Abstract
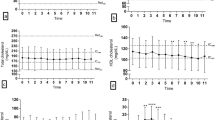
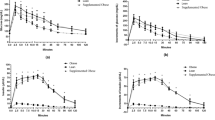
Circulating levels of monosaccharides can act as a reflection of systemic glucose/ energy metabolism. Characteristic changes observed in these levels can be seen in patients with diabetes and other metabolic disorders. There have been a few reports describing the significance of mannose metabolism as an energy source under physiological and pathological conditions. However, the relationship between circulating levels of mannose and the pathophysiology of diabetes mellitus are unknown in dogs. This study examined circulating levels of mannose between healthy control and diabetic dogs and evaluated the clinical significance of mannose levels in dogs. Diabetic dogs demonstrated a higher circulating level of mannose in comparison to normal healthy control dogs. Plasma mannose was positively correlated with plasma glucose and fructosamine, respectively. Interestingly, plasma mannose levels were affected by plasma insulin levels. In the context of feeding and glucose tolerance tests, plasma mannose levels responded to changes in circulating insulin levels. Circulating plasma mannose levels decreased after feeding in both control and diabetic animals in spite of observed insulin level differences. However, when glucose tolerance tests were given, a positive correlation between mannose levels and insulin levels was observed. Therefore, plasma mannose levels obtained via glucose tolerance testing may be used as a new diagnostic method for evaluating insulin resistance or deficiency in diabetic dogs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BCS:
-
body condition score
- BW:
-
body weight
- DM:
-
diabetes mellitus
- FPG:
-
fasting plasma glucose
- [glucose]:
-
glucose concentration
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- IGT:
-
impaired glucose tolerance
- [insulin]:
-
insulin concentration
- IVGTT:
-
intravenous glucose tolerance test
- [mannose]:
-
mannose concentration
- RER:
-
resting energy requirement
References
Alton, G., Hasilik, M., Niehues, R., Panneerselvam, K., Etchison, J.R., Fana, F. and Freeze, H.H., 1998. Direct utilization of mannose for mammalian glycoprotein biosynthesis. Glycobiology, 8, 285–295. doi:10.1093/glycob/8.3.285
Barr, R.G., Nathan, D.M., Meigs, J.B. and Singer, D.E., 2002. Tests of glycemia for the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Annals of Internal Medicine, 137, 263–272
Birlouez-Aragon, I., Ravelontseheno, L., Villate-Cathelineau, B., Cathelineau, G. and Abitbol, G., 1993. Disturbed galactose metabolism in elderly and diabetic humans is associated with cataract formation. The Journal of Nutrition, 123, 1370–1376
De la Horra, M.C., Cano, M., Peral, M.J., García-Delgado, M., Durán, J.M., Calonge, M.L. and Ilundáin, A.A., 2001. Na(+)-dependent D-mannose transport at the apical membrane of rat small intestine and kidney cortex. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1512, 225–230. doi:10.1016/S0005-2736(01)00322-4
Gerrits, P.M. and Tsalikian, E., 1993. Diabetes and fructose metabolism. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 58, 796S–799S
Laakso, M. and Lehto, S., 1998. Epidemiology of risk factors for cardiovascular disease in diabtes and impaired glucose tolerance. Atheroscoerosis, 173, S65–S73. doi:10.1016/S0021-9150(97)00314-6
Neth, O., Hann, I., Turner, M.W. and Klein, N.J., 2001. Deficiency of mannose-binding lectin and burden of infection in children with malignancy: a prospective study. Lancet, 358, 614–618. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(01)05776-2
Ogier-Denis, E., Blais, A., Houri, J.J., Voisin, T., Trugnan, G. and Codogno, P., 1994. The emergence of a basolateral 1-deoxymannojiricycin-sensitive mannose carrier is a function of intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. Evidence for a new inhibitory effect of 1-deoxymannojirimycin of facilitative mannose transport. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269, 4285–4290
Panneerselvam, K. and Freeze, H.H., 1996a. Mannose corrects altered N-glycosylation in carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome fibroblasts. The Journal of clinical investigation, 97, 1478–1487. doi:10.1172/JCI118570
Panneerselvam, K. and Freeze, H.H., 1996b. Mannose enters mammalian cells using a specific transporter that it insensitive to glucose. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 9417–9421. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.16.9417
Panneerselvam, K., Etchison, J.R. and Freeze, H.H., 1997. Human fibroblasts prefer mannose over glucose as a source of mannose for N-glycosylation. Evidence for the functional importance of transported mannose. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 23123–23129. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.37.23123
Pitkänen, E., 1996. Mannose, mannitol, fructose and 1,5-anhydroglucitol concentrations measured by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry in blood plasma of diabetic patients. Clinica chimica acta, 251, 91–103. doi:10.1016/0009-8981(96)06284-5
Pitkänen, O.M., Vanhanen, H. and Pitkänen, E., 1999. Metabolic syndrome is associated with changes in D-mannose metabolism. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation, 59, 607–612. doi:10.1080/00365519950185094
Reusch, C.E., Liehs, M.R., Hoyer, M. and Vochezer, R., 1993. Fructosamine. A new parameter for diagnosis and metabolic control in diabetic dogs and cats. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 7, 177–182
Sato, T., Katayama, K., Arai, T., Sako, T. and Tazaki, H., 2007. Simultaneous determination of serum mannose and glucose concentrations in dogs using high performance liquid chromatography. Research in Veterinary Science, 84, 26–29. doi:10.1016/j.rvsc.2007.03.002
Sone, H., Shimano, H., Ebinuma, H., Takahashi, A., Yano, Y., Iida, K.T., Suzuki, H., Toyoshima, H., Kawakami, Y., Okuda, Y., Noguchi, Y., Ushizawa, K., Saito, K. and Yamada, N., 2003. Physiological changes in circulating mannose levels in normal, glucose-intolerant, and diabetic subjects. Metabolism, 52, 1019–1027. doi:10.1016/S0026-0495(03)00153-7
Taguchi, T., Yamashita, E., Mizutani, T., Nakajima, H., Yabuuchi, M., Asano, N. and Miwa, I., 2005. Hepatic glycogen breakdown is implicated in the maintenance of plasma mannose concentration. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism, 288, E534–E540. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00451.2004
Taguchi, T., Miwa, I., Mizutani, T., Nakajima, H., Fukumura, Y., Kobayashi, I., Yabuuchi, M. and Miwa, I., 2003. Determination of D-mannose in plasma by HPLC. Clinical Chemistry, 49, 181–183. doi:10.1373/49.1.181
Wood, F.C. Jr. and Cahill, G.F. Jr., 1963. Mannose utilization in man. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 42, 1300–1312. doi:10.1172/JCI104814
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the ‘Academic Frontier’ Project Grant for Private Universities awarded from Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT), 2005–2009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, A., Sato, T., Lee, P. et al. Clinical significance of plasma mannose concentrations in healthy and diabetic dogs. Vet Res Commun 33, 439–451 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-008-9190-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-008-9190-3