Abstract
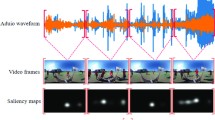
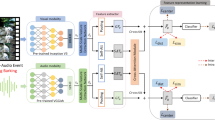
Visual and audio events simultaneously occur and both attract attention. However, most existing saliency prediction works ignore the influence of audio and only consider vision modality. In this paper, we propose a multi-task learning method for audio–visual saliency prediction and sound source localization on multi-face video by leveraging visual, audio and face information. Specifically, we first introduce a large-scale database of multi-face video in visual-audio condition, containing eye-tracking data and sound source annotations. Using this database, we find that sound influences human attention, and conversely attention offers a cue to determine sound source on multi-face video. Guided by these findings, an audio–visual multi-task network (AVM-Net) is introduced to predict saliency and locate sound source. AVM-Net consists of three branches corresponding to visual, audio and face modalities. The visual branch has a two-stream architecture to capture spatial and temporal information. Face and audio branches encode audio signals and faces, respectively. Finally, a spatio-temporal multi-modal graph is constructed to model the interaction among multiple faces. With joint optimization of these branches, the intrinsic correlation of the tasks of saliency prediction and sound source localization is utilized and their performance is boosted by each other. Experiments show that the proposed method outperforms 12 state-of-the-art saliency prediction methods, and achieves competitive results in sound source localization.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Note that the number of faces in each video segment is generally consistent across frames, and therefore \(\{\textbf{F}_t\}_{t=1}^T\) are with the same dimension.
References
Alcázar, J. L., Caba, F., Mai, L., Perazzi, F., Lee, J. Y., Arbeláez, P., & Ghanem, B. (2020). Active speakers in context. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 12465–12474).
Arandjelovic, R., & Zisserman, A. (2018). Objects that sound. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 435–451).
Aytar, Y., Vondrick, C., & Torralba, A. (2016). Soundnet: Learning sound representations from unlabeled video. ar**v preprint ar**v:1610.09001
Bak, C., Kocak, A., Erdem, E., & Erdem, A. (2017). Spatio-temporal saliency networks for dynamic saliency prediction. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 20(7), 1688–1698.
Bellitto, G., ProiettoSalanitri, F., Palazzo, S., Rundo, F., Giordano, D., & Spampinato, C. (2021). Hierarchical domain-adapted feature learning for video saliency prediction. International Journal of Computer Vision, 129, 3216–3232.
Boccignone, G., Cuculo, V., D’Amelio, A., Grossi, G., & Lanzarotti, R. (2018). Give ear to my face: Modelling multimodal attention to social interactions. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV).
Borji, A. (2019). Saliency prediction in the deep learning era: Successes and limitations. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 43, 679–700.
Borji, A., & Itti, L. (2012). State-of-the-art in visual attention modeling. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 35(1), 185–207.
Bylinskii, Z., Judd, T., Oliva, A., Torralba, A., & Durand, F. (2018). What do different evaluation metrics tell us about saliency models? IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 41(3), 740–757.
Cerf, M., Harel, J., Einhäuser, W., & Koch, C. (2008). Predicting human gaze using low-level saliency combined with face detection. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 241–248).
Chakravarty, P., & Tuytelaars, T. (2016). Cross-modal supervision for learning active speaker detection in video. In European conference on computer vision (pp. 285–301). Springer.
Chen, H,, **e, W., Afouras, T., Nagrani, A., Vedaldi, A., & Zisserman, A. (2021). Localizing visual sounds the hard way. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 16867–16876).
Chen, Z. M., Wei, X. S., Wang, P., & Guo, Y. (2019). Multi-label image recognition with graph convolutional networks. In The IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR).
Chung, J. S., & Zisserman, A. (2016). Out of time: Automated lip sync in the wild. In Asian conference on computer vision (pp. 251–263). Springer.
Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Serra, G., & Cucchiara, R. (2018). Predicting human eye fixations via an LSTM-based saliency attentive model. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 27(10), 5142–5154.
Coutrot, A., & Guyader, N. (2013). Toward the introduction of auditory information in dynamic visual attention models. In 2013 14th International workshop on image analysis for multimedia interactive services (WIAMIS) (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Coutrot, A., & Guyader, N. (2014a). An audiovisual attention model for natural conversation scenes. In 2014 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP) (pp. 1100–1104). IEEE.
Coutrot, A., & Guyader, N. (2014). How saliency, faces, and sound influence gaze in dynamic social scenes. Journal of Vision, 14(8), 5.
Coutrot, A., & Guyader, N. (2015). An efficient audiovisual saliency model to predict eye positions when looking at conversations. In 2015 23rd European signal processing conference (EUSIPCO) (pp. 1531–1535). IEEE.
