Abstract
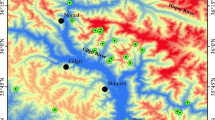
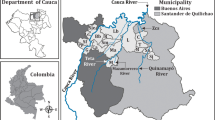
Buyat Bay (BB), North Sulawesi, Indonesia, was a submarine tailings disposal (STD) site for an industrial gold mine that extracted mercury (Hg)-containing ores from 1996 to 2004. To evaluate the distribution and influence of such a Hg release into the environment, particularly into BB, we quantified the total mercury (THg) and methyl mercury (MeHg) in the surface sediments (beach, river estuary, and marine) and biota of the bay, as well as the scalp hair of residents in the adjacent community. A nearby body of water, Totok Bay, polluted by Hg from artisanal gold mining, and a reference area of the Bajo Coast (Bajo) free of any anthropogenic sources of Hg were also sampled. Both THg and MeHg were detected in all samples measured showed concentrations to be highest at the artisanal mining site, intermediate at the STD site and at their lowest in the control area. THg and MeHg concentrations in marine biota and human hair increased with trophic levels and were significantly higher at the STD site than among the controls. Besides examining the source and distribution of Hg, its accumulation in biota, and its potential impact on humans, we also studied the role of the mine management so as to provide a recommendation for future actions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi, H., & Nishimura, H. (1991). Speciation of mercury in the environment. In T. Suzuki, N. Imura & T. W. Clarkson (Eds.), Advances in Mercury Toxicology (pp. 53–76). New York: Plenum.
Akagi, H., Malm, O., Branches, F. J. P., Kinjo, Y., Kashima, Y., Guimaraes, J. R. D., et al. (1995). Human exposure to mercury due to gold-mining in the Tapajos river basin, Amazon, Brazil: Speciation of mercury in human hair, blood and urine. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 80, 85–94.
Baker, R. F., Blanchfield, P. J., Paterson, M. J., Flett, R. J., & Wesson, L. (2004). Evaluation of nonlethal methods for the analysis of mercury in fish tissue. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, 133, 568–576.
Blackwood, G. M., & Edinger, E. N. (2007). Mineralogy and trace element relative solubility patterns of shallow marine sediments affected by submarine tailings disposal and artisanal gold mining, Buyat–Ratototok district, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Environmental Geology, 52, 803–818.
Blanchette, M. C., Hynes, T. P., Kwong, Y. T. J., Anderson, M. R., Veinott, G., Payne, J. F., et al. (2001). A chemical and ecotoxicological assessment of the impact of marine tailings disposal. Tailings and Mine Waste ‘01. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp. 323–331.
Bustamante, P., Lahaye, V., Durnez, C., Churlaud, C., & Caurant, F. (2006). Total and organic Hg concentrations in cephalopods from the North Eastern Atlantic waters: Influence of geographical origin and feeding ecology. Science of the Total Environment, 368, 585–596.
De Lacerda, L. D. (2003). Updating global Hg emissions from small-scale gold mining and assessing its environmental impacts. Environmental Geology, 43, 308–314.
De Lacerda, L. D., & Salomons, W. (1998). Mercury from gold and silver mining: A chemical time bomb? (p. 146). Berlin: Springer.
De Luna, C. J., & Rosales-Hoz, L. (2004). Heavy metals in tissues of gray whales Eschrichtius robustus, and in sediments of Ojo de Lebre Lagoon in Mexico. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72, 460–466.
Desta, Z., Borgstrøm, R., Rosseland, B. O., & Dadebo, E. (2007). Lower than expected mercury concentration in piscivorous African sharptooth catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell). Science of the Total Environment, 376, 134–142.
Dickman, M. D., Leung, K. M. C., & Koo, L. C. L. (1999). Mercury in human hair and fish: Is there a Hong Kong male sub-fertility connection? Marine Pollution Bulletin, 9(1–12), 352–356.
Edinger, E. N., Siregar, P. R., & Blackwood, G. M. (2007). Heavy metal concentrations in shallow marine sediments affected by submarine tailings disposal and artisanal gold mining, Buyat–Ratototok district, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Environmental Geology, 52, 701–714.
Effendi, A. C. (1978). Geologic map of the Manado Quadrangle. North Sulawesi: Geological Survey of Indonesia.
Fowler, J., & Cohen, L. (1990). Practical statistics for field biology (p. 227). England: Wiley.
Frery, N., Maury-Brachet, R., Maillot, E., Deheeger, M., de Merona, B., & Boudou, A. (2001). Gold-mining activities and mercury contamination of native Amerindian communities in French Guiana: Key role of fish in dietary uptake. Environmental Health Perspectives, 109(5), 449–456.
Gemici, U. (2004). Impact of acid mine drainage from the abandoned Halikoy Mercury Mine (Western Turkey) on surface and groundwaters. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72, 482–489.
