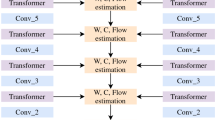
Abstract
The occlusion problem remains a crucial challenge in optical flow estimation (OFE). Despite the recent significant progress brought about by deep learning, most existing deep learning OFE methods still struggle to handle occlusions; in particular, those based on two frames cannot correctly handle occlusions because occluded regions have no visual correspondences. However, there is still hope in multi-frame settings, which can potentially mitigate the occlusion issue in OFE. Unfortunately, multi-frame OFE (MOFE) remains underexplored, and the limited studies on it are mainly specially designed for pyramid backbones or else obtain the aligned previous frame’s features, such as correlation volume and optical flow, through time-consuming backward flow calculation or non-differentiable forward war** transformation. This study proposes an efficient MOFE framework named SplatFlow to address these shortcomings. SplatFlow introduces the differentiable splatting transformation to align the previous frame’s motion feature and designs a Final-to-All embedding method to input the aligned motion feature into the current frame’s estimation, thus remodeling the existing two-frame backbones. The proposed SplatFlow is efficient yet more accurate, as it can handle occlusions properly. Extensive experimental evaluations show that SplatFlow substantially outperforms all published methods on the KITTI2015 and Sintel benchmarks. Especially on the Sintel benchmark, SplatFlow achieves errors of 1.12 (clean pass) and 2.07 (final pass), with surprisingly significant 19.4% and 16.2% error reductions, respectively, from the previous best results submitted. The code for SplatFlow is available at https://github.com/wwsource/SplatFlow.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availibility
All datasets used are publicly available. Code is available at https://github.com/wwsource/SplatFlow.
References
Aslani, S., & Mahdavi-Nasab, H. (2013). Optical flow based moving object detection and tracking for traffic surveillance. International Journal of Electrical, Computer, Energetic, Electronic and Communication Engineering, 7(9), 1252–1256.
Bailer C., Taetz B. & Stricker D. (2015) Flow fields: Dense correspondence fields for highly accurate large displacement optical flow estimation. In ICCV (pp. 4015–4023). IEEE.
Bao W., Lai W.-S., Ma C., Zhang X., Gao Z. & Yang M.-H. (2019) Depth-aware video frame interpolation. In CVPR (pp. 3703–3712). IEEE.
Bar-Haim A. & Wolf L. (2020) Scopeflow: Dynamic scene sco** for optical flow. In CVPR (pp. 7998–8007). IEEE.
Bhat G., Danelljan M., Van Gool L. & Timofte R. (2020) Know your surroundings: Exploiting scene information for object tracking. In ECCV (pp. 205–221). Springer.
Brox T., Bregler C. & Malik J. (2009) Large displacement optical flow. In CVPR (pp. 41–48). IEEE.
Butler D. J., Wulff J. & Stanley G. B., Black M. J. (2012) A naturalistic open source movie for optical flow evaluation. In ECCV (pp. 611–625). Springer.
Caballero J., Ledig C., Aitken A., Acosta A., Totz J., Wang Z. & Shi W. (2017) Real-time video super-resolution with spatio-temporal networks and motion compensation. In CVPR (pp. 4778–4787). IEEE.
Cheng J., Tsai Y.-H., Wang S., & Yang M.-H. (2017) Segflow: Joint learning for video object segmentation and optical flow. In ICCV (pp. 686–695). IEEE.
Choi, Y.-W., Kwon, K.-K., Lee, S.-I., Choi, J.-W., & Lee, S.-G. (2014). Multi-robot map** using omnidirectional-vision slam based on fisheye images. ETRI Journal, 36(6), 913–923.
Cun, X., Xu, F., Pun, C.-M., & Gao, H. (2018). Depth-assisted full resolution network for single image-based view synthesis. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 39(2), 52–64.
Doersch, C., Gupta, A., Markeeva, L., Recasens, A., Smaira, L., Aytar, Y., Carreira, J., Zisserman, A., & Yang, Y. (2022). Tap-vid: A benchmark for tracking any point in a video. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35, 13610–13626.
