) in an oxygen-limited atmosphere. The biochars were used in batch experiments for adsorption of copper (Cu) ions in aqueous solution. The influence of various environmental conditions, including solution pH, solid-to-liquid ratio, contact time, and environmental temperature, on Cu removal were systematically investigated. To explore the adsorption mechanisms and ascertain the contribution of acid-soluble minerals, adsorption kinetics and isotherm analyses, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were performed. The results showed that the removal rate reached 99.6% when the experimental condition was a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1 g L−1, pH of 6.0, and the initial Cu concentration of 30 mg L−1. The pseudo-second-order model and the two-compartment kinetic model well fitted with the Cu adsorption kinetics process onto RSBC700, whereas the Freundlich, Temkin, and Dubinin–Radushkevich (D–R) models best described the Cu adsorption isotherm process on RSBC700. Higher temperatures improved Cu removal from solution with the maximum adsorption capacity being 52.5 mg g−1 at 45 °C. The influence of co-existing Ca2+ and Mg2+ on Cu removal by RSBC700 was limited, whereas tetracycline exhibited some inhibition effect. The role of acid-soluble minerals in biochar for Cu removal cannot be ignored, especially in treatment using RSBC500 (contribution rate at 47.2–57.1%). The mechanism underlying Cu removal by rice straw biochar involved electrostatic interaction, complexation, cation–π interaction, and precipitation. Therefore, high temperature-derived rice straw biochar can be expected to an adsorbent to alleviate Cu pollution in wastewater.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah, M. M., Ahmad, M. N., Walker, G., Leahy, J. J., & Kwapinski, W. (2019). Batch and continuous systems for Zn, Cu, and Pb metal ions adsorption on spent mushroom compost biochar. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 58(17), 7296–7307.
Ahmad, M., Rajapaksha, A. U., Lim, J. E., Zhang, M., Bolan, N., Mohan, D., Vithanage, M., Lee, S. S., & Ok, Y. S. (2014). Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: a review. Chemosphere, 99, 19–33.
Batool, S., Idrees, M., Hussain, Q., & Kong, J. (2017). Adsorption of copper (II) by using derived–farmyard and poultry manure biochars: efficiency and mechanism. Chemical Physics Letters, 689, 190–198.
Biswas, S., Meikap, B. C., & Sen, T. K. (2019). Adsorptive removal of aqueous phase copper (Cu2+) and nickel (Ni2+) metal ions by synthesized biochar–biopolymeric hybrid adsorbents and process optimization by response surface methodology (RSM). Water Air Soil Pollution, 230(8), 23.
Biswas, S., Siddiqi, H., Meikap, B. C., Sen, T. K., & Khiadani, M. (2020). Preparation and characterization of raw and inorganic acid-activated pine cone biochar and its application in the removal of aqueous-phase Pb2+ metal ions by adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollution, 231(1), 17.
Blanchard, G., Maunaye, M., & Martin, G. (1984). Removal of heavy metals from waters by means of natural zeolites. Water Research, 18(12), 1501–1507.
Bogusz, A., Oleszczuk, P., & Dobrowolski, R. (2015). Application of laboratory prepared and commercially available biochars to adsorption of cadmium, copper and zinc ions from water. Bioresource Technology, 196, 540–549.
Boni, M. R., Chiavola, A., & Marzeddu, S. (2020). Remediation of lead-contaminated water by virgin coniferous wood biochar adsorbent: batch and column application. Water Air Soil Pollution, 231(4), 16.
Chen, X., Chen, G., Chen, L., Chen, Y., Lehmann, J., McBride, M. B., & Hay, A. G. (2011). Adsorption of copper and zinc by biochars produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution. Bioresource Technology, 102(19), 8877–8884.
Chen, Q., Zheng, J., Wen, L., Yang, C., & Zhang, L. (2019). A multi–functional–group modified cellulose for enhanced heavy metal cadmium adsorption: performance and quantum chemical mechanism. Chemosphere, 224, 509–518.
Deng, J., Liu, Y., Liu, S., Zeng, G., Tan, X., Huang, B., Tang, X., Wang, S., Hua, Q., & Yan, Z. (2017). Competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II) onto chitosan–pyromellitic dianhydride modified biochar. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 506, 355–364.
