Abstract
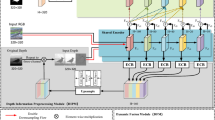
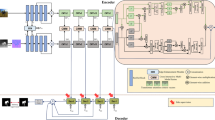
Recently, RGB-D salient object detection (SOD) has aroused widespread research interest. Existing methods tend to treat equally features at different levels and lead to inadequate interaction with cross-level features. Furthermore, many methods rely on the stacking of convolution layers or the use of dilated convolutions to increase the receptive field to extract high-level semantic features. However, these approaches may not effectively obtain context information, resulting in the loss of semantic information. In this paper, we propose a novel multi-level feature and context information fusion network (MFCINet) for RGB-D SOD, which mainly includes a detail enhancement fusion module (DEFM), semantic enhancement fusion module (SEFM), and multi-scale receptive field enhancement module (MREM). Concretely, we first design a detail enhancement fusion module (DEFM) and a semantic enhancement fusion module (SEFM) by introducing a combination of dual attention mechanisms to better fuse the rich details in low-level features and the rich semantic information in high-level features, respectively. Subsequently, a multi-scale receptive field enhancement module (MREM) is deployed to obtain the rich context semantic information in the network with the help of the parallel operation of convolution cores and skip connections, which are input into the subsequent dense connection pyramid decoder for SOD. Experimental results on five common datasets show that our model outperforms the 17 state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Tsai MF, Tseng HJ (2021) Enhancing the identification accuracy of deep learning object detection using natural language processing. J Supercomput 77:6676–6691
Zhou Y, Zheng X, Ouyang W et al (2023) A strip dilated convolutional network for semantic segmentation. Neural Process Lett 55:4439–4459
Yu Y, Li H, Shi H et al (2023) Question-guided feature pyramid network for medical visual question answering. Expert Syst Appl 214:119148
Ma F, Shou MZ, Zhu L, et al (2022) Unified transformer tracker for object tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 8781–8790
Jeevan G, Zacharias GC, Nair MS et al (2022) An empirical study of the impact of masks on face recognition. Pattern Recogn 122:108308
Wei J, Wang S, Huang Q (2020) F\(^3\)net: fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 12321–12328
Wang B, Chen Q, Zhou M, et al (2020) Progressive feature polishing network for salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 12128–12135
Kong Y, Feng M, Li X et al (2021) Spatial context-aware network for salient object detection. Pattern Recogn 114:107867
Wang G, Chen C, Fan DP, et al (2021) From semantic categories to fixations: A novel weakly-supervised visual-auditory saliency detection approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 15119–15128
Sun Y, **a C, Gao X et al (2022) Aggregating dense and attentional multi-scale feature network for salient object detection. Digit Signal Process 130:103747
Peng H, Li B, **ong W, et al (2014) RGBD salient object detection: a benchmark and algorithms. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp 92–109
Ju R, Liu Y, Ren T et al (2015) Depth-aware salient object detection using anisotropic center-surround difference. Signal Process: Image Commun 38:115–126
Feng D, Barnes N, You S, et al (2016) Local background enclosure for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2343–2350
Huang Z, Chen HX, Zhou T et al (2021) Multi-level cross-modal interaction network for RGB-D salient object detection. Neurocomputing 452:200–211
Zhang W, Ji GP, Wang Z, et al (2021) Depth quality-inspired feature manipulation for efficient RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp 731–740
**a C, Duan S, Ge B et al (2022) HDNet: multi-modality hierarchy-aware decision network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Signal Process Lett 29:2577–2581
Wang J, Chen S, Lv X et al (2022) Guided residual network for RGB-D salient object detection with efficient depth feature learning. Vis Comput 38(5):1803–1814
Liang F, Duan L, Ma W et al (2021) Context-aware network for RGB-D salient object detection. Pattern Recogn 111:107630
Wu J, Zhou W, Luo T et al (2021) Multiscale multilevel context and multimodal fusion for RGB-D salient object detection. Signal Process 178:107766
Singh SK, Srivastava R (2022) CSA-net: deep cross-complementary self attention and modality-specific preservation for saliency detection. Neural Process Lett 54(6):5587–5613
Zhai Y, Fan DP, Yang J et al (2021) Bifurcated backbone strategy for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:8727–8742
Wang X, Li S, Chen C et al (2020) Data-level recombination and lightweight fusion scheme for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:458–471
Chen S, Fu Y (2020) Progressively guided alternate refinement network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp 520–538
Piao Y, Ji W, Li J, et al (2019) Depth-induced multi-scale recurrent attention network for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 7254–7263
Zhang M, Zhang Y, Piao Y, et al (2020) Feature reintegration over differential treatment: a top-down and adaptive fusion network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp 4107–4115
Zhao Z, Huang Z, Chai X et al (2023) Depth enhanced cross-modal cascaded network for RGB-D salient object detection. Neural Process Lett 55:361–384
Borji A, Cheng MM, Hou Q et al (2019) Salient object detection: a survey. Comput Vis Media 5:117–150
Zhou L, Yang Z, Zhou Z et al (2017) Salient region detection using diffusion process on a two-layer sparse graph. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(12):5882–5894
Zhu W, Liang S, Wei Y, et al (2014) Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2814–2821
Shen X, Wu Y (2012) A unified approach to salient object detection via low rank matrix recovery. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 853–860
