Abstract
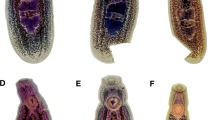
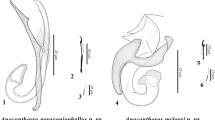
With only six recognised genera, the family Clinostomidae Lühe, 1901 remains a global research interest of parasitologists and ecologists. Recent efforts have focused on providing molecular data to investigate species diversity, elucidate life-cycles, and make inferences on the group’s evolutionary history. Of the clinostomid genera, the monotypic Ithyoclinostomum Witenberg, 1926 has remained more enigmatic compared to the commonly encountered Clinostomum Leidy, 1856. Recent morphological and molecular evidence from metacercariae suggests a second Ithyoclinostomum species may exist in freshwater cichlids in Central America and Mexico. In a recent survey of great blue herons Ardea herodias L. from commercial catfish production farms in Mississippi, USA, two specimens of an abnormally large (> 20 mm) clinostomid were encountered in the oesophagus of a single bird. These specimens were identified as an Ithyoclinostomum sp. morphologically distinct from the only nominal species Ithyoclinostomum dimorphum (Diesing, 1850). Using morphological and molecular data these adult specimens were confirmed as conspecific with the larval metacercariae previously described from Central America and Mexico and represent the novel species, Ithyoclinostomum yamagutii n. sp.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S. F., Gish, W., Miller, W., Myers, E. W., & Lipman, D. J. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology,215, 403–410.
Aguirre-Macedo, M. L., Scholz, T., González-Solís, D., Vidal-Martínez, V. M., Posel, P., Arjona-Torres, G., et al. (2001). Larval helminths parasitizing freshwater fishes from the Atlantic coast of Nicaragua. Comparative Parasitology,68, 42–51.
Baer, J. G. (1933). Note sur un nouveau trématode, Clinostomum lophophallum sp. nov., avec quelques considerations générales sur la famille des Clinostmoidae. Revue Suisse de Zoologie,40, 317–342.
Belei, F., Ferreira, S. R., Perin, L. M., Braga, F. R., Sampaio, W. M. S., de Araújo, J. V., et al. (2013). First report of Austrodiplostomum compactum and Ithyoclinostomum dimorphum in trahira (Hoplias malabaricus) from the middle course of the Rio Doce, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Arquivos do Instituto de Biologia,80, 249–252.
Bengtsson-Palme, J., Ryberg, M., Hartmann, M., Branco, S., Wang, Z., Godhe, A., et al. (2013). Improved software detection and extraction of ITS1 and ITS2 from ribosomal ITS sequences of fungi and other eukaryotes for analysis of environmental sequencing data. Methods in Ecology and Evolution,4, 914–919.
Benigno, R. N. M., Knoff, M., Matos, E. R., Gomes, D. C., Pinto, R. M., & Clemente, S. C. S. (2014). Morphological aspects of Clinostomidae metacercariae (Trematoda: Digenea) in Hoplerytrinus unitaeniatus and Hoplias malabaricus (Pisces: Erythrinidae) of the Neotropical region, Brazil. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências,86, 733–744.
Braun, M. (1899). Üeber Clinostomum Leidy. Zoologischer Anzeiger,22, 484–493.
Braun, M. (1901). Die Arten der Gattung Clinostomum Leidy. Zoologische Jahrbücher. Abteilung für Systematik Ökologie und Geographie der Tiere,14, 1–48.
Briosio-Aguilar, R., García-Varela, M., Hernández-Mena, D. I., Rubio-Godoy, M., & Pérez-Ponce de León, G. (2018). Morphological and molecular characterization of an enigmatic clinostomid trematode (Digenea: Clinostomidae) parasitic as metacercariae in the body cavity of freshwater fishes (Cichlidae) across Middle America. Journal of Helminthology,93, 461–474.
Caffara, M., Locke, S. A., Cristanini, C., Davidovich, N., Markovich, M. P., & Fioravanti, M. L. (2016). A combined morphometric and molecular approach to identifying metacercariae of Euclinostomum heterostomum (Digenea: Clinostomidae). Journal of Parasitology,102, 239–248.
Caffara, M., Locke, S. A., Gustinelli, A., Marcogliese, D. J., & Fioravanti, M. L. (2011). Morphological and molecular differentiation of Clinostomum complanatum and Clinostomum marginatum (Digenea: Clinostomidae) metacercariae and adults. Journal of Parasitology,97, 884–891.
Caffara, M., Locke, S. A., Halajian, A., Luus-Powell, W. J., Benini, D., Tedesco, P., et al. (2019). Molecular data show Clinostomoides Dollfus, 1950 is a junior synonym of Clinostomum Leidy, 1856, with redescription of metacercariae of Clinostomum brieni n. comb. Parasitology,146, 805–813.
Chagas de Souza, D. C., Correa, L. L., & Tavares-Dias, M. (2018). Ithyoclinostomum dimorphum Diesing, 1850 (Digenea, Clinostomidae) in Hoplias malabaricus (Erythrinidae) with the first report of infection of the eyes. Helminthologia,55, 343–349.