Deng, J., Li, X., Wei, X., Liu, Y., Liang, J., Tang, N., Song, B., Chen, X., & Cheng, X. (2019). Sulfamic acid modified hydrochar derived from sawdust for removal of benzotriazole and Cu(II) from aqueous solution: adsorption behavior and mechanism. Bioresource Technology, 290, 121765.
Dubinin, M.M. & Radushkevich, L.V. (1947) The equation of the characteristic curve of the activated charcoal. Proceedings of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics Academy of Sciences, 55, 331-337.
Faheem, Du, J. K., Bao, J. G., Hassan, M. A., Irshad, S., Talib, M. A., & Zheng, H. (2020). Efficient capture of phosphate and cadmium using biochar with multifunctional amino and carboxylic moieties: kinetics and mechanism. Water Air Soil Pollution, 231(1), 16.
Fan, S. & Zhang, L. (2019) Production and characterization of tea waste-based biochar and its application in treatment of Cd–containing wastewater. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery.
Fan, S., Tang, J., Wang, Y., Li, H., Zhang, H., Tang, J., Wang, Z., & Li, X. (2016). Biochar prepared from co–pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and tea waste for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and mechanism. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 220, 432–441.
Fan, S., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Wang, Z., **e, Z., & Tang, J. (2018). Removal of tetracycline from aqueous solution by biochar derived from rice straw. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(29), 29529–29540.
Fan, J., Li, Y., Yu, H., Li, Y., Yuan, Q., **ao, H., Li, F., & Pan, B. (2020). Using sewage sludge with high ash content for biochar production and Cu(II) sorption. Science of the Total Environment, 713, 136663.
Foo, K. Y., & Hameed, B. H. (2010). Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chemical Engineering Journal, 156(1), 2–10.
Freundlich, H. (1907). Über die adsorption in lösungen. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 57(1), 385–470.
Hadjittofi, L., Prodromou, M., & Pashalidis, I. (2014). Activated biochar derived from cactus fibres–preparation, characterization and application on Cu (II) removal from aqueous solutions. Bioresource Technology, 159, 460–464.
Ho, Y. S., & McKay, G. (1999). Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 34(5), 451–465.
Hokkanen, S., Bhatnagar, A., & Sillanpää, M. (2016). A review on modification methods to cellulose-based adsorbents to improve adsorption capacity. Water Research, 91, 156–173.
Hua, M., Zhang, S., Pan, B., Zhang, W., Lv, L., & Zhang, Q. (2012). Heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by nanosized metal oxides: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 211, 317–331.
Idrees, M., Batool, S., Kalsoom, T., Yasmeen, S., Kalsoom, A., Raina, S., Zhuang, Q., & Kong, J. (2018). Animal manure-derived biochars produced via fast pyrolysis for the removal of divalent copper from aqueous media. Journal of Environmental Management, 213, 109–118.
Jiang, J., Yongbo, P., Min, Y., Zhineng, H., Dejian, W., & Renkou, X. (2015). Rice straw-derived biochar properties and functions as Cu (II) and cyromazine sorbents as influenced by pyrolysis temperature. Pedosphere, 25(5), 781–789.
Jung, K. W., Lee, S. Y., Choi, J. W., & Lee, Y. J. (2019). A facile one–pot hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite/biochar nanocomposites: adsorption behavior and mechanisms for the removal of copper (II) from aqueous media. Chemical Engineering Journal, 369, 529–541.
Kim, B. S., Lee, H. W., Park, S. H., Baek, K., Jeon, J. K., Cho, H. J., Jung, S. C., Kim, S. C., & Park, Y. K. (2016). Removal of Cu2+ by biochars derived from green macroalgae. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(2), 985–994.
Kołodyńska, D., Wnętrzak, R., Leahy, J. J., Hayes, M. H. B., Kwapiński, W., & Hubicki, Z. (2012). Kinetic and adsorptive characterization of biochar in metal ions removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 197, 295–305.
Lagergren, S. (1898). About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K SvenVetenskapsak Handl, 24, 1–39.
Langmuir, I. (1918). The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 40(9), 1361–1403.
Latorre, M., Troncoso, R., & Uauy, R. (2019). Chapter 4—biological aspects of copper. In N. Kerkar & E. A. Roberts (Eds.), Clinical and translational perspectives on Wilson disease (pp. 25–31). Academic Press.