Dosovitskiy, A., Fischer, P., Ilg, E., Häusser, P., Hazırbaş, C., Golkov, V., Van Der Smagt, P., Cremers, D., & Brox, T. (2015). Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). http://lmb.informatik.uni-freiburg.de/Publications/2015/DFIB15
Droste, R., Jiao, J., & Noble, J. A. (2020). Unified image and video saliency modeling. In Proceedings of the 16th European conference on computer vision (ECCV).
Gao, R., Feris, R., & Grauman, K. (2018). Learning to separate object sounds by watching unlabeled video. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 35–53).
Hara, K., Kataoka, H., & Satoh, Y. (2018). Can spatiotemporal 3D CNNs retrace the history of 2D CNNs and imagenet? In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 6546–6555).
Harel, J., Koch, C., & Perona. P. (2007). Graph-based visual saliency. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 545–552)
Hossein Khatoonabadi, S., Vasconcelos, N., Bajic, I. V., & Shan, Y. (2015). How many bits does it take for a stimulus to be salient? In CVPR.
Hu, D., Qian, R., Jiang, M., Tan, X., Wen, S., Ding, E., Lin, W., & Dou, D. (2020). Discriminative sounding objects localization via self-supervised audiovisual matching. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33, 10077–10087.
Huan, X., Shen, C., Boix, X., & Zhao, Q. (2015) Salicon: Reducing the semantic gap in saliency prediction by adapting deep neural networks. In ICCV.
Ioffe, S., & Szegedy, C. (2015) Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In International conference on machine learning, PMLR (pp. 448–456).
Itti, L., Koch, C., & Niebur, E. (1998). A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 11, 1254–1259.
Jain, S., Yarlagadda, P., Jyoti, S., Karthik, S., Subramanian, R., & Gandhi, V. (2020) Vinet: Pushing the limits of visual modality for audio–visual saliency prediction. ar**v preprint ar**v:2012.06170
Jia, R., Wang, X., Pang, S., Zhu, J., & Xue, J. (2020). Look, listen and infer. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM international conference on multimedia (pp. 3911–3919).
Jiang, L., Xu, M., Liu, T., Qiao, M., & Wang, Z. (2018) Deepvs: A deep learning based video saliency prediction approach. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 602–617).
Jiang, L., Xu, M., Wang, Z., & Sigal, L. (2021). Deepvs2.0: A saliency-structured deep learning method for predicting dynamic visual attention. International Journal of Computer Vision, 129(1), 203–224.
Judd, T., Ehinger, K., Durand, F., & Torralba, A. (2009). Learning to predict where humans look. In 2009 IEEE 12th international conference on computer vision (pp. 2106–2113). IEEE.
Kayser, C., Petkov, C. I., Lippert, M., & Logothetis, N. K. (2005). Mechanisms for allocating auditory attention: An auditory saliency map. Current Biology, 15(21), 1943–1947.
Knyazev, B., Taylor, G. W., & Amer, M. (2019). Understanding attention and generalization in graph neural networks. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 4202–4212).
Kumar, K., Chen, T., & Stern, R. M. (2007). Profile view lip reading. In 2007 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing-ICASSP’07 (vol. 4, pp. IV–429). IEEE.
Le Meur, O., Le Callet, P., & Barba, D. (2007). Predicting visual fixations on video based on low-level visual features. Vision Research, 47(19), 2483–2498.
Li, J., Tian, Y., & Huang, T. (2014). Visual saliency with statistical priors. International Journal of Computer Vision, 107(3), 239–253.
Li, J., Tian, Y., Huang, T., & Gao, W. (2010). Probabilistic multi-task learning for visual saliency estimation in video. International Journal of Computer Vision, 90(2), 150–165.
Li, Z., Qin, S., & Itti, L. (2011). Visual attention guided bit allocation in video compression. Image and Vision Computing, 29(1), 1–14.
Liu, Y., Qiao, M., Xu, M., Li, B., Hu, W., & Borji, A. (2020). Learning to predict salient faces: A novel visual-audio saliency model. In A. Vedaldi, H. Bischof, T. Brox, & J. M. Frahm (Eds.), Computer Vision-ECCV 2020 (pp. 413–429). Springer.
Liu, Y., Zhang, S., Xu, M., & He, X. (2017). Predicting salient face in multiple-face videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 4420–4428).
Marighetto, P., Coutrot, A., Riche, N., Guyader, N., Mancas, M., Gosselin, B., & Laganiere, R. (2017) Audio–visual attention: Eye-tracking dataset and analysis toolbox. In 2017 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP) (pp. 1802–1806).
Merritt, L., Vanam, R. (2006). x264: A high performance h.264/avc encoder. online]. https://www.neuron2net/library/avc/overview_x264_v8_5.pdf
Min, K., & Corso, J. J. (2019). Tased-net: Temporally-aggregating spatial encoder-decoder network for video saliency detection. ar**v preprint ar**v:1908.05786
Owens, A., & Efros, A. A. (2018). Audio-visual scene analysis with self-supervised multisensory features. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 631–648).
