Abstract
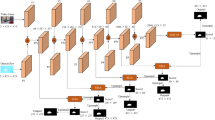
Static and moving objects often occur in real-life videos. Most video object segmentation methods only focus on extracting and exploiting motion cues to perceive moving objects. Once faced with the frames of static objects, the moving object predictors may predict failed results caused by uncertain motion information, such as low-quality optical flow maps. Besides, different sources such as RGB, depth, optical flow and static saliency can provide useful information about the objects. However, existing approaches only consider either the RGB or RGB and optical flow. In this paper, we propose a novel adaptive multi-source predictor for zero-shot video object segmentation (ZVOS). In the static object predictor, the RGB source is converted to depth and static saliency sources, simultaneously. In the moving object predictor, we propose the multi-source fusion structure. First, the spatial importance of each source is highlighted with the help of the interoceptive spatial attention module (ISAM). Second, the motion-enhanced module (MEM) is designed to generate pure foreground motion attention for improving the representation of static and moving features in the decoder. Furthermore, we design a feature purification module (FPM) to filter the inter-source incompatible features. By using the ISAM, MEM and FPM, the multi-source features are effectively fused. In addition, we put forward an adaptive predictor fusion network (APF) to evaluate the quality of the optical flow map and fuse the predictions from the static object predictor and the moving object predictor in order to prevent over-reliance on the failed results caused by low-quality optical flow maps. Experiments show that the proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on three challenging ZVOS benchmarks. And, the static object predictor precisely predicts a high-quality depth map and static saliency map at the same time.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achanta, R., Hemami, Sheila, Estrada, F., & Süsstrunk, S. (2009). Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In CVPR (pp. 1597–1604).
An, N., Zhao, X.-G., & Hou, Z.-G. (2016). Online rgb-d tracking via detection-learning-segmentation. In ICPR (pp. 1231–1236).
Chen, Q., Liu, Z., Zhang, Y., Fu, K., Zhao, Q., & Du, H. (2021). Rgb-d salient object detection via 3d convolutional neural networks. In AAAI (pp. 1063–1071).
Chen, Q., Liu, Z., Zhang, Y., Fu, K., Zhao, Q., & Du, H. (2021). Rgb-d salient object detection via 3d convolutional neural networks. In AAAI (pp. 1063–1071).
Chen, X., Lin, K.-Y., Wang, J., Wu, W., Qian, C., Li, H., & Zeng, G. (2020). Bi-directional cross-modality feature propagation with separation-and-aggregation gate for rgb-d semantic segmentation. In ECCV (pp. 561–577).
Cheng, J., Tsai, Y.-H., Wang, S., & Yang, M.-H. (2017). Segflow: Joint learning for video object segmentation and optical flow. In ICCV (pp. 686–695).
Cheng, Y., Cai, R., Li, Z., Zhao, X., & Huang, K. (2017). Locality-sensitive deconvolution networks with gated fusion for rgb-d indoor semantic segmentation. In CVPR (pp. 3029–3037).
Cheng, Y., Fu, H., Wei, X., **ao, J., & Cao, X. (2014). Depth enhanced saliency detection method. In ICIMCS (p. 23)
De Boer, P.-T., Kroese, D. P., Mannor, S., & Rubinstein, R. Y. (2005). A tutorial on the cross-entropy method. Annals of operations research, 134, 19–67.
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., & Fei-Fei, L. (2009). Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In CVPR (pp. 248–255).
Deng, Z., Hu, X., Zhu, L., Xu, X., Qin, J., Han, G., & Heng, P.-A. (2018). R3net: Recurrent residual refinement network for saliency detection. In IJCAI (pp. 684–690).
Faisal, M., Akhter, I., Ali, M., & Hartley, R. (2019). Exploiting geometric constraints on dense trajectories for motion saliency. 3(4). ar**v preprint ar**v:1909.13258
Fan, D.-P., Cheng, M.-M., Liu, Y., Li, T., & Borji, A. (2017). Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps. In ICCV (pp. 4548–4557).