Lee, M. E., Park, J. H., & Chung, J. W. (2019). Comparison of the lead and copper adsorption capacities of plant source materials and their biochars. Journal of Environmental Management, 236, 118–124.
Li, M., Liu, Q., Guo, L., Zhang, Y., Lou, Z., Wang, Y., & Qian, G. (2013). Cu(II) removal from aqueous solution by Spartina alterniflora derived biochar. Bioresource Technology, 141, 83–88.
Li, H., Dong, X., da Silva, E. B., de Oliveira, L. M., Chen, Y., & Ma, L. Q. (2017). Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere, 178, 466–478.
Lin, L. N., Song, Z. G., Huang, Y. C., Khan, Z. H., & Qiu, W. W. (2019). Removal and oxidation of arsenic from aqueous solution by biochar impregnated with Fe–Mn oxides. Water Air Soil Pollution, 230(5), 13.
Liu, H., Jiang, G. M., Zhuang, H. Y., & Wang, K. J. (2008). Distribution, utilization structure and potential of biomass resources in rural China: with special references of crop residues. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 12(5), 1402–1418.
Liu, S., Xu, W.-H., Liu, Y.-G., Tan, X.-F., Zeng, G.-M., Li, X., Liang, J., Zhou, Z., Yan, Z.-L., & Cai, X.-X. (2017). Facile synthesis of Cu (II) impregnated biochar with enhanced adsorption activity for the removal of doxycycline hydrochloride from water. Science of the Total Environment, 592, 546–553.
McLintock, I. (1967). The Elovich equation in chemisorption kinetics. Nature, 216(5121), 1204–1205.
Meng, J., Feng, X., Dai, Z., Liu, X., Wu, J., & Xu, J. (2014). Adsorption characteristics of Cu(II) from aqueous solution onto biochar derived from swine manure. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21(11), 7035–7046.
Mohan, D., Sarswat, A., Ok, Y. S., & Pittman, C. U. (2014). Organic and inorganic contaminants removal from water with biochar, a renewable, low cost and sustainable adsorbent—a critical review. Bioresource Technology, 160, 191–202.
Nicolaou, E., Philippou, K., Anastopoulos, I., & Pashalidis, I. (2019). Copper adsorption by magnetized pine–needle biochar. Processes, 7(12), 903.
Nie, T., Hao, P., Zhao, Z., Zhou, W., & Zhu, L. (2019). Effect of oxidation–induced aging on the adsorption and co-adsorption of tetracycline and Cu2+ onto biochar. Science of the Total Environment, 673, 522–532.
Park, J. H., Wang, J. J., Kim, S. H., Cho, J. S., Kang, S. W., Delaune, R. D., Han, K. J., & Seo, D. C. (2017). Recycling of rice straw through pyrolysis and its adsorption behaviors for Cu and Zn ions in aqueous solution. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 533, 330–337.
Pellera, F. M., Giannis, A., Kalderis, D., Anastasiadou, K., Stegmann, R., Wang, J. Y., & Gidarakos, E. (2012). Adsorption of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solutions on biochars prepared from agricultural by-products. Journal of Environmental Management, 96(1), 35–42.
Peng, H., Gao, P., Chu, G., Pan, B., Peng, J., & **ng, B. (2017). Enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) by phosphoric acid-modified biochars. Environmental Pollution, 229, 846–853.
Phoungthong, K., & Suwunwong, T. (2020). Magnetic biochar derived from sewage sludge of concentrated natural rubber latex (CNRL) for the removal of Al3+ and Cu2+ ions from wastewater. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 46(1), 385–407.
Shen, T., Tang, Y., Lu, X. Y., & Meng, Z. (2018). Mechanisms of copper stabilization by mineral constituents in sewage sludge biochar. Journal of Cleaner Production, 193, 185–193.
Son, E. B., Poo, K. M., Chang, J. S., & Chae, K. J. (2018). Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions using engineered magnetic biochars derived from waste marine macro-algal biomass. Science of the Total Environment, 615, 161–168.
Song, Z., Lian, F., Yu, Z., Zhu, L., **ng, B., & Qiu, W. (2014). Synthesis and characterization of a novel MnOx-loaded biochar and its adsorption properties for Cu2+ in aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 242, 36–42.
