Abstract
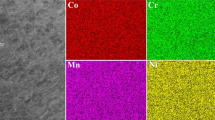
Medium-entropy alloys (MEAs) exhibit excellent mechanical properties and unique deformation mechanism at cryogenic temperatures. However, limited studies have been conducted to explore their cryogenic temperature wear behaviors and thus hinder their further cryogenic applications. Here, we report a mono-phased heterogeneous CoCrNi MEA composed of fully recrystallized grains and non-recrystallized grains that shows a favorable combination of strength and ductility. Meanwhile, a decreased coefficient of friction and improved wear resistance are revealed with the decreasing temperatures (0 °C → –120 °C). The wear mechanism shows an apparent transition from brittle fracture to mild plastic deformation when temperature decreases. The enhancement of strength-ductility for heterogeneous CoCrNi MEA at lower temperature leads to a reduction of ploughing coefficient and superior plastic response, thus resulting in excellent wear resistance. The present work provides a convenient route for preparing strength-ductility balanced and wear-resistant alloys for cryogenic applications.
Graphical Abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
Yeh, J.W., Chen, S.K., Lin, S.J., Gan, J.Y., Chin, T.S., Shun, T.T., Tsau, C.H., Chang, S.Y.: Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299–303 (2004)
Cantor, B., Chang, I.T.H., Knight, P., Vincent, A.J.B.: Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375–377, 213–218 (2004)
Zhang, Y., Zuo, T.T., Tang, Z., Gao, M.C., Dahmen, K.A., Liaw, P.K., Lu, Z.P.: Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 61, 1–93 (2014)
Li, W., **e, D., Li, D., Zhang, Y., Gao, Y., Liaw, P.K.: Mechanical behavior of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 118, 100777 (2021)
George, E.P., Raabe, D., Ritchie, R.O.: High-entropy alloys. Nat. Rev. Mater. 4, 515–534 (2019)
Du, Y., Zhou, Q., Pei, X., Wang, H., Wang, H., Liu, W.: Enhancing the tribological performance of the TiZrHfCuBe high entropy bulk metallic glass by Sn addition. Tribol. Int. 171, 107529 (2022)
Lu, K., Knöpfle, F., Chauhan, A., Litvinov, D., Schneider, M., Laplanche, G., Aktaa, J.: Elevated-temperature cyclic deformation mechanisms of CoCrNi in comparison to CoCrFeMnNi. Scripta Mater. 220, 114926 (2022)
Laplanche, G., Kostka, A., Reinhart, C., Hunfeld, J., Eggeler, G., George, E.P.: Reasons for the superior mechanical properties of medium-entropy CrCoNi compared to high-entropy CrMnFeCoNi. Acta Mater. 128, 292–303 (2017)
Laplanche, G., Kostka, A., Horst, O.M., Eggeler, G., George, E.P.: Microstructure evolution and critical stress for twinning in the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 118, 152–163 (2016)
An, Q., An, R., Wang, C., Wang, H.: Ductile-to-brittle transition in fracture behaviors of common solder alloys over a temperature range down to −150 °C. Mater. Today Commun. 29, 102962 (2021)
Yang, K., Li, Y., Hong, Z., Du, S., Ma, T., Liu, S., **, X.: The dominating role of austenite stability and martensite transformation mechanism on the toughness and ductile-to-brittle-transition temperature of a quenched and partitioned steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 820, 141517 (2021)
Rackwitz, J., Yu, Q., Yang, Y., Laplanche, G., George, E.P., Minor, A.M., Ritchie, R.O.: Effects of cryogenic temperature and grain size on fatigue-crack propagation in the medium-entropy CrCoNi alloy. Acta Mater. 200, 351–365 (2020)
Yang, M., Zhou, L., Wang, C., Jiang, P., Yuan, F., Ma, E., Wu, X.: High impact toughness of CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy at liquid-helium temperature. Scripta Mater. 172, 66–71 (2019)
