Abstract
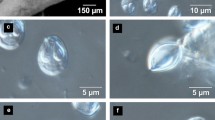
A previously undescribed Myxobolus sp. was isolated from the cranial nerves and ganglia of the spotfin hatchetfish Thoracocharax stellatus (Kner) that exhibited neurologic signs following importation from Colombia. Associated plasmodia formed space-occupying masses within nerves, compressing neuronal cell bodies and causing axonal degeneration. Myxospores from these fish were morphologically and molecularly distinct from other myxobolids infecting the central nervous system of characins. In valvular view, spores are pyriform with a rounded posterior and tapering anterior aspect. Myxospore bodies are 17.0–19.4 (mean 18.4) µm long and 8.2–9.3 (mean 8.8) µm wide. Polar capsules are asymmetrical and pyriform with a neck-like projection at the apical end. The small polar capsule measures 4.3–5.9 × 2.2–3.1 (mean 5.0 × 2.6) µm, while the large polar capsule measures 9.1–10.7 × 4.9–6.3 (mean 9.9 × 5.4) µm wide. The sequence generated for the small subunit rRNA (18S) gene did not directly match any sequences available on GenBank, but demonstrated 92% nucleotide similarity to Myxobolus axelrodi Camus, Dill, Rosser, Pote & Griffin, 2017 infecting Paracheirodon axelrodi (Schultz). This study provides the first morphological, histological and molecular characterisation of Myxobolus stellatus n. sp. from the spotfin hatchetfish.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, S. D., Bartošová-Sojková, P., Whipps, C. M., & Bartholomew, J. L. (2015). Approaches for characterizing myxozoan species. In: Okamura, B., Gruhl, A. & Bartholomew, J. L. (Eds), Myxozoan evolution, ecology and development. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, pp. 111–123.
Azevedo, C., Feltran, R., Rocha, S., Matos, E., Maciel, E., Oliveira, E., et al. (2018). Simultaneous occurrence of two new myxosporean species infecting the central nervous system of Hypopygus lepturus from Brazil. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms,131, 143–156.
Azevedo, R. K., Vieira, D. H. M. D., Vieira, G. H., Silva, R. J., Matos, E., & Abdallah, V. D. (2014). Phylogeny, ultrastructure and histopathology of Myxobolus lomi sp. nov., a parasite of Prochilodus lineatus (Valenciennes, 1836) (Characiformes: Prochilodontidae) from the Peixes River, Sao Paulo State. Brazil. Parasitology International,63, 303–307.
Barta, J. R., Marin, D. S., Liberator, P. A., Dshkevicz, M., Anderson, J. W., Feighner, S. D., et al. (1997). Phylogenetic relationships among eight Eimeria species infecting domestic fowl inferred using complete small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Journal of Parasitology,83, 262–271.
Camus, A. C., Dill, J. A., Rosser, T. G., Pote, L. M., & Griffin, M. J. (2017). Myxobolus axelrodi n. sp. (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) a parasite infecting the brain and retinas of the cardinal tetra Paracheirodon axelrodi (Teleostei: Characidae). Parasitology Research,116, 387–397.
Chemes, S. B., & Takemoto, R. (2011). Diversity of parasites from Middle Parana system freshwater fishes, Argentina. International Journal of Biodiversity and Conservation,3, 249–266.
De Araújo, R. S., Corrêa, F., De Sousa, F. B., Ramos, A. B. M. A., Neto, J. L. S., & Matos, E. R. (2018). Ocorrencia de Myxobolus sp. (Myxozoa) em Thoracocharax stellatus (Kner, 1858) (Characiformes) em um Igarape da Floresta Amazonica, Para, Brasil. Brazilian Journal of Aquatic Science & Technology,21, 16–20.
Griffin, M. J., & Goodwin, A. E. (2011). Thelohanellus toyamai (syn. Myxobolus toyamai) infecting the gills of koi Cyprinus carpio in the Eastern United States. Journal of Parasitology,97, 493–503.
Griffin, M. J., Pote, L. M., Wise, D. J., Greenway, T. E., Mauel, M. J., & Camus, A. C. (2008). A novel Henneguya species from channel catfish described by morphological, histological and molecular characterization. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health,20, 127–135.
Guo, Q., Huang, M., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., & Gu, Z. (2018). Morphological plasticity in Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882: a taxonomic dilemma case and renaming of a parasite species of the common carp. Parasites & Vectors,11, 399.
Hallet, S. L., & Diamant, A. (2001). Ultrastructure and small-subunit ribosomal DNA sequence of Henneguya lesteri n. sp. (Myxosporea), a parasite of sand whiting Sillago analis (Sillaginidae) from the coast of Queensland. Australia. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms,46, 197–212.
Hanson, L. A., Lin, D., Pote, L. M., & Shivaji, R. (2001). Small subunit rRNA gene comparisons of four actinosporean species to establish a polymerase chain reaction test for the causative agent of proliferative gill disease in channel catfish. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health,13, 117–123.
ICZN (2012). International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature: Amendment of articles 8, 9, 10, 21 and 78 of the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature to expand and refine methods of publication. Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature,69, 161–169.