Costa, D. P. C., Monteiro, C. M., & Brasil-Sato, M. C. (2015). Digenea of Hoplias intermedius and Hoplias malabaricus (Actinopterygii, Erythrinidae) from upper São Francisco River, Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Parasitología Veterinária,24, 129–135.
Delgado, A. E., Tantalean, M. V., Martínez, R. R., & Mondragón, A. M. (2017). Trematodos en Hoplerythrinus unitaeniatus (Erythrinidae) <<Shuyo>> and Pterodoras granulosus (Doradidae) <<Cahuara>> in Yurimaguas, Loreto, Peru. Revista de Investigación Veterinaria Perú,28, 461–467.
Dias, M. L. G. G., Santos, M. J., Souza, G. T. R., Machado, M. H., & Pavanelli, G. C. (2003). Scanning electron microscopy of Ithyoclinostomum dimorphum (Trematoda: Clinostomidae), a parasite of Ardea cocoi (Aves: Ardeidae). Parasitology Research,90, 355–358.
Diesing, K. M. (1850). Systema helminthum, Volume 1. Vindobonae: Braumüller, 679 pp.
Edney, J. M. (1950). Productivity in Clinostomum marginatum (Trematoda: Clinostomatidae). Transactions of the American Microscopical Society,69, 186–188.
Gallio, M., da Silva, A. S., Soares, J. F., da Silva, M. K., Salomão, E. L., & Monteiro, S. G. (2007). Ocorrência de metacercárias de Ithyoclinostomum dimorphum em traíras no Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil: relato de caso. Estudos de Biología,29, 337–339.
Gustinelli, A., Caffara, M., Florio, D., Otachi, E. O., Wathuta, E. M., & Fioravanti, M. L. (2010). First description of the adult stage of Clinostomum cutaneum Paperna, 1964 (Digenea: Clinostomidae) from grey herons Ardea cinerea L. and a redescription of the metacercaria from the Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus niloticus (L.) in Kenya. Systematic Parasitology,76, 39–51.
Hunter, G. W., & Hunter, W. S. (1934). The life cycle of the yellow grub of fish. Journal of Parasitology,20, 325.
Jhansilakshmibai, K., & Madhavi, R. (1997). Euclinostomum heterostomum (Rudolphi, 1809) (Trematoda): Life-cycle, growth and development of the metacercaria and adult. Systematic Parasitology,38, 51–64.
Kanev, I., Radev, V., & Fried, B. (2002). Family Clinostomidae Lühe, 1901. In: Gibson, D. I., Jones, A. & Bray, R. A. (Eds), Keys to the Trematoda, Vol. 1 (pp. 113–120). Wallingford, UK: CAB International.
Katoh, K., Misawa, K., Kuma, K., & Miyata, T. (2002). MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Research,30, 3059–3066.
Katoh, K., & Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Molecular Biology and Evolution,30, 772–780.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., & Tamura, K. (2016). MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Molecular Biology and Evolution,33, 1870–1874.
Lent, H., & Freitas, J. F. T. (1937). Pesquisas helminológicas realizadas no Estado do Pará. I. Trematoda. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz,32, 449–460.
Locke, S. A., Caffara, M., Marcogliese, D. J., & Fioravanti, M. L. (2015). A large-scale molecular survey of Clinostomum (Digenea, Clinostomidae). Zoologica Scripta,44, 203–217.
Lunaschi, L. I., & Drago, F. B. (2009). Digenean parasites of six species of birds from Formosa Province, Argentina. Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad,80, 39–46.
Machado, M. H., Pavanelli, G. C., & Takemoto, R. M. (1996). Structure and diversity of endoparasitic infracommunities and the trophic level of Pseudoplatystoma corruscans and Schizodon borelli (Osteichthyes) of the High Paraná River. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz,91, 441–448.
Minh, B. Q., Nguyen, M. A. T., & von Haeseler, A. (2013). Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Molecular Biology and Evolution,30, 1188–1195.
Nei, M., & Kumar, S. (2000). Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. New York: Oxford University Press.
Nguyen, L., Schmidt, H. A., von Haesler, A., & Minh, B. Q. (2015). IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies. Molecular Biology and Evolution,32, 268–274.
Overstreet, R. M., & Curran, S. S. (2004). Defeating diplostomoid dangers in USA catfish aquaculture. Folia Parasitologica,51, 153–165.
Pérez-Ponce de León, G., García-Varela, M., Pinacho-Pinacho, C. D., Sereno-Uribe, A., & Poulin, R. (2016). Species delimitation in trematodes using DNA sequences: Middle-American Clinostomum as a case study. Parasitology,143, 1773–1789.
Pinto, R. M., Barros, L. A., Tortelly, L., Teixeira, R. F., & Gomes, D. C. (2004). Prevalence and pathology of helminths of ciconiiform birds from the Brazilian swamplands. Journal of Helminthology, 78, 259–264.
