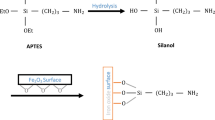
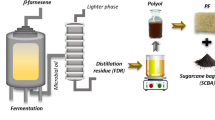
Abstract
The aim of this work is the employment of char waste in the synthesis of silicon foams for oil spill remediation and the comparison analysis with carbon nanotubes-filled foams. The foams are obtained by foaming a slurry constituted by a silicone matrix with CNT or char filler (7.7 wt%) in presence of a Sn-based catalyst. All the investigated materials present a foam morphology with an open/closed cell structure. Each foam was tested in three used common oils (kerosene, crude oil, and pump oil). Also, hydrophilic behavior of the foam was investigated. CNT showed a 700% sorption capacity in light oils (almost 7 goil/gfoam in kerosene); on the contrary, char foam evidenced the higher sorption efficiency in heavier oils; in particular, it reaches 130% in pump oil (1.3 goil/gfoam). All the filled foams are reusable. The reuse increases the foam efficiency and decreases the economic and environmental impacts.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboul-Gheit. (2006). Adsorption of spilled oil from seawater by waste plastic. Oil & Gas Science and Technology-Rev. IFP, 61(2), 259–268.
Adebajo, M. O., Frost, R. L., Kloprogge, J. T., Carmody, O., & Kokot, S. (2003). Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: a review of synthesis and absorbing properties. Journal of Porous Materials, 10(3), 159–170.
Al-Majed, A. A., Adebayo, A. R., & Hossain, M. E. (2012). A sustainable approach to controlling oil spills. Journal of Environmental Management, 113, 213–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.07.034.
Baughman, R. H. (2002). Carbon nanotubes—the route toward applications. Science, 297(5582), 787–792. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1060928.
Calabrese, L., Bonaccorsi, L., Freni, A., & Proverbio, E. (2017a). Silicone composite foams for adsorption heat pump applications. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 12, 27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2017.04.002.
Calabrese, L., Bonaccorsi, L., Freni, A., & Proverbio, E. (2017b). Synthesis of SAPO-34 zeolite filled macrocellular foams for adsorption heat pump applications: a preliminary study. Applied Thermal Engineering, 124, 1312–1318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.06.121.
Calabrese, L., Bonaccorsi, L., Bruzzaniti, P., Freni, A., & Proverbio, E. (2018). Morphological and functional aspects of zeolite filled siloxane composite foams. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 135(2), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.45683.
Choi, H. (1992). Natural sorbents in oil spill cleanup, 26(4), 772–776. doi:https://doi.org/10.1021/es00028a016.
Daling, P. S., & Strom, T. (1999). Weathering of oils at sea: model/field data comparisons. Spill Science & Technology Bulletin, 5(1), 63–74.
Fazio, E., Piperopoulos, E., Abdul Rahim, S. H., Lanza, M., Faggio, G., Mondio, G., et al. (2013). Correlation between carbon nanotube microstructure and their catalytic efficiency towards the p-coumaric acid degradation. Current Applied Physics, 13(4). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2012.11.016.
Graham, L. J., Hale, C., Maung-Douglass, E., Sempier, S., Swann, L., & Wilson, M. (2016). Oil spill science: Chemical dispersant and their role in oil spill response. MASGP-15-015.
Gui, X., Li, H., Wang, K., Wei, J., Jia, Y., Li, Z., et al. (2011). Recyclable carbon nanotube sponges for oil absorption. Acta Materialia, 59(12), 4798–4804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2011.04.022.
Guo, P., Saw, W. L., Van Eyk, P. J., Stechel, E. B., De Nys, R., Ashman, P. J., & Nathan, G. J. (2017). Gasification reactivity and physicochemical properties of the chars from raw and torrefied wood, grape marc, and macroalgae. Energy and Fuels, 31(3), 2246–2259. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b02215.
Gupta, Vinod K., & Saleh, T. A. (2013). Sorption of pollutants by porous carbon, carbon nanotubes and fullerene- an overview. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. Springer. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-1524-1.
Gupta, S., & Tai, N. H. (2016). Carbon materials as oil sorbents: a review on the synthesis and performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. Royal Society of Chemistry. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta08321d.
Gupta, Vinod Kumar, Ali, I., Saleh, T. A., Nayak, A., & Agarwal, S. (2012). Chemical treatment technologies for waste-water recycling - an overview. RSC Advances. Royal Society of Chemistry. doi:https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ra20340e.
Gupta, Vinod Kumar, Kumar, R., Nayak, A., Saleh, T. A., & Barakat, M. A. (2013). Adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution onto carbon nanotubes: a review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science. Elsevier B.V. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2013.03.003.