Doersch C., Yang Y., Vecerik M., Gokay D., Gupta A., Aytar Y., Carreira J. & Zisserman A. (2023) Tapir: Tracking any point with per-frame initialization and temporal refinement. ar**v preprint ar**v:2306.08637
Dosovitskiy A., Fischer P., Ilg E., Hausser P., Hazirbas C., Golkov V., Van Der Smagt P., Cremers D. & Brox T. (2015) Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In ICCV (pp. 2758–2766). IEEE.
Gao C., Saraf A., Huang J.-B. & Kopf J. (2020) Flow-edge guided video completion. In ECCV (pp. 713–729). Springer.
Geiger A., Lenz P., & Urtasun R. (2012) Are we ready for autonomous driving? The Kitti vision benchmark suite. In CVPR (pp. 3354–3361). IEEE.
Gibson J. J. (1950) The perception of the visual world. Houghton Mifflin.
Godard C., Mac Aodha O., & Brostow G. J. (2017) Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency. In CVPR (pp. 270–279). IEEE.
Harley A. W., Fang Z., & Fragkiadaki K. (2022) Particle video revisited: Tracking through occlusions using point trajectories. In ECCV (pp. 59–75). Springer.
Horn, B. K., & Schunck, B. G. (1981). Determining optical flow. Artificial Intelligence, 17(1–3), 185–203.
Hu P., Niklaus S., Sclaroff S., & Saenko K. (2022) Many-to-many splatting for efficient video frame interpolation. In CVPR (pp. 3553–3562). IEEE.
Hui T.-W., Tang X., & Loy C. C. (2018) Liteflownet: A lightweight convolutional neural network for optical flow estimation. In CVPR (pp. 8981–8989). IEEE.
Hui, T.-W., Tang, X., & Loy, C. C. (2020). A lightweight optical flow CNN-revisiting data fidelity and regularization. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 43(8), 2555–2569.
Hur J. & Roth S. (2019) Iterative residual refinement for joint optical flow and occlusion estimation. In CVPR ( pp. 5754–5763). IEEE.
Ilg E., Mayer N., Saikia T., Keuper M., Dosovitskiy A., & Brox T. (2017) Flownet 2.0: Evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks. In CVPR (pp. 2462–2470). IEEE.
Irani, M. (1999). Multi-frame optical flow estimation using subspace constraints. In ICCV (pp. 626–633). IEEE.
Jason J. Y., Harley A. W., & Derpanis K. G. (2016) Back to basics: Unsupervised learning of optical flow via brightness constancy and motion smoothness. In ECCV (pp. 3–10). Springer.
Jiang H., Sun D., Jampani V., Yang M.-H., Learned-Miller E., & Kautz J. (2018) Super Slomo: High quality estimation of multiple intermediate frames for video interpolation. In CVPR (pp. 9000–9008). IEEE.
Jiang S., Campbell D., Lu Y., Li H., & Hartley R. (2021a) Learning to estimate hidden motions with global motion aggregation. In ICCV (pp. 9772–9781). IEEE.
Jiang S., Lu Y., Li H., & Hartley R. (2021b) Learning optical flow from a few matches. In CVPR (pp. 16,592–16,600). IEEE.
Jonschkowski R., Stone A., Barron J. T., Gordon A., Konolige K., & Angelova A. (2020) What matters in unsupervised optical flow. In ECCV (pp. 557–572). Springer.
Kondermann D., Nair R., Honauer K., Krispin K., Andrulis J., Brock A., Gussefeld B., Rahimimoghaddam M., Hofmann S., Brenner C. & Jahne B. (2016). The HCI benchmark suite: Stereo and flow ground truth with uncertainties for urban autonomous driving. In CVPR workshops (pp. 19–28). IEEE.
Li Z., Dekel T., Cole F., Tucker R., Snavely N., Liu C., & Freeman W. T. (2019) Learning the depths of moving people by watching frozen people. In CVPR (pp. 4521–4530). IEEE.