Guo, N., Zhao, Y., Long, S., Song, B., Hu, J., Gan, B., Chai, L., Guo, S.: Microstructure and mechanical properties of (CrCoNi)97Al1.5Ti1.5 medium entropy alloy twisted by free-end-torsion at room and cryogenic temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 797, 140101 (2020)
Otto, F., Dlouhý, A., Somsen, C., Bei, H., Eggeler, G., George, E.P.: The influences of temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 61, 5743–5755 (2013)
Sohn, S.S., Kwiatkowski da Silva, A., Ikeda, Y., Kormann, F., Lu, W., Choi, W.S., Gault, B., Ponge, D., Neugebauer, J., Raabe, D.: Ultrastrong medium-entropy single-phase alloys designed via severe lattice distortion. Adv. Mater. 31, 1807142 (2019)
Chang, R., Fang, W., Yan, J., Yu, H., Bai, X., Li, J., Wang, S., Zheng, S., Yin, F.: Microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrNi-Mo medium entropy alloys: Experiments and first-principle calculations. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 62, 25–33 (2021)
He, F., Yang, Z., Liu, S., Chen, D., Lin, W., Yang, T., Wei, D., Wang, Z., Wang, J., Kai, J.J.: Strain partitioning enables excellent tensile ductility in precipitated heterogeneous high-entropy alloys with gigapascal yield strength. Int. J. Plasticity 144, 103022 (2021)
Lu, K.: Making strong nanomaterials ductile with gradients. Science 345, 1455–1456 (2014)
Wu, X., Jiang, P., Chen, L., Yuan, F., Zhu, Y.T.: Extraordinary strain hardening by gradient structure. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, 7197–7201 (2014)
Wang, Y., Yang, M., Ma, X., Wang, M., Yin, K., Huang, A., Huang, C.: Improved back stress and synergetic strain hardening in coarse-grain/nanostructure laminates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 727, 113–118 (2018)
Wu, X., Yang, M., Yuan, F., Wu, G., Wei, Y., Huang, X., Zhu, Y.: Heterogeneous lamella structure unites ultrafine-grain strength with coarse-grain ductility. P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 14501–14505 (2015)
Li, J., Cao, Y., Gao, B., Li, Y., Zhu, Y.: Superior strength and ductility of 316L stainless steel with heterogeneous lamella structure. J. Mater. Sci. 53, 10442–10456 (2018)
Li, Z., Pradeep, K.G., Deng, Y., Raabe, D., Tasan, C.C.: Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength-ductility trade-off. Nature 534, 227–230 (2016)
Du, X.H., Li, W.P., Chang, H.T., Yang, T., Duan, G.S., Wu, B.L., Huang, J.C., Chen, F.R., Liu, C.T., Chuang, W.S., Lu, Y., Sui, M.L., Huang, E.W.: Dual heterogeneous structures lead to ultrahigh strength and uniform ductility in a Co-Cr-Ni medium-entropy alloy. Nat. Commun. 11, 2390 (2020)
Chang, R., Fang, W., Yu, H., Bai, X., Zhang, X., Liu, B., Yin, F.: Heterogeneous banded precipitation of (CoCrNi)93Mo7 medium entropy alloys towards strength–ductility synergy utilizing compositional inhomogeneity. Scripta Mater. 172, 144–148 (2019)
Wu, S.W., Wang, G., Wang, Q., Jia, Y.D., Yi, J., Zhai, Q.J., Liu, J.B., Sun, B.A., Chu, H.J., Shen, J., Liaw, P.K., Liu, C.T., Zhang, T.Y.: Enhancement of strength-ductility trade-off in a high-entropy alloy through a heterogeneous structure. Acta Mater. 165, 444–458 (2019)
Jo, Y.H., Jung, S., Choi, W.M., Sohn, S.S., Kim, H.S., Lee, B.J., Kim, N.J., Lee, S.: Cryogenic strength improvement by utilizing room-temperature deformation twinning in a partially recrystallized VCrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Nat. Commun. 8, 15719 (2017)
Du, Y., Zhou, Q., Jia, Q., Shi, Y., Wang, H., Wang, J.: Imparities of shear avalanches dynamic evolution in a metallic glass. Mater. Res. Lett. 8, 357–363 (2020)