Goulet, R. R., Holmes, J., Page, B., Poissant, L., Siciliano, S. D., Lean, D. R. S., et al. (2007). Mercury transformations and fluxes in sediments of a riverine wetland. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71, 3393–3406.
Hammerschmidt, C., & Fitzgerald, W. F. (2004). Geochemical controls on the production and distribution of methylmercury in near-shore marine sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 1487–1495.
Hendrayana, H. (2005). Geology of Kotabunan and Ratatotk Districts and relationship with hydrogeology. Conference Proceeding. International Seminar on Mining, Environment, and Sustainable Development: a lesson from the gold mining controversy in Buyat Bay, North Sulawesi, Indonesia, Manado, Indonesia, 32 pp.
Ikingura, J. R., & Akagi, H. (1999). Methylmercury production and distribution in aquatic systems. Science of the Total Environment, 234, 109–118.
James, L. P. (1994). The mercury “tromol” mill: An innovative gold recovery technique, and a possible environmental concern. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 50, 493–500.
JPHA (2001). Preventive measures against environmental mercury pollution and its health effects (p. 112). Japan: Japan Public Health Association.
Kambey, J. L., Farrell, A. P., & Bendell-Young, L. I. (2001). Influence of illegal gold mining on mercury levels in fish of North Sulawesi’s Minahasa Peninsula (Indonesia). Environmental Pollution, 114, 299–302.
Kerebungu, F. (2005). Social environmental study on people of Buyat. Conference Proceeding. International Seminar on Mining, Environment, and Sustainable Development: A lesson from the gold mining controversy in Buyat Bay, North Sulawesi, Indonesia, Manado, Indonesia, 104–111.
Limbong, D., Kumampung, J., Rimper, J., Arai, T., & Miyazaki, N. (2003). Emission and environmental implications of mercury from artisanal gold mining in north Sulawesi, Indonesia. Science of the Total Environment, 302, 227–236.
Malm, O. (1998). Gold mining as a source of mercury exposure in the Brazilian Amazon. Environmental Research, A7, 73–78.
Mason, R. P., Morel, F. M. M., & Hemond, H. F. (1995). The role of microorganisms in elemental mercury formation in natural waters. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 80, 775–787.
Matsuyama, A., Liya, Q., Yasutake, A., Yamaguchi, M., Aramaki, R., **aojie, L., et al. (2004). Distribution of methylmercury in an area polluted by mercury containing wastewater from an organic chemical factory in China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 73, 846–852.
Ogola, J. S., Mitullah, W. V., & Omulo, M. A. (2002). Impact of gold mining on the environmental and human health: A case study in the Migori Gold Belt, Kenya. Environmental Geochemistry & Health, 24, 141–158.
Pacyna, E. G., Pacyna, J. M., Fudala, J., Strzelecka-Jastrzab, E., Hlawiczka, S., & Panasiuk, D. (2006). Mercury emissions to the atmosphere from anthropogenic sources in Europe in 2000 and their scenarios until 2020. Science of the Total Environment, 370, 147–156.
Pfeiffer, W. C., & Lacerda, L. D. (1988). Mercury inputs into the Amazon Region, Brazil. Environmental Technology Letters, 9, 325–330.
Turner, S. J., Flindell, P. A., Hendri, D., Hardjana, I., Lauricella, P. F., Lindsay, R. P., et al. (1994). Sediment-hosted gold mineralisation in the Ratatotok District, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 50, 317–336.
Williams, T. M., Weeks, J. M., Apostol, A. N., Jr., & Miranda, C. R. (1999). Assessment of mercury contamination and human exposure associated with coastal disposal of waste from cinnabar mining operation, Palawan, Philippines. Environmental Geology, 39(1), 51–60.
Yasuda, Y., Matsuyama, A., Yasutake, A., Yamaguchi, M., Aramaki, R., **aojie, L., et al. (2004). Mercury distribution in farmlands downstream from an acetaldehyde producing chemical company in Qingzhen City, Guizhou, People’s Republic of China. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 72, 445–451.
Yokoo, E. M., Valente, J. G., Grattan, L., Schmidt, S. L., Platt, I., & Silbergeld, E. K. (2003). Low level methylmercury exposure affects neuropsychological function in adults (p. 11). Environmental Health: A Global Access Science Source. License BioMed Central Ltd.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the National Institute for Minamata Disease (NIMD), Japan, and the Faculty of Fisheries and Marine Sciences, Sam Ratulangi University, Indonesia, for supporting this investigation. Additional support was provided by an NSERC Discovery Grant and by Memorial University internal grants to the third author. We are also grateful to Mr. Tsuruda who provided variable assistance in the laboratory at the Natural Sciences Laboratory, NIMD. This paper is dedicated to the memory of Baby Andini.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lasut, M.T., Yasuda, Y., Edinger, E.N. et al. Distribution and Accumulation of Mercury Derived from Gold Mining in Marine Environment and Its Impact on Residents of Buyat Bay, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Water Air Soil Pollut 208, 153–164 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0155-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0155-0