Pritchard, M. H., & Kruse, G. O. W. (1982). The collection and preservation of animal parasites. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 141 pp.
Rambaut, A. (2014). FigTree: Tree figure drawing tool v. 1.4.2. Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh. Retrieved from http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/.
Reis, T. S. (2014). Caracterização morfológica e molecular de endoparasitoss de Hoplias affinis malabaricus Bloch, 1794 (Characiformes: Erythrinidae) provenientes do Rio Araguaia, Tocantins, Brasil. PhD dissertation, Universidade Feral do Tocantins, Brazil.
Ronquist, F., & Huelsenbeck, J. P. (2003). MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics,19, 1571–1574.
Rosser, T. G., Alberson, N. R., Woodyard, E. T., Cunningham, F. L., Pote, L. M., & Griffin, M. J. (2017). Clinostomum album n. sp. and Clinostomum marginatum (Rudolphi, 1819), parasites of the great egret Ardea alba L. from Mississippi, USA. Systematic Parasitology,94, 35–49.
Rosser, T. G., Baumgartner, W. A., Alberson, N. R., Noto, T. W., Woodyard, E. T., King, D. T., et al. (2018). Clinostomum poteae n. sp. (Digenea: Clinostomidae), in the trachea of a double-crested cormorant Phalacrocorax auritus Lesson, 1831 and molecular data linking the life-cycle stages of Clinostomum album Rosser, Alberson, Woodyard, Cunningham, Pote & Griffin, 2017 in Mississippi, USA. Systematic Parasitology,95, 543–566.
Sereno-Uribe, A. L., García-Varela, M., Pinacho-Pinacho, C. D., & Pérez-Ponce de León, G. (2018). Three new species of Clinostomum Leidy, 1856 (Trematoda) from Middle American fish-eating birds. Parasitology Research,117, 2171–2185.
Sereno-Uribe, A. L., Pinacho-Pinacho, C. D., García-Varela, M., & Pérez-Ponce de León, G. (2013). Using mitochondrial and ribosomal DNA sequences to test the taxonomic validity of Clinostomum complanatum Rudolphi, 1814 in fish-eating birds and freshwater fishes in Mexico, with the description of a new species. Parasitology Research,112, 2855–2870.
Skrjabin, K. I. (1947) Family Clinostomatidae Lühe, 1901. In Trematodes of animals and man: Basic trematodology, Volume 1, 1st edn. Moscow: Academy of Sciences of the USSR, pp. 64–97.
Szidat, L. (1969). Structure, development, and behavior of new strigeatoid metacercariae from subtropical fishes of South America. Journal of the Fisheries Research Board of Canada,26, 753–786.
Travassos, L., Freitas, J. T., & Kohn, A. (1969). Trematódeos do Brasil. Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz,67, 1–886.
Trifinopoulos, J., Nguyen, L. T., von Haesler, A., & Minh, B. Q. (2016). W-IQ-TREE: A fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Research,44(W1), W232–W235.
Weiblen, A. M., & Brandão, D. A. (1992). Levantamento parasitológico em Hoplias malabaricus Bloch (1794) (traíra) de águas da região de Santa Maria-RS. Ciência Rural,22, 203–208.
Witenberg, G. G. (1926). Versuch einer Monographie der Trematodenunterfamilie Harmostominae Braun. Zoologische Jahrbücher. Abteilung für Systematic, Ökologie und Geographie der Tiere,51, 167–254.
Woodyard, E. T., Rosser, T. G., & Rush, S. A. (2017). Alligator wrestling: Morphological, molecular, and phylogenetic data on Odhneriotrema incommodum (Leidy, 1856) (Digenea: Clinostomidae) from Alligator mississippiensis Daudin, 1801 in Mississippi, USA. Parasitology Research,116, 2981–2993.
Yamaguti, S. (1958). Systema helminthum. Volume I. The digenetic trematodes of vertebrates. New York: Interscience, 1575 pp.
Yamaguti, S. (1971). Synopsis of digenetic trematodes of vertebrates. Volume 1. Tokyo, Japan: Keigaku Publishing Co, 1074 pp.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Stephen Clements, Katie Hanson-Dorr, Lanna Durst, and Raleigh Middleton for their assistance in collecting herons for this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Mississippi State University College of Veterinary Medicine, Office of Research and Graduate Studies Internal Grants Programme and United States Department of Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable institutional, national and international guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed (IACUC QA 2853).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article was registered in the Official Register of Zoological Nomenclature (ZooBank) as CBE79808-8564-42D6-97D1-272A37ACD63D. This article was published as an Online First article on the online publication date shown on this page. The article should be cited by using the doi number. This is the version of record.
This article is part of the Topical Collection Digenea.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosser, T.G., Woodyard, E.T., Mychajlonka, M.N. et al. Ithyoclinostomum yamagutii n. sp. (Digenea: Clinostomidae) in the great blue heron Ardea herodias L. (Aves: Ardeidae) from Mississippi, USA. Syst Parasitol 97, 69–82 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-019-09892-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-019-09892-6