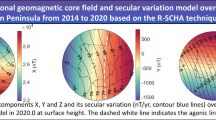
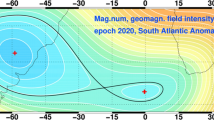
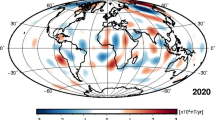
Abstract
We analyse models describing time changes of the Earth’s core magnetic field (secular variation) covering the historical period (several centuries) and the more recent satellite era (previous decade), and we illustrate how both the information contained in the data and the a priori information (regularisation) affect the result of the ill-posed geomagnetic inverse problem. We show how data quality, frequency and selection procedures govern part of the temporal changes in the secular variation norms and spectra, which are sometimes difficult to dissociate from true changes of the core state. We highlight the difficulty of resolving the time variability of the high degree secular variation coefficients (i.e. the secular acceleration), arising for instance from the challenge to properly separate sources of internal and of external origin. In addition, the regularisation process may also result in artificial changes in the model norms and spectra. Model users should keep in mind that such features can be mis-interpreted as the signature of physical mechanisms (e.g. diffusion). Finally, we present perspectives concerning core field modelling: imposing dynamical constraints (e.g. by means of data assimilation) reduces the non-uniqueness of the geomagnetic inverse problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G.E. Backus, Kinematics of geomagnetic secular variation in a perfectly conducting core. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 263, 239–266 (1968)
G.E. Backus, Non-uniqueness of the external geomagnetic field determined by surface intensity measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 75, 6337–6341 (1970)
G.E. Backus, Bayesian inference in geomagnetism. Geophys. J. 92, 125–142 (1988)
C.D. Beggan, K.A. Whaler, S. Macmillan, Biased residuals of core flow models from satellite-derived “virtual observatories”. Geophys. J. Int. 177(2), 463–475 (2009)
J. Bloxham, Simultaneous stochastic inversion for geomagnetic main field and secular variations I: a large scale inverse problem. J. Geophys. Res. 92, 11597–11608 (1987)
J. Bloxham, D. Gubbins, Geomagnetic field analysis—IV. Testing the frozen-flux hypothesis. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 84, 139–152 (1986)
J. Bloxham, A. Jackson, Simultaneous stochastic inversion for geomagnetic main field and secular variation II: 1820–1980. J. Geophys. Res. 94, 15753–15769 (1989)
J. Bloxham, A. Jackson, Time-dependent map** of the magnetic field at the core–mantle boundary. J. Geophys. Res. 97, 19537–19563 (1992)
J. Bloxham, D. Gubbins, A. Jackson, Geomagnetic secular variation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 329, 415–502 (1989)
J.C. Cain, W.E. Daniels, S.J. Hendricks, D.C. Jensen, An evaluation of the main geomagnetic field, 1940–1962. J. Geophys. Res. 70, 3647–3674 (1965)
J.C. Cain, R.A. Langel, S.J. Hendricks, First magnetic field results from the ogo-2 satellite, Technical report, Goddard Space Flight Center NASA (1966)
J.C. Cain, S.J. Hendricks, R.A. Langel, W.V. Hudson, A proposed model for the International Geomagnetic Reference Field—1965. J. Geomag. Geoelectr. 19, 335–355 (1967)
E. Canet, A. Fournier, D. Jault, Forward and adjoint quasi-geostrophic models of the geomagnetic secular variation. J. Geophys. Res. 114, B11101 (2009). doi:10.1029/2008JB006189
A. Chulliat, K. Telali, World monthly means database project. Publ. Inst. Geophys. Pol. Acad. Sci. C 99(398), 537–552 (2007)
C.G. Constable, R.L. Parker, P.N. Stark, Geomagnetic field models incorporating frozen-flux constraints. Geophys. J. Int. 113, 419–433 (1993)
C. De Boor, A Practical Guide to Splines. Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol. 27 (Springer, Berlin, 2001)
C.C. Finlay, Hydromagnetic waves in Earth’s core and their influence on geomagnetic secular variations, PhD thesis, University of Leeds, UK, 2005
C.C. Finlay, Historical variations of the geomagnetic axial dipole. Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 70 (2008)
C.C. Finlay, A. Jackson, Equatorially dominated magnetic field change at the surface of Earth’s core. Science 300, 2084–2086 (2003)
A. Fournier, C. Eymin, T. Alboussière, A case for variational geomagnetic data assimilation: insights from a one-dimensional, nonlinear and sparsely observed MHD system. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 14, 1–18 (2007)
N. Gillet, A. Jackson, C.C. Finlay, Maximum entropy regularisation of time-dependent geomagnetic field models. Geophys. J. Int. 171, 1005–1016 (2007)
N. Gillet, M.A. Pais, D. Jault, Ensemble inversion of time-dependent core flow models. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 10, Q06004 (2009). doi:10.1029/2008GC002290
D. Gubbins, Can the Earth’s magnetic field be sustained by core oscillation? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2, 409–412 (1975)
D. Gubbins, Dynamics of the secular variation. Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 68, 170–182 (1991)
D. Gubbins, A formalism for the inversion of geomagnetic data for core motions with diffusion. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 98, 193–206 (1996)
D. Gubbins, Geomagnetic constraint on stratification at the top of the core. Earth Planets Space 59, 661–664 (2007)
D. Gubbins, N. Roberts, Use of the frozen flux approximation in the interpretation of archeomagnetic and paleomagnetic data. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 73, 675–687 (1983)