Wang, J.C., Liu, Y.J., Liang, S.X., Zhang, Y.S., Wang, L.Q., Sercombe, T.B., Zhang, L.C.: Comparison of microstructure and mechanical behavior of Ti-35Nb manufactured by laser powder bed fusion from elemental powder mixture and prealloyed powder. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 105, 1–16 (2022)
Kishore, K., Kumar, R.G., Chandan, A.K.: Critical assessment of the strain-rate dependent work hardening behaviour of AISI 304 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 803, 140675 (2021)
Yasnikov, I.S., Vinogradov, A., Estrin, Y.: Revisiting the Considère criterion from the viewpoint of dislocation theory fundamentals. Scripta Mater. 76, 37–40 (2014)
Gludovatz, B., Hohenwarter, A., Catoor, D., Chang, E.H., George, E.P., Ritchie, R.O.: A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 345, 1153–1158 (2014)
Miao, J., Slone, C.E., Smith, T.M., Niu, C., Bei, H., Ghazisaeidi, M., Pharr, G.M., Mills, M.J.: The evolution of the deformation substructure in a Ni-Co-Cr equiatomic solid solution alloy. Acta Mater. 132, 35–48 (2017)
Ding, Q., Fu, X., Chen, D., Bei, H., Gludovatz, B., Li, J., Zhang, Z., George, E.P., Yu, Q., Zhu, T., Ritchie, R.O.: Real-time nanoscale observation of deformation mechanisms in CrCoNi-based medium- to high-entropy alloys at cryogenic temperatures. Mater. Today 25, 21–27 (2019)
Otto, F., Hanold, N.L., George, E.P.: Microstructural evolution after thermomechanical processing in an equiatomic, single-phase CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy with special focus on twin boundaries. Intermetallics 54, 39–48 (2014)
Bhattacharjee, P.P., Sathiaraj, G.D., Zaid, M., Gatti, J.R., Lee, C., Tsai, C.-W., Yeh, J.-W.: Microstructure and texture evolution during annealing of equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys. Compd. 587, 544–552 (2014)
Liu, W.H., Wu, Y., He, J.Y., Nieh, T.G., Lu, Z.P.: Grain growth and the Hall-Petch relationship in a high-entropy FeCrNiCoMn alloy. Scripta Mater. 68, 526–529 (2013)
Liu, Y.J., Wang, H.L., Li, S.J., Wang, S.G., Wang, W.J., Hou, W.T., Hao, Y.L., Yang, R., Zhang, L.C.: Compressive and fatigue behavior of beta-type titanium porous structures fabricated by electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 126, 58–66 (2017)
Zhu, Y., Ameyama, K., Anderson, P.M., Beyerlein, I.J., Gao, H., Kim, H.S., Lavernia, E., Mathaudhu, S., Mughrabi, H., Ritchie, R.O., Tsuji, N., Zhang, X., Wu, X.: Heterostructured materials: superior properties from hetero-zone interaction. Mater. Res. Lett. 9, 1–31 (2020)
Wu, Z., Bei, H., Pharr, G.M., George, E.P.: Temperature dependence of the mechanical properties of equiatomic solid solution alloys with face-centered cubic crystal structures. Acta Mater. 81, 428–441 (2014)
Yang, M., Pan, Y., Yuan, F., Zhu, Y., Wu, X.: Back stress strengthening and strain hardening in gradient structure. Mater. Res. Lett. 4, 145–151 (2016)
Sathiyamoorthi, P., Kim, H.S.: High-entropy alloys with heterogeneous microstructure: Processing and mechanical properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 123, 100709 (2020)
Zhu, Y., Wu, X.: Perspective on hetero-deformation induced (HDI) hardening and back stress. Mater. Res. Lett. 7, 393–398 (2019)
Hua, D., **a, Q., Wang, W., Zhou, Q., Li, S., Qian, D., Shi, J., Wang, H.: Atomistic insights into the deformation mechanism of a CoCrNi medium entropy alloy under nanoindentation. Int. J. Plasticity 142, 102997 (2021)
Bowden, F.P., Tabor, D.: Friction, lubrication and wear: A survey of work during the last decade. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 17, 1521–1544 (2002)
Ye, Y.X., Liu, C.Z., Wang, H., Nieh, T.G.: Friction and wear behavior of a single-phase equiatomic TiZrHfNb high-entropy alloy studied using a nanoscratch technique. Acta Mater. 147, 78–89 (2018)