Fan, D.-P., Gong, C., Cao, Y., Ren, B., Cheng, M.-M., & Borji, A. (2018). Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. ar**v preprint ar**v:1805.10421).
Fan, D.-P., Lin, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhu, M., & Cheng, M.-M. (2020). Rethinking rgb-d salient object detection: Models, data sets, and large-scale benchmarks. IEEE TNNLS, 32, 2075–2089.
Fan, D.-P., Zhai, Y., Borji, A., Yang, J., & Shao, L. (2020). Bbs-net: Rgb-d salient object detection with a bifurcated backbone strategy network. In ECCV (pp. 275–292).
Fan, D.-P., Zhai, Y., Borji, A., Yang, J., & Shao, L. (2020). Bbs-net: Rgb-d salient object detection with a bifurcated backbone strategy network. In ECCV (pp. 275–292).
Fu, K., Fan, D.-P., Ji, G.-P., & Zhao, Q. (2020). Jl-dcf: Joint learning and densely-cooperative fusion framework for rgb-d salient object detection. In CVPR (pp. 3052–3062).
Fu, K., Fan, D.-P., Ji, G.-P., & Zhao, Q. (2020). Jl-dcf: Joint learning and densely-cooperative fusion framework for rgb-d salient object detection. In CVPR (pp. 3052–3062).
Fu, K., Fan, D.-P., Ji, G.-P., & Zhao, Q. (2020). Jl-dcf: Joint learning and densely-cooperative fusion framework for rgb-d salient object detection. In CVPR (pp. 3052–3062).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2015). Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification. In ICCV (pp. 1026–1034).
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In CVPR (pp. 770–778).
Hou, Q., Cheng, M.-M., Hu, X., Borji, A., Tu, Z., & Torr, P. H. S. (2017). Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In CVPR (pp. 3203–3212).
Hui, T.-W., Tang, X., & Change Loy, C. (2018). Liteflownet: A lightweight convolutional neural network for optical flow estimation. In CVPR (pp. 8981–8989).
Jain, S. D., **ong, B., and Grauman, K. (2017). Fusionseg: Learning to combine motion and appearance for fully automatic segmentation of generic objects in videos. In CVPR (pp. 2117–2126).
Ji, G.-P., Fu, K., Wu, Z., Fan, D.-P., Shen, J., & Shao, L. (2021). Full-duplex strategy for video object segmentation. In ICCV (pp. 4922–4933)
Ji, W., Li, J., Yu, S., Zhang, M., Piao, Y., Yao, S., Bi, Q., Ma, K., Zheng, Y., Lu, H., et al. (2021). Calibrated rgb-d salient object detection. In CVPR (pp. 9471–9481).
Ji, W., Li, J., Yu, S., Zhang, M., Piao, Y., Yao, S., Bi, Q., Ma, K., Zheng, Y., Lu, H., et al. (2021). Calibrated rgb-d salient object detection. In CVPR (pp. 9471–9481).
Ji, W., Li, J., Zhang, M., Piao, Y., & Lu, H. (2020). Accurate rgb-d salient object detection via collaborative learning. In ECCV (pp. 52–69).
Ji, W., Li, J., Zhang, M., Piao, Y., & Lu, H. (2020). Accurate rgb-d salient object detection via collaborative learning. In ECCV (pp. 52–69)
Ju, R., Ge, L., Geng, W., Ren, T., & Wu, G. (2014). Depth saliency based on anisotropic center-surround difference. In ICIP (pp. 1115–1119).
Jun Koh, Y., & Kim, C.-S. (2017). Primary object segmentation in videos based on region augmentation and reduction. In CVPR (pp. 3442–3450).
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. ar**v preprint ar**v:1412.6980.
Li, S., Seybold, B., Vorobyov, A., Lei, X., & Jay Kuo, C.-C. (2018). Unsupervised video object segmentation with motion-based bilateral networks. In ECCV (pp. 207–223).