Liu M., He X., & Salzmann M. (2018) Geometry-aware deep network for single-image novel view synthesis. In CVPR (pp. 4616–4624). IEEE.
Liu P., Lyu M., King I., & Xu J. (2019) Selflow: Self-supervised learning of optical flow. In CVPR (pp. 4571–4580). IEEE.
Loshchilov I. & Hutter F. (2017) Decoupled weight decay regularization. ar**, and cost volume. In CVPR (pp. 8934–8943). IEEE.
Sun, D., Yang, X., Liu, M.-Y., & Kautz, J. (2019). Models matter, so does training: An empirical study of CNNs for optical flow estimation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 42(6), 1408–1423.
Tao X., Gao H., Liao R., Wang J., & Jia J. (2017) Detail-revealing deep video super-resolution. In ICCV (pp. 4472–4480). IEEE.
Teed Z. & Deng J. (2020) Raft: Recurrent all-pairs field transforms for optical flow. In ECCV (pp. 402–419). Springer.
Volz S., Bruhn A., Valgaerts L., & Zimmer H. (2011) Modeling temporal coherence for optical flow. In ICCV (pp. 1116–1123). IEEE.
Wang J., Zhong Y., Dai Y., Zhang K., Ji P., & Li H. (2020) Displacement-invariant matching cost learning for accurate optical flow estimation. ar**v preprint ar**v:2010.14851
Wang Y., Yang Y., Yang Z., Zhao L., Wang P., & Xu W. (2018) Occlusion aware unsupervised learning of optical flow. In CVPR (pp. 4884–4893). IEEE.
Weinzaepfel P., Revaud J., Harchaoui Z., & Schmid C. (2013) Deepflow: Large displacement optical flow with deep matching. In ICCV (pp. 1385–1392). IEEE.
Wulff J., Sevilla-Lara L., & Black M. J. (2017) Optical flow in mostly rigid scenes. In CVPR (pp. 4671–4680). IEEE.
Xu H., Yang J., Cai J., Zhang J., & Tong X. (2021) High-resolution optical flow from 1d attention and correlation. In ICCV (pp. 10,498–10,507). IEEE.
Xu, L., Jia, J., & Matsushita, Y. (2011). Motion detail preserving optical flow estimation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 34(9), 1744–1757.
Xu R., Li X., Zhou B., & Loy C. C. (2019) Deep flow-guided video inpainting. In CVPR (pp. 3723–3732). IEEE.
Yang, G., & Ramanan, D. (2019). Volumetric correspondence networks for optical flow. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 32, 794–805.
Yang G. & Ramanan D. (2020) Upgrading optical flow to 3d scene flow through optical expansion. In CVPR (pp. 1334–1343). IEEE.
Ye B., Chang H., Ma B., Shan S., & Chen X. (2022) Joint feature learning and relation modeling for tracking: A one-stream framework. In ECCV (pp. 341–357). Springer.
Yin Z., Darrell T., & Yu F. (2019) Hierarchical discrete distribution decomposition for match density estimation. In CVPR (pp. 6044–6053). IEEE.
Zhang F., Woodford O. J., Prisacariu V. A., & Torr P. H. (2021) Separable flow: Learning motion cost volumes for optical flow estimation. In ICCV (pp. 10,807–10,817). IEEE.
Zhao S., Sheng Y., Dong Y., Chang E. I. & Xu Y., (2020) Maskflownet: Asymmetric feature matching with learnable occlusion mask. In CVPR (pp. 6278–6287). IEEE.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China No. 2021YFB3100800, the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61973311, 62376283 and 62006239, the Defense industrial Technology Development Program (JCKY2020550B003) and the Key Stone grant (JS2023-03) of the National University of Defense Technology (NUDT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Yasuyuki Matsushita.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Zhang, Y., Li, J. et al. SplatFlow: Learning Multi-frame Optical Flow via Splatting. Int J Comput Vis (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-024-01993-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-024-01993-0