Xu X, Chen J, Zhang H et al (2022) SA-DPNet: structure-aware dual pyramid network for salient object detection. Pattern Recogn 127:108624
Niu Y, Geng Y, Li X, et al (2012) Leveraging stereopsis for saliency analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 454–461
Zhou W, Zhu Y, Lei J et al (2021) Ccafnet: crossflow and cross-scale adaptive fusion network for detecting salient objects in RGB-D images. IEEE Trans Multimedia 24:2192–2204
Li G, Liu Z, Ye L, et al (2020) Cross-modal weighting network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp 665–681
Zhao X, Zhang L, Pang Y, et al (2020) A single stream network for robust and real-time RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp 646–662
Luo W, Li Y, Urtasun R et al (2016) Understanding the effective receptive field in deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 29:4898–4906
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, et al (2017) Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2881–2890
Chen LC, Zhu Y, Papandreou G, et al (2018) Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp 801–818
Li C, Cong R, Piao Y, et al (2020a) RGB-D salient object detection with cross-modality modulation and selection. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, pp 225–241
Li G, Liu Z, Ling H (2020) ICNet: Information conversion network for RGB-D based salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 29:4873–4884
Ju R, Ge L, Geng W, et al (2014) Depth saliency based on anisotropic center-surround difference. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, pp 1115–1119
Cheng Y, Fu H, Wei X, et al (2014) Depth enhanced saliency detection method. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service, pp 23–27
Zhang C, Cong R, Lin Q, et al (2021) Cross-modality discrepant interaction network for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp 2094–2102
Borji A, Cheng MM, Jiang H et al (2015) Salient object detection: a benchmark. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5706–5722
Fan DP, Cheng MM, Liu Y, et al (2017) Structure-measure: a new way to evaluate foreground maps. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 4548–4557
Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F, et al (2009) Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1597–1604
Fan DP, Gong C, Cao Y, et al (2018) Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. ar**v preprint ar**v:1805.10421
Han J, Chen H, Liu N et al (2017) CNNs-based RGB-D saliency detection via cross-view transfer and multiview fusion. IEEE Trans Cybern 48(11):3171–3183
Zhao JX, Cao Y, Fan DP, et al (2019) Contrast prior and fluid pyramid integration for RGBD salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3927–3936
Chen Z, Cong R, Xu Q et al (2020) Dpanet: depth potentiality-aware gated attention network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:7012–7024
Fan DP, Lin Z, Zhang Z et al (2020) Rethinking RGB-D salient object detection: models, data sets, and large-scale benchmarks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 32(5):2075–2089
Chen C, Wei J, Peng C et al (2021) Depth-quality-aware salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:2350–2363
Zhang Z, Lin Z, Xu J et al (2021) Bilateral attention network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:1949–1961
Li C, Cong R, Kwong S et al (2020) ASIF-net: attention steered interweave fusion network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans Cybern 51(1):88–100
Zhu X, Li Y, Fu H et al (2021) RGB-D salient object detection via cross-modal joint feature extraction and low-bound fusion loss. Neurocomputing 453:623–635
Wang F, Pan J, Xu S et al (2022) Learning discriminative cross-modality features for RGB-D saliency detection. IEEE Trans Image Process 31:1285–1297
Zhang M, Ren W, Piao Y, et al (2020) Select, supplement and focus for RGB-D saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3472–3481
Sun P, Zhang W, Wang H, et al (2021) Deep RGB-D saliency detection with depth-sensitive attention and automatic multi-modal fusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1407–1417
Zhao X, Pang Y, Zhang L, et al (2022) Self-supervised pretraining for RGB-D salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 3463–3471
Liu N, Zhang N, Wan K, et al (2021) Visual saliency transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 4722–4732
Pang Y, Zhao X, Zhang L, et al (2021) Transcmd: cross-modal decoder equipped with transformer for RGB-D salient object detection. ar**v preprint ar**v:2112.02363
Liu Z, Wang Y, Tu Z, et al (2021) Tritransnet: RGB-D salient object detection with a triplet transformer embedding network. In: Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, pp 4481–4490
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62102003), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (2108085QF258), Anhui Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022B623), the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province (GXXT-2021-006, GXXT-2022-038), Central guiding local technology development special funds (202107d06020001), the Institute of Energy, Hefei Comprehensive National Science Center under (21KZS217), and University-Level General Projects of Anhui University of Science and Technology (xjyb2020-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C. **a and D. Chen developed the overall research idea and wrote the main manuscript text, X. Gao collected the data and designed the experiments, X. Fang and B. Ge performed data analysis, Y. Zhang and Kuan-Ching Li edited the final version for clarity and accuracy, Ke Yang interpreted the data and provided critical insights into the findings.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
**a, C., Chen, D., Gao, X. et al. MFCINet: multi-level feature and context information fusion network for RGB-D salient object detection. J Supercomput 80, 2487–2513 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-023-05561-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-023-05561-0