Iwanowicz, L. R., Iwanowicz, D. D., Pote, L. M., Blazer, V. S., & Schill, W. B. (2008). Morphology and 18S rDNA of Henneguya gurlei (Myxosporea) from Ameiurus nebulosus (Siluriformes) in North Carolina. Journal of Parasitology,94, 46–57.
Katoh, K., Misawa, K., Kuma, K., & Miyata, T. (2002). MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Research,30, 3059–3066.
Katoh, K., & Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution,30, 772–780.
Kent, M. L., & Hoffman, G. L. (1984). Two new species of Myxozoa, Myxobolus inaequus sp. n. and Henneguya theca sp. n. from the brain of a South American knife fish, Eigenmannia virescens (V.). Journal of Protozoology,31, 91–94.
Kent, M. L., Khattra, J., Hedrick, R. P., & Devlin, R. H. (2000). Tetracapsula renicola n. sp. (Myxozoa: Saccosporidae); the PKX myxozoan - the cause of proliferative kidney disease of salmonid fishes. Journal of Parasitology,86, 103–111.
Ksepka, S. P., Rash, J. M., Whelan, N., & Bullard, S. A. (2019). A new species of Myxobolus (Myxozoa: Bivalvulida) infecting the medulla oblongata and nerve cord of brook trout Salvelinus fontinalis in southern Appalachia (New River, NC, USA). Parasitology Research,118, 3241–3252.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., & Tamura, K. (2016). MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution,33, 1870–1874.
Molnár, K. (2002). Site preference of fish myxosporeans in the gill. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms,48, 197–207.
Molnár, K. (2007). Site preference of myxozoans in the kidneys of Hungarian fishes. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms,78, 45–53.
Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2000). Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics. New York: Oxford University Press.
Noga, E. J. (2010). Fish disease diagnosis and treatment. Ames, IA: Wiley-Blackwell.
Parker, J. D., & Warner, M. C. (1970). Effects of fixation, dehydration, and staining on dimensions of myxosporidian and microsporidian spores. Journal of Wildlife Diseases, 6, 448–456.
Ronquist, F., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2003). MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics,19, 1571–1574.
Rosser, T. G., Baumgartner, W. A., Barger, M. A., & Griffin, M. J. (2017). Myxobolus lepomis n. sp. (Cnidaria: Myxobolidae), a gill myxozoan infecting Lepomis marginatus Holbrook and Lepomis miniatus Jordan (Perciformes: Centrarchidae), in the Big Thicket National Preserve, Texas, USA. Systematic Parasitology,94, 535–545.
Spencer, L. T., & Bancroft, J. D. (2013). Tissue processing. In: Suvarna, S. K., Layton, C. Bancroft, J. D. (Eds) Bancroft’s theory and practice of histological techniques. London: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 105–123.
Stilwell, J. M., Camus, A. C., Leary, J. H., Khoo, L. H., & Griffin, M. J. (2019a). Pathologic changes associated with respiratory compromise and morbidity due to massive interlamellar Henneguya exilis infection in channel x blue hybrid catfish. Journal of Parasitology,105, 686–692.
Stilwell, J. M., Stilwell, N. K., Camus, A. C., Griffin, M. J., & Rosser, T. G. (2019b). A morphological, molecular, and histopathological redescription of Henneguya nyongensis Fomena & Bouix, 1996 infecting the gills of Peter’s elephantnose fish, Gnathonemus petersii (Günther, 1862), imported from Nigeria. Systematic Parasitology,86, 767–776.
Tavares-Dias, M., Lemos, J. R. G., & Martins, M. L. (2010). Parasitic fauna of eight species of ornamental freshwater fish species from the middle Negro River in the Brazilian Amazon region. Revista Brasileira de Parasitologica Veterinaria,19, 103–107.
Whittington, R. J., & Chong, R. (2007). Global trade in ornamental fish from an Australian perspective: the case for revised import risk analysis and management strategies. Preventative Veterinary Medicine,81, 92–116.
Wise, D. J., Griffin, M. J., Terhune, J. S., Pote, L. M., & Khoo, L. H. (2008). Induction and evaluation of proliferative gill disease in channel catfish fingerlings. Journal of Aquatic Animal Health,20, 236–244.
Yokoyama, H., & Ogawa, K. (2015). The resurrection of Myxobolus toyamai with a validation of a stunted polar capsule based on morphological evidence. Parasitology International,64, 43–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national, and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as C1909070-FD65-43F8-B14A-4CF8F1B0F28A. This article was published as an Online First article on the online publication date shown on this page. The article should be cited by using the doi number. This is the Version of Record.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stilwell, J.M., Petty, B.D., Camus, A.C. et al. Characterisation of Myxobolus stellatus n. sp. (Cnidaria: Myxobolidae) infecting the cranial nerves and ganglia of the spotfin hatchetfish Thoracocharax stellatus (Kner) (Characiformes: Gasteropelecidae) from Colombia. Syst Parasitol 97, 305–314 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-020-09911-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-020-09911-x