Gupta, S., Da He, W., & Tai, N. H. (2016). A comparative study on superhydrophobic sponges and their application as fluid channel for continuous separation of oils and organic solvents from water. Composites Part B: Engineering, 101, 99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.06.002.
Kakhramanly, Y. N., & Azizov, A. G. (2014). Mechanism of crude oil and petroleum-product sorption from water surfaces by random polypropylene based polymer foam sorbents. Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils, 49(6), 545–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-014-0482-8.
Messina, G., Modafferi, V., Santangelo, S., Tripodi, P., Donato, M. G., Lanza, M., et al. (2008). Large-scale production of high-quality multi-walled carbon nanotubes: role of precursor gas and of Fe-catalyst support. Diamond and Related Materials, 17, 1482–1488.
Milone, C., Piperopoulos, E., Ansari, S., Faggio, G., & Santangelo, S. (2015). Highly versatile and efficient process for CNT oxidation in vapor phase by means of Mg(NO3)-HNO3-H2O ternary mixture. Fullerenes, Nanotubes, and Carbon Nanostructures, 23(1), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1080/1536383X.2013.858132.
Motta, F. L., Stoyanov, S. R., & Soares, J. B. P. (2018). Application of solidifiers for oil spill containment: a review. Chemosphere, 194, 837–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.11.103.
Nartey, O. D., & Zhao, B. (2014). Biochar preparation, characterization, and adsorptive capacity and its effect on bioavailability of contaminants: an overview. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2014, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/715398.
Nwadiogbu, J. O., Ajiwe, V. I. E., & Okoye, P. A. C. (2016). Removal of crude oil from aqueous medium by sorption on hydrophobic corncobs: equilibrium and kinetic studies, 10, 56–63.
Olga, V. R., Darina, V. I., Alexandr, A. I., & Alexandra, A. O. (2014). Cleanup of water surface from oil spills using natural sorbent materials. Procedia Chemistry, 10, 145–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2014.10.025.
Piperopoulos, E., Calabrese, L., Mastronardo, E., Proverbio, E., & Milone, C. (2018a). Synthesis of reusable silicone foam containing carbon nanotubes for oil spill remediation. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 135, 46067–46078. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46067.
Piperopoulos, E., Calabrese, L., Mastronardo, E., Rahim, S. H. A., Proverbio, E., & Milone, C. (2018b). Assessment of sorption kinetics of carbon nanotube-based composite foams for oil recovery application. Jounal of Applied Polymer Science. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47374.
Ren, X., Chen, C., Nagatsu, M., & Wang, X. (2011). Carbon nanotubes as adsorbents in environmental pollution management: a review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 170, 395–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.08.045.
Sakthivel, T., Reid, D. L., Goldstein, I., Hench, L., & Seal, S. (2013). Hydrophobic high surface area zeolites derived from fly ash for oil spill remediation. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(11), 5843–5850. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3048174.
Saleem, J, Bazargan, A., Barford, J., & Mckay, G. (2014). Oil spill remedy using bi-axially oriented polymer films. In Water Pollution XII (pp. 145–152).
Saleem, J., Ning, C., Barford, J., & Mckay, G. (2015). Combating oil spill problem using plastic waste. Waste Management, 44, 34–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.06.003.
Tewari, S., & Sirvaiya, A. (2015). Oil spill remediation and its regulation. International Journal Of Engineering Research and General Science, 1(6), 2394–8299.
Worthington, M. J. H., J, S. C., J, E. L., A, C. J., T, G. C., K, L. S., et al. (2018). Sustainable polysulfides for oil spill remediation: repurposing industrial waste for environmental benefit. Advanced Sustainable Systems, 2(6), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.201800024.
Yan, Q., Toghiani, H., Cai, Z., & Zhang, J. (2014). Formation of nanocarbon spheres by thermal treatment of woody char from fast pyrolysis process. Wood and Fiber Science, 46(4), 437–450.
Zhao, X., Li, L., Li, B., Zhang, J., & Wang, A. (2014). Durable superhydrophobic/superoleophilic PDMS sponges and their applications in selective oil absorption and in plugging oil leakages. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2(43), 18281–18287. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta04406a.
Zheng Yongmei, Cheng Qunfeng, Hou Yong**, Y. C. (2015). Bio-inspired wettability surfaces: developments in micro- and nanostructures. https://www.crcpress.com/Bio-Inspired-Wettability-Surfaces-Developments-in-Micro%2D%2Dand-Nanostructures/Yongmei-Qunfeng-Yong**-Chen/p/book/9789814463607. Accessed 6 December 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piperopoulos, E., Calabrese, L., Mastronardo, E. et al. Sustainable Reuse of Char Waste for Oil Spill Recovery Foams. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 293 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04671-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04671-2