Lin, T.-Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., & Belongie, S. (2017). Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In CVPR (pp. 2117–2125).
Liu, H., Wenshan, W., Wang, X., & Qian, Y. (2018). Rgb-d joint modelling with scene geometric information for indoor semantic segmentation. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 77, 22475–22488.
Liu, J.-J., Hou, Q., Cheng, M.-M., Feng, J., & Jiang, J. (2019). A simple pooling-based design for real-time salient object detection. In CVPR (pp. 3917–3926).
Liu, W., Rabinovich, A., & Berg, A.C. (2015). Parsenet: Looking wider to see better. ar**v preprint ar**v:1506.04579
Lu, X., Wang, W., Ma, C., Shen, J, Shao, Ling, & Porikli, F. (2019). See more, know more: Unsupervised video object segmentation with co-attention siamese networks. In CVPR (pp. 3623–3632).
Lukezic, A., Kart, U., Kapyla, J., Durmush, A., Kamarainen, J.-K., Matas, J., & Kristan, M. (2019). Cdtb: A color and depth visual object tracking dataset and benchmark. In ICCV (pp. 10013–10022).
Niu, Y., Geng, Y., Li, X., & Liu, F. (2012). Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis. In CVPR (pp. 454–461).
Ocal, M., & Mustafa, A. (2020). Realmonodepth: Self-supervised monocular depth estimation for general scenes. ar**v preprint ar**v:2004.06267.
Ochs, P., Malik, J., & Brox, T. (2013). Segmentation of moving objects by long term video analysis. IEEE TPAMI, 36, 1187–1200.
Pang, Y., Zhang, L., Zhao, X., & Lu, H. (2020). Hierarchical dynamic filtering network for rgb-d salient object detection. In ECCV (pp. 235–252).
Pang, Y., Zhang, L., Zhao, X., & Lu, H. (2020). Hierarchical dynamic filtering network for rgb-d salient object detection. In ECCV (pp. 235–252).
Pang, Y., Zhao, X., Zhang, L., & Lu, H. (2020). Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection. In CVPR (pp. 9413–9422).
Papazoglou, A., & Ferrari, V. (2013). Fast object segmentation in unconstrained video. In ICCV (pp. 1777–1784).
Paszke, A., Gross, S., Massa, F., Lerer, A., Bradbury, J., Chanan, G., Killeen, T., Lin, Z., Gimelshein, N., Antiga, L., Desmaison, A., Kopf, A., Yang, E., DeVito, Z., Raison, M., Tejani, A., Chilamkurthy, S., Steiner, B., Fang, L., Bai, J., & Chintala, S. (2019). Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In NeurIPS, (Vol. 32)
Peng, H., Li, B., **ong, W., Hu, W., & Ji, R. (2014). Rgbd salient object detection: A benchmark and algorithms. In ECCV (pp. 92–109).
Perazzi, F., Krähenbühl, P., Pritch, Y., & Hornung, A. (2012). Saliency filters: Contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In CVPR (pp. 733–740).
Perazzi, F., Pont-Tuset, J., McWilliams, B., Van Gool, L., Gross, M., & Sorkine-Hornung, A. (2016). A benchmark dataset and evaluation methodology for video object segmentation. In CVPR (pp. 724–732).
Piao, Y., Ji, W., Li, J., Zhang, M., & Lu, H. (2019). Depth-induced multi-scale recurrent attention network for saliency detection. In ICCV (pp. 7254–7263).
Pillai, S., Ambruş, R., & Gaidon, A. (2019). Superdepth: Self-supervised, super-resolved monocular depth estimation. In ICRA (pp. 9250–9256).
Prest, A., Leistner, C., Civera, J., Schmid, C., & Ferrari, V. (2012). Learning object class detectors from weakly annotated video. In CVPR (pp. 3282–3289).
