Abstract
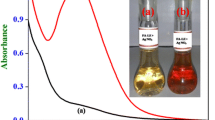
It is observed that Ag(I) catalyzes the rate of substitution of phenylhydrazine (PhNHNH2) into hexacyanoferrate(II), producing a cherry red colored complex, [Fe(CN)5PhNHNH2]3−. The reaction was monitored at 488 nm leading to the formation of the complex under the conditions: [Fe(CN)6]4− (5.0 × 10−3 mol dm−3), PhNHNH2 (2.0 × 10−3 mol dm−3), temperature (25 ± 0.1 °C), pH (2.8 ± 0.02), and ionic strength, I (0.02 mol dm−3), (KNO3). Under optimum conditions, absorbance at fixed times (A t ) is linearly related to Ag(I) in the concentration range 10.79–97.08 ng cm−3, in the presence of several diverse ions. The highest percentage error and relative standard deviations in the entire range of Ag(I) determination are found to be 2.5% and 0.16, with a detection limit of 8.75 ng cm−3 of silver(I). The experimental accuracies expressed in terms of percentage recoveries are in the range of 97.87–102.50. The method was successfully applied for the determination of Ag(I) in a few synthetic samples and found to be in good agreement with those obtained from atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS). The validity of the proposed method has also been tested for Ag(I) determination in spiked drinking water samples. The present catalytic kinetic method (CKM) is highly sensitive, selective, reproducible, and inexpensive. A review of recently published catalytic spectrophotometric methods for determination of Ag(I) has also been presented for comparison.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAS:
-
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
- BPT:
-
4,7-biphenyl-1,10-phenanthroline
- CKM:
-
Catalytic kinetic method
- DRD:
-
Dynamic range of detection
- DTPA:
-
Diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- HEDTA:
-
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)ethylenediaminetriacetic acid
- HMBPTS:
-
2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzophenonethiosemicarbazide
- IDA:
-
Imino-diacetic acid
- NTA:
-
Nitrilotriacetic acid
- PhNHNH2 :
-
Phenylhydrazine
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- SMs:
-
Synthetic mixtures
- SPM:
-
Spectrophotometric method
References
Nebeker AV, McAuliffe CK, Mshar R, Stevens DF (1983) Toxicol Chem 2:95
Patein G, Robin L (1909) Bull Gen Ther 58:898
Hill WR, Pillsubury Argyria DM (1939) The pharmacology of silver. William Wilkinson, Baltimore
Dietl HW, Anzil AP, Mchraein P (1984) Clin Neuropathol 3:32
Fowler BA, Nordberg GF (1986) Handbook on the toxicology of metals, vol II, 2nd edn. Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam, p 521
Jackson KW, Qiao H (1992) Anal Chem 64:50R
Avila AK, Curtius AJ (1994) J Anal At Spectrom 9:543
Bermejo-Barrera P, Moreda-Pineiro A, Bermejo-Barrera A (1996) Talanta 43:35
Kabasakalis V (1994) Anal Lett 27:2789
Dole AJ, Cardwell TJ, Scollary GR (1998) Electroanalysis 10:21
Wang J, Martinez T (1988) Anal Chim Acta 207:95
Mottola HA (1988) In: Winefordner JD (ed) Kinetic aspects of analytical chemistry in chemical analysis, vol 96. Wiley Interscience, New York
Yatsimirskii KB (1966) Kinetic methods of analysis. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Kawashima T, Nakano S, Tabata M, Tanaka M (1997) Trends Anal Chem 16:132
Prasad S, Halafithi T (2003) Mikrochim Acta 142:237
Prasad S (2003) Assian J Chem 15:1
Nagaraja P, Mattighatta S, Kumar H, Yathirajan HS (2002) Anal Sci 18:815 and refs. therein
Sulka GD, Jaskula M (1999) Anal Chim Acta 394:185
Pourreza N, Parham H, Hashmi F (2003) J Anal Chem 58(4):333
Hermandez Cordoba M, Sanchez-Pedreno C, Vinas Lopez-Pelegrin P (1985) Quim Anal (Barcelona) 4(2):159
Prasad KMMK, Subashchandran KP (1992) Assian J Chem 4:715
Ensafi AA, Abbasi S (1997) Anal Lett 30:327
Zhaosheng Z, Yaoguang W, Fengyuan L, Jianhua Z (1988) Fenxi Huaxue 16:138
Tabatabafe M, Nateghi MR, Mosavi SJ (2006) Anal Sci 22:1601
Safavi A, Mirzajani R (2002) Anal Sci 18:329
Shimei F, Huijun L, Guiyou M, Weiying G (1996) Environ Prot Chem Ind 16:234
Venkateshwarlu T, Raman S, Reddy BR (1990) Indian J Chem Sect A 29A:930 and refs. therein
Chuanying G, Xuguang Z, Guiyou M (1993) Lihua Jianyan 29:35
Reddy KV, Chennaiah A, Reddy PR, Reddy TS (2003) Chem Anal (Warsaw) 48:733
Qin W, Guohua C, **hu Y, Du Bin (2003) Anal Lett 36:627
Mingli W, ** F (1990) Lihua Jianyan 2:29
Reddy KPPRM, Chowdry PG, Reddy VK, Reddy PR (2007) Annali di Chimica 97:1207
Haghighi B, Safavi A (1999) Fresenius J Anal Chem 365:654
Naik RM, Tewari RK, Singh PK, Tewari A, Prasad S (2005) Transition Met Chem 30:968
Naik RM, Sarkar J, Chaturvedi DD (2005) Int J Chem Kin 37:222
Prasad S (2003) Transition Met Chem 28:1
Naik RM, Tewari RK, Singh PK. Yadav SBS (2007) Int J Chem Kin 39:447
Weast RC (1969) CRC hand book of chemistry and physics, 49th edn. The Chemical Rubber Co., Ohio, D-79
Naik RM, Tiwari RK, Singh PK, Verma AK (2007) Inorg React Mech 6:217
Eaton WA, George P, Hanaria GH (1967) J Phys Chem 71:2016
Mukherjee R, Dhar BB, Banerjee R, Mukhopadhyay S (2006) J Coord Chem 59:1157
Prasad S (2005) J Anal Chem 60:581
Raman S, Reddy BR (1989) Indian J Chem 28A:599
Raman S Reddy BR (1984) Indian J Chem 23A:48
Raman S, Reddy BR (1984) Proc Indian Ntn Sci Acad 50A:33
Raman S, Reddy BR (1984) Indian J Chem 23A:616
Acknowledgment
The corresponding author, Dr. R. M. Naik is grateful to Council of Scientific Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi, India for providing financial assistance to perform this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, R.M., Tiwari, R.K., Singh, P.K. et al. Kinetic determination of silver at trace level based on its catalytic effect on a ligand substitution reaction. Transition Met Chem 33, 615–623 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-008-9088-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11243-008-9088-5