Song, J., He, Q., Hu, X., Zhang, W., Wang, C., Chen, R., Wang, H., & Mosa, A. (2019). Highly efficient removal of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) by biochar derived from Artemisia argyi stem. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(13), 13221–13234.
Tang, S., Shao, N., Zheng, C., Yan, F., & Zhang, Z. (2019). Amino–functionalized sewage sludge–derived biochar as sustainable efficient adsorbent for Cu(II) removal. Waste Management, 90, 17–28.
Temkin, M. (1940). Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta physiochim, URSS, 12, 327–356.
Tong, X. J., Li, J. Y., Yuan, J. H., & Xu, R. K. (2011). Adsorption of Cu(II) by biochars generated from three crop straws. Chemical Engineering Journal, 172(2), 828–834.
Trakal, L., Šigut, R., Šillerová, H., Faturíková, D., & Komárek, M. (2014). Copper removal from aqueous solution using biochar: effect of chemical activation. Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 7(1), 43–52.
Wang, H., Gao, B., Wang, S., Fang, J., Xue, Y., & Yang, K. (2015a). Removal of Pb(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by biochar derived from KMnO4 treated hickory wood. Bioresource Technology, 197, 356–362.
Wang, Z., Liu, G., Zheng, H., Li, F., Ngo, H. H., Guo, W., Liu, C., Chen, L., & **ng, B. (2015b). Investigating the mechanisms of biochar’s removal of lead from solution. Bioresource Technology, 177, 308–317.
**ao, X., Chen, B., & Zhu, L. (2014). Transformation, morphology, and dissolution of silicon and carbon in rice straw-derived biochars under different pyrolytic temperatures. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(6), 3411–3419.
**ao, J., Hu, R., & Chen, G. (2020). Micro-nano-engineered nitrogenous bone biochar developed with a ball–milling technique for high-efficiency removal of aquatic Cd(II), Cu(II) and Pb(II). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 387, 121980.
Xu, X., Cao, X., & Zhao, L. (2013a). Comparison of rice husk- and dairy manure-derived biochars for simultaneously removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions: role of mineral components in biochars. Chemosphere, 92(8), 955–961.
Xu, X., Cao, X., Zhao, L., Wang, H., Yu, H., & Gao, B. (2013b). Removal of Cu, Zn, and Cd from aqueous solutions by the dairy manure-derived biochar. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 20(1), 358–368.
Yang, G. X., & Jiang, H. (2014). Amino modification of biochar for enhanced adsorption of copper ions from synthetic wastewater. Water Research, 48, 396–405.
Yang, F., Zhang, S., Li, H., Li, S., Cheng, K., Li, J. S., & Tsang, D. C. W. (2018). Corn straw-derived biochar impregnated with α-FeOOH nanorods for highly effective copper removal. Chemical Engineering Journal, 348, 191–201.
Yin, Z., Liu, Y., Liu, S., Jiang, L., Tan, X., Zeng, G., Li, M., Liu, S., Tian, S., & Fang, Y. (2018). Activated magnetic biochar by one-step synthesis: enhanced adsorption and coadsorption for 17β-estradiol and copper. Science of the Total Environment, 639, 1530–1542.
Zhou, L., Huang, Y., Qiu, W., Sun, Z., Liu, Z., & Song, Z. (2017). Adsorption properties of nano-MnO2-biochar composites for copper in aqueous solution. Molecules, 22(1), 173.
Zhu, Y. Y., Dai, W. C., Deng, K., Pan, T., & Guan, Z. J. (2020). Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by Fe–Mn oxide–modified biochar. Water Air Soil Pollution, 231(2), 17.
Zuo, X., Liu, Z., & Chen, M. (2016). Effect of H2O2 concentrations on copper removal using the modified hydrothermal biochar. Bioresource Technology, 207, 262–267.
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51809001), Natural Science Foundation of the Education Department of Anhui Province (KJ2018A0125).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 5259 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mei, Y., Li, B. & Fan, S. Biochar from Rice Straw for Cu2+ Removal from Aqueous Solutions: Mechanism and Contribution Made by Acid-Soluble Minerals. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 420 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04791-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04791-9