Qin, X., Zhang, Z., Huang, C., Dehghan, M., Zaiane, O. R., & Jagersand, M. (2020). U2-net: Going deeper with nested u-structure for salient object detection. Pattern Recognition, 106, 107404.
Qin, X., Zhang, Z., Huang, C., Gao, C., Dehghan, M., & Jagersand, M. (2019). Basnet: Boundary-aware salient object detection. In CVPR (pp. 7479–7489).
Ranftl, R., Lasinger, K., Hafner, D., Schindler, K., & Koltun, V. (2020). Towards robust monocular depth estimation: Mixing datasets for zero-shot cross-dataset transfer. In IEEE TPAMI.
Ranjan, A., & Black, M.J. (2017). Optical flow estimation using a spatial pyramid network. In CVPR (pp. 4161–4170).
Rasoulidanesh, M., Yadav, S., Herath, S., Vaghei, Y., & Payandeh, S. (2019). Deep attention models for human tracking using rgbd. Sensors, 19, 750.
Ren, S., Liu, W., Liu, Y., Chen, H., Han, G., & He, S. (2021). Reciprocal transformations for unsupervised video object segmentation. In CVPR (pp. 15455–15464).
Siam, M., Jiang, C., Lu, S., Petrich, L., Gamal, M., Elhoseiny, M., & Jagersand, M. (2019). Video object segmentation using teacher-student adaptation in a human robot interaction (hri) setting. In ICRA (pp. 50–56).
Song, H., Wang, W., Zhao, S., Shen, J., & Lam, K.-M. (2018). Pyramid dilated deeper convlstm for video salient object detection. In ECCV (pp. 715–731).
Sun, D., Yang, X., Liu, M.Y., & Kautz, J. (2018). Pwc-net: Cnns for optical flow using pyramid, war**, and cost volume. In CVPR (pp. 8934–8943).
Sun, P., Zhang, W., Wang, H., Li, S., & Li, X. (2021). Deep rgb-d saliency detection with depth-sensitive attention and automatic multi-modal fusion. In CVPR (pp. 1407–1417).
Sun, P., Zhang, W., Wang, H., Li, S., & Li, X. (2021). Deep rgb-d saliency detection with depth-sensitive attention and automatic multi-modal fusion. In CVPR (pp. 1407–1417).
Teed, Z., & Deng, J. (2020). Raft: Recurrent all-pairs field transforms for optical flow. In ECCV (pp. 402–419).
Tokmakov, P., Alahari, K., & Schmid, C. (2017). Learning motion patterns in videos. In CVPR (pp. 3386–3394).
Tokmakov, P., Alahari, K., & Schmid, C. (2017). Learning video object segmentation with visual memory. In ICCV (pp. 4481–4490).
Tsai, Y.-H., Zhong, G., & Yang, M.-H. (2016). Semantic co-segmentation in videos. In ECCV (pp. 760–775).
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, L., & Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need. In NeurIPS (pp. 5998-6008)
Wang, W., & Neumann, U. (2018). Depth-aware cnn for rgb-d segmentation. In ECCV (pp. 135–150).
Wang, W., Lu, X., Shen, J., Crandall, D.J., & Shao, L. (2019). Zero-shot video object segmentation via attentive graph neural networks. In ICCV (pp. 9236–9245).
Wang, W., Shen, J., & Porikli, F. (2015). Saliency-aware geodesic video object segmentation. In CVPR (pp. 3395–3402).
Wang, W., Song, H., Zhao, S., Shen, J., Zhao, S., Hoi, S. C. H., & Ling, H. (2019). Learning unsupervised video object segmentation through visual attention. In CVPR (pp. 3064–3074).
Wang, Z., Simoncelli, E. P., & Bovik, A. C. (2003). Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In The Thrity-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers) 2003 (Vol. 2, pp. 1398–1402).
Wei, J., Wang, S., & Huang, Q. (2020). \(\text{F}^3\)net: fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In AAAI (pp. 12321–12328).
Yang, G., & Ramanan, D. (2019). Volumetric correspondence networks for optical flow. In NeurIPS (pp. 794–805).