Pan, J., Ferrer, C. C., McGuinness, K., O’Connor, N. E., Torres, J., Sayrol, E., & Giro-i Nieto, X. (2017). Salgan: Visual saliency prediction with generative adversarial networks. ar**v preprint ar**v:1701.01081
Rajashekar, U., Van Der Linde, I., Bovik, A. C., & Cormack, L. K. (2008). Gaffe: A gaze-attentive fixation finding engine. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 17(4), 564–573.
Roth, J., Chaudhuri, S., Klejch, O., Marvin, R., Gallagher, A., Kaver, L., Ramaswamy, S., Stopczynski, A., Schmid, C., **, Z., et al. (2020). Ava active speaker: An audio-visual dataset for active speaker detection. In ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE international conference on acoustics (pp. 4492–4496). IEEE: Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP).
Senocak, A., Oh, T. H., Kim, J., Yang, M. H., & So Kweon, I. (2018). Learning to localize sound source in visual scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 4358–4366).
Senocak, A., Oh, T. H., Kim, J., Yang, M. H., & Kweon, I. S. (2019). Learning to localize sound sources in visual scenes: Analysis and applications. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2952095
Simonyan, K., & Zisserman, A. (2015). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. In 3rd International conference on learning representations, ICLR 2015, conference track proceedings.
Souly, N., & Shah, M. (2016). Visual saliency detection using group lasso regularization in videos of natural scenes. International Journal of Computer Vision, 117(1), 93–110.
SR-Research. (2010). Eyelink 1000 plus. https://www.sr-research.com/products/eyelink-1000-plus/
Tavakoli, H. R., Borji, A., Rahtu, E., & Kannala, J. (2019). Dave: A deep audio–visual embedding for dynamic saliency prediction. ar**v preprint ar**v:1905.10693
Thomas, C. L. (2016). Opensalicon: An open source implementation of the salicon saliency model. Technical Report. TR-2016-02, University of Pittsburgh.
Tian, Y., Shi, J., Li, B., Duan, Z., & Xu, C. (2018). Audio–visual event localization in unconstrained videos. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 247–263).
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., & Paluri, M. (2015). Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 4489–4497).
Tsiami, A., Katsamanis, A., Maragos, P., & Vatakis, A. (2016). Towards a behaviorally-validated computational audiovisual saliency model. In 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics (pp. 2847–2851). IEEE: Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP).
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, L., & Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 30, 5998–6008.
Veličković, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Lio, P., & Bengio, Y. (2017). Graph attention networks. ar**v preprint ar**v:1710.10903
Wang, W., & Shen, J. (2017). Deep visual attention prediction. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 27(5), 2368–2378.
Wang, W., Shen, J., Guo, F., Cheng, M. M., & Borji, A. (2018). Revisiting video saliency: A large-scale benchmark and a new model. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 4894–4903).
**e, S., Sun, C., Huang, J., Tu, Z., & Murphy, K. (2018). Rethinking spatiotemporal feature learning: Speed-accuracy trade-offs in video classification. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 305–321).
**ngjian, S., Chen, Z., Wang, H., Yeung, D. Y., Wong, W. K., & Woo, W. C. (2015). Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 802–810).
Xu, M., Jiang, L., Ye, Z., & Wang, Z. (2016). Bottom-up saliency detection with sparse representation of learnt texture atoms. Pattern Recognition, 60, 348–360.
Xu, M., Liu, Y., Hu, R., & He, F. (2018). Find who to look at: Turning from action to saliency. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 27(9), 4529–4544.
Zanca, D., Melacci, S., & Gori, M. (2019). Gravitational laws of focus of attention. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence.
Zhang, J., & Sclaroff, S. (2016). Exploiting surroundedness for saliency detection: A Boolean map approach. In IEEE TPAMI (pp. 889–902).
Zhang, K., Zhang, Z., Li, Z., & Qiao, Y. (2016). Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 23(10), 1499–1503.
Zhao, H., Gan, C., Rouditchenko, A., Vondrick, C., McDermott, J., & Torralba, A. (2018). The sound of pixels. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV) (pp. 570–586).
Zhou, B., Khosla, A., Lapedriza, A., Oliva, A., & Torralba, A. (2016). Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 2921–2929).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jiri Matas.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61922009, 61902401, 61876013, 62250001, 62231002, 62192785, 61972071, and by the Bei**g Natural Science Foundation under Grants JQ20020 and M22005.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, M., Liu, Y., Xu, M. et al. Joint Learning of Audio–Visual Saliency Prediction and Sound Source Localization on Multi-face Videos. Int J Comput Vis 132, 2003–2025 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01950-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01950-3