Abstract
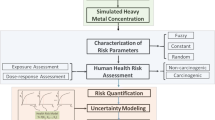
This study presented an integrated approach for evaluating environmental risks associated with hydrocarbon-contaminated sites through incorporation of a multiphase multi-component modeling system within a general risk assessment framework. The uncertainties associated with risk evaluation criteria were emphasized and effectively addressed through the development of a fuzzy-set approach. This development was based on (a) simulation of the fate of the contaminant in the subsurface to calculate contaminant concentrations in groundwater; (b) examination of the excess lifetime cancer risk (ELCR) distributions; (c) quantification of uncertainties in ELCR evaluation criteria using fuzzy membership functions; (d) categorization of the related risk levels into low, low-to-medium, medium, medium-to-high, and high, and (e) assessment of risk levels based on ELCR distribution and fuzzy evaluation criteria. The developed fuzzy risk assessment approach (FRA) was applied to a hydrocarbon-contaminated site in western Canada. Three remediation scenarios with different efficiencies (0, 60, and 90%) and planning periods (10, 20, 40, and 60 years later) were considered, and the spatial and temporal variations of risk values were examined. The temporal variation of membership values for different risk levels at locations of interest was also identified. The FRA is useful for the decision maker to gain insight into the environmental risks by considering uncertainties and to make more realistic remediation decisions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batchelor, B., Valdés, J. and Araganth, V.: 1998, ‘Stochastic risk assessment of sites contaminated by hazardous wastes’, J. Environ. Eng. 124, 380–388.
Bennett, D. H., James, A. L., McKone, T. E. and Oldenburg, C. M.: 1998, ‘On uncertainty in remediation analysis: Variance propagation from subsurface transport to exposure modeling’, Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safe. 62, 117–129.
Chen, S. J., Hwang, C. L., Beckmann, M. J. and Krelle, W.: 1992, Fuzzy Multiple Attribute Decision Making: Methods and Applications, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Chen, Z., Huang, G. H. and Chakma, A.: 2000, ‘Risk assessment of a petroleum-contaminated site through a multi-phase and multi-component modeling approach’, J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 26, 273–282.
Chen, Z., Huang, G. H. and Chakma, A.: 2003, ‘Hybrid fuzzy-stochastic modeling approach for assessing environmental risks at contaminated groundwater systems’, J. Environ. Eng. 129, 79–88.
Cheng, S.: 2000, ‘Development of a Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision Support System for Municiapl Solid Waste Management’, M.ASc. thesis, University of Regina, Regina, Canada.
Cho, H. N., Choi, H. H. and Kim, Y. B.: 2002, ‘A risk assessment methodology for incorporating uncertainties using fuzzy concepts’, Reliab. Eng. Syst. Safety. 78, 173–183.
Duke, L. D. and Taggart, M.: 2000, ‘Uncertainty factors in screening ecological risk assessments’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 19, 1668–1680.
Johnson, B. B. and Slovic, P.: 1998, ‘Lay views on uncertainty in environmental health risk assessment’, J. Risk Res. 1, 261–279.
Labieniec, P. A., Dzombak, D. A. and Siegrist, R. L.: 1997, ‘Evaluation of uncertainty in a site-specific risk assessment’, J. Environ. Eng. 123, 234–243.
Lai, Y. J. and Hwang, C. L.: 1992, Fuzzy Mathematical Programming Methods and Applications, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Lee, L. J. H., Chan, C. C., Chung, C. W., Ma, Y. C., Wang, G. S. and Wang, J. D.: 2002, ‘Health risk assessment on residents exposed to chlorinated hydrocarbons contaminated in groundwater of a hazardous waste site’, J. Toxicol. Environ. Health., Part A 65, 219–235.
Lee, Y. W., Dahab, M. F. and Bogardi, I.: 1995, ‘Nitrate-risk assessment using fuzzy-set approach’, J. Environ. Eng. 121, 245–256.
Li, J. B.: 2003, ‘Development of an Inexact Environmental Modeling System for the Management of Petroleum-Contaminated Sites’, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Regina, Regina, SK, Canada.
Li, J. B., Huang, G. H., Chakma, A., Zeng, G. M. and Liu, L.: 2003, ‘Integrated fuzzy-stochastic modeling of petroleum contamination in subsurface’, Energy Sources 25, 547–563.
Mohamed, A. M. O. and Cote, K.: 1999, ‘Decision analysis of polluted sites – a fuzzy set approach’, Waste Manage. 19, 519–533.
NRTEE (National Round Table on the Environment and the Economy): 1997, ‘Contaminated Site Issues in Canada: Backgrounder’, Ottawa, Canada.
USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency): 1989, ‘Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Volume I: Human Health Evaluation Manual (Part A)’, USEPA 540/1-89/002, Washington, D.C.
USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency): 1992, ‘Guidelines for Exposure Assessment’, USEPA 600Z-92/001, Washington, DC.
USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency): 2004, ‘Integrated Risk Information System: Benzene (CASRN 71-43-2)’, http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0276.htm, accessed on July 12, 2004.
UTA (University of Texas at Austin): 2000, ‘Technical Documentation for UTCHEM-9.0: A Three-Dimensional Chemical Flood Simulator’, Center for Petroleum and Geosystems Engineering, University of Texas at Austin, TX.
Wang, T. A. and McTernan, W. F.: 2002, ‘The development and application of a multilevel decision analysis model for the remediation of contaminated groundwater under uncertainty’, J. Environ. Manage. 64, 221–235.
Zadeh, L. A.: 1965, ‘Fuzzy sets’, Inf. Control. 8, 338–353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Liu, L., Huang, G. et al. A Fuzzy-Set Approach for Addressing Uncertainties in Risk Assessment of Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Site. Water Air Soil Pollut 171, 5–18 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-9005-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-9005-x