Yang, S., Zhang, L., Qi, J., Lu, H., Wang, S., & Zhang, X. (2021). Learning motion-appearance co-attention for zero-shot video object segmentation. In ICCV (pp. 1564–1573).
Zhang, L., Dai, J., Lu, H., He, Y., & Wang, G. (2018). A bi-directional message passing model for salient object detection. In CVPR (pp. 1741–1750).
Zhang, L., Zhang, J., Lin, Z., Měch, R., Lu, H., & He, Y. (2020). Unsupervised video object segmentation with joint hotspot tracking. In ECCV (pp. 490–506).
Zhang, X., Wang, T., Qi, J., Lu, H., & Wang, G. (2018). Progressive attention guided recurrent network for salient object detection. In CVPR (pp. 714–722).
Zhang, Z., Cui, Z., Xu, C., Yan, Y., Sebe, N., & Yang, J. (2019). Pattern-affinitive propagation across depth, surface normal and semantic segmentation. In CVPR (pp. 4106–4115).
Zhao, J.-X., Liu, J.-J., Fan, D.-P., Cao, Y., Yang, J., & Cheng, M.-M. (2019). Egnet: Edge guidance network for salient object detection. In ICCV (pp. 8779–8788).
Zhao, J., Zhao, Y., Li, J., & Chen, X. (2020). Is depth really necessary for salient object detection? In ACM MM (pp. 1745–1754).
Zhao, J., Zhao, Y., Li, J., & Chen, X. (2020). Is depth really necessary for salient object detection? In ACM MM (pp. 1745–1754).
Zhao, S., Sheng, Y., Dong, Y., Chang, E. I., Xu, Y., et al. (2020). Maskflownet: Asymmetric feature matching with learnable occlusion mask. In CVPR (pp. 6278–6287).
Zhao, T., & Wu, X. (2019). Pyramid feature attention network for saliency detection. In CVPR (pp. 3085–3094).
Zhao, X., Pang, Y., Yang, J., Zhang, L., & Lu, H. (2021). Multi-source fusion and automatic predictor selection for zero-shot video object segmentation. In ACM MM (pp. 2645–2653).
Zhao, X., Pang, Y., Zhang, L., Lu, H., & Ruan, X. (2022). Self-supervised pretraining for rgb-d salient object detection. In AAAI).
Zhao, X., Pang, Y., Zhang, L., Lu, H., & Zhang, L. (2020). Suppress and balance: A simple gated network for salient object detection. In ECCV (pp. 35–51).
Zhao, X., Zhang, L., Pang, Y., Lu, H., & Zhang, L. (2020). A single stream network for robust and real-time rgb-d salient object detection. In ECCV (pp. 646–662).
Zhen, M., Li, S., Zhou, L., Shang, J., Feng, H., Fang, T., & Quan, L. (2020). Learning discriminative feature with crf for unsupervised video object segmentation. In ECCV (pp. 445–462).
Zhou, T., Fu, H., Chen, G., Zhou, Y., Fan, D.-P., & Shao, L. (2021). Specificity-preserving rgb-d saliency detection. In ICCV (pp. 4681–4691).
Zhou, T., Fu, H., Chen, G., Zhou, Y., Fan, D.-P., & Shao, L. (2021). Specificity-preserving rgb-d saliency detection. In ICCV (pp. 4681–4691).
Zhou, T., Wang, S., Zhou, Y., Yao, Y., Li, J., & Shao, L. (2020). Motion-attentive transition for zero-shot video object segmentation. In AAAI (pp. 13066–13073).
Acknowledgements
**aoqi Zhao and Shijie Chang contributed equally to this work. This work was supported by the National Key R &D Program of China #2018AAA0102001 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China #62276046.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Karteek Alahari.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Chang, S., Pang, Y. et al. Adaptive Multi-Source Predictor for Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 132, 3232–3250 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-024-02024-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-024-02024-8