Lafaye, S., Gauthier, C., Schirrer, R.: The ploughing friction: analytical model with elastic recovery for a conical tip with a blunted spherical extremity. Tribo. Lett. 21, 95–99 (2006)
Jia, Q., He, W., Hua, D., Zhou, Q., Du, Y., Ren, Y., Lu, Z., Wang, H., Zhou, F., Wang, J.: Effects of structure relaxation and surface oxidation on nanoscopic wear behaviors of metallic glass. Acta Mater. 232, 117934 (2022)
Zhou, Q., Han, W., Luo, D., Du, Y., **e, J., Wang, X.-Z., Zou, Q., Zhao, X., Wang, H., Beake, B.D.: Mechanical and tribological properties of Zr–Cu–Ni–Al bulk metallic glasses with dual-phase structure. Wear 474–475, 203880 (2021)
Zhou, Q., Luo, D., Hua, D., Ye, W., Li, S., Zou, Q., Chen, Z., Wang, H.: Design and characterization of metallic glass/graphene multilayer with excellent nanowear properties. Friction (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40544-021-0581-6
Liu, C., Li, Z., Lu, W., Bao, Y., **a, W., Wu, X., Zhao, H., Gault, B., Liu, C., Herbig, M., Fischer, A., Dehm, G., Wu, G., Raabe, D.: Reactive wear protection through strong and deformable oxide nanocomposite surfaces. Nat. Commun. 12, 5518 (2021)
Zhou, Q., Ren, Y., Du, Y., Han, W., Hua, D., Zhai, H., Huang, P., Wang, F., Wang, H.: Identifying the significance of Sn addition on the tribological performance of Ti-based bulk metallic glass composites. J. Alloys. Compd. 780, 671–679 (2019)
Luo, D., Zhou, Q., Ye, W., Ren, Y., Greiner, C., He, Y., Wang, H.: Design and characterization of self-lubricating refractory high entropy alloy-based multilayered films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 13, 55712–55725 (2021)
Greiner, C., Gagel, J., Gumbsch, P.: Solids under extreme shear: Friction-mediated subsurface structural transformations. Adv Mater. 31, 1806705 (2019)
Heczko, M., Mazánová, V., Slone, C.E., Shih, M., George, E.P., Ghazisaeidi, M., Polák, J., Mills, M.J.: Role of deformation twinning in fatigue of CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy at room temperature. Scripta Mater. 202, 113985 (2021)
Lin, K., Chen, S.-C., Lin, H.-C., Yen, H.-W.: Enhancement in mechanical properties through an FCC-to-HCP phase transformation in an Fe-17.5Mn-10Co-12.5Cr-5Ni-5Si (in at%) medium-entropy alloy. J. Alloys. Compd. 898, 162765 (2022)
Cheng, W., Liu, W., Fan, X., Yuan, S.: Cooperative enhancements in ductility and strain hardening of a solution-treated Al–Cu–Mn alloy at cryogenic temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 790, 139707 (2020)
Wang, J., Zhao, Y., Zhou, W., Zhao, Q., Lei, C., Zeng, W.: In-situ study on tensile deformation and damage evolution of metastable β titanium alloy with lamellar microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 824, 141790 (2021)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52175188, 52104386), Shanghai Sailing Program, State Key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior of Materials (No. 20222412) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 3102019JC001).
Funding
The Natural Science Foundation of China, 52175188, Qing Zhou, 52104386, Yixuan He, Shanghai Sailing Program and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, 3102019JC001, Haifeng Wang, State Key Laboratory for Mechanical Behavior of Materials, 20222412, Qing Zhou
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Z., Ren, Y., Luo, D. et al. Improved Wear Resistance of a Heterogeneous CoCrNi Medium-Entropy Alloy at Cryogenic Temperature. Tribol Lett 70, 96 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-022-01643-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-022-01643-x