D. Gubbins, A.L. Jones, C. Finlay, Fall in earth’s magnetic field is erratic. Science 312, 900–903 (2006)
R. Holme, Modelling of attitude error in vector magnetic data: application to ørsted data. Earth Planets Space 52, 1187–1197 (2000)
R. Holme, N. Olsen, Core surface flow modeling from high-resolution secular variation. Geophys. J. Int. 166, 518–528 (2006)
G. Hulot, N. Olsen, T.J. Sabaka, The present field, in Treatise in Geophysics, Geomagnetism, vol. 5, ed. by M. Kono, G. Schubert (2007), pp. 33–75
A. Jackson, Kelvin’s theorem applied to the Earth’s core. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 452, 2195–2201 (1996)
A. Jackson, Intense equatorial flux spots on the surface of the Earth’s core. Nature 424, 760–763 (2003)
A. Jackson, C.C. Finlay, Geomagnetic secular variation and applications to the core, in Treatise in Geophysics, Geomagnetism, vol. 5, ed. by M. Kono, G. Schubert (2007), pp. 147–193
A. Jackson, A.R.T. Jonkers, M.R. Walker, Four centuries of geomagnetic secular variation from historical records. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 358, 957–990 (2000)
A. Jackson, C.G. Constable, M.R. Walker, R.L. Parker, Models of Earth’s main magnetic field incorporating flux and radial vorticity constraints. Geophys. J. Int. 171, 133–144 (2007a)
A. Jackson, C.G. Constable, N. Gillet, Maximum entropy regularisation of the geomagnetic core field inverse problem. Geophys. J. Int. 171, 995–1004 (2007b)
A.R.T. Jonkers, A. Jackson, A. Murray, Four centuries of geomagnetic data from historical records. Rev. Geophys. 41 (2003). doi:10.1029/2002RG000115
E. Kalnay, Atmospheric Modeling, Data Assimilation and Predictability (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2003)
M. Korte, C.G. Constable, Continuous geomagnetic models for the past 7 millennia II: CALS7K. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 6, 2–16 (2005). doi:10.1029/2004GC000801
M. Korte, F. Donadini, C.G. Constable, The geomagnetic field for 0–3 ka, Part II: a new series of time-varying global models. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 10, 06008 (2009). doi:10.1029/2008GC002297
W. Kuang, A. Tangborn, W. Jiang, D. Liu, Z. Sun, J. Bloxham, Z. Wei, MoSST–DAS: the first generation geomagnetic data assimilation framework. Commun. Comput. Phys. 3, 85–108 (2008)
R.A. Langel, The main field, in Geomagnetism, vol. I, ed. by J.A. Jacobs (Academic Press, London, 1987), pp. 249–512
R.A. Langel, R.H. Estes, Large-scale, near-Earth magnetic fields from external sources and the corresponding induced internal field. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 2487–2494 (1985)
R.A. Langel, R.H. Estes, G.D. Mead, Some new methods in geomagnetic field modeling applied to the 1960–1980 epoch. J. Geomag. Geoelectr. 34, 327–349 (1982)
V. Lesur, I. Wardinski, The second version of the GFZ reference internal magnetic field model: GRIMM-2, in IAGA meeting, Sopron, Hungary (2009)
V. Lesur, S. Macmillan, A. Thomson, The BGS magnetic field candidate models for the 10th generation IGRF. Earth Planets Space 57, 1157–1163 (2005)
V. Lesur, I. Wardinski, M. Rother, M. Mandea, GRIMM: the GFZ reference internal magnetic model based on vector satellite and observatory data. Geophys. J. Int. 173, 382–394 (2008)
V. Lesur, I. Wardinski, S. Asari, B. Minchev, M. Mandea, Modelling the Earth’s core magnetic field under flow constraints. Earth Planets Space (2009, submitted)
D. Liu, A. Tangborn, W. Kuang, Observing system simulation experiments in geomagnetic data assimilation. J. Geophys. Res. 112, 08103 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006JB004691
M. Mandea, N. Olsen, A new approach to directly determine the secular variation from magnetic satellite observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, 15306 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006GL026616
S. Maus, CHAMP magnetic mission, in Encyclopedia of Geomagnetism and Paleomagnetism, ed. by D. Gubbins, E. Herrero-Bervera (Springer, Heidelberg, 2007)
S. Maus, S. Macmillan, F. Lowes, T. Bondar, Evaluation of candidate geomagnetic field models for the 10th generation of IGRF. Earth Planets Space 57, 1173–1181 (2005)
S. Maus, S. McLean, D. Dater, H. Lühr, M. Rother, W. Mai, S. Choi, NGDC/GFZ candidate models for the 10th generation International Geomagnetic Reference Field. Earth Planets Space 57, 1151–1156 (2005)
S. Maus, M. Rother, C. Stolle, W. Mai, S. Choi, H. Luhr, D. Cooke, C. Roth, Third generation of the Potsdam magnetic model of the Earth (pomme). Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 7 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006GC001269
S. Maus, F. Yin, H. Lühr, C. Manoj, M. Rother, J. Rauberg, I. Michaelis, C. Stolle, R.D. Müller, Resolution of direction of oceanic magnetic lineations by the sixth-generation lithospheric magnetic field model from champ satellite magnetic measurements. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 9, Q07021 (2007). doi:10.10292008001949
S. McLean, S. Macmillan, S. Maus, V. Lesur, A. Thomson, D. Dater, The US/UK World Magnetic Model for 2005–2010, Technical report, NOAA (2004). NESDIS/NGDC-1
M.S. O’Brien, C.G. Constable, R.L. Parker, Frozen flux modeling for epochs 1915 and 1980. Geophys. J. Int. 128, 434–450 (1997)
N. Olsen, A model of the geomagnetic field and its secular variation for epoch 2000 estimated from Ørsted data. Geophys. J. Int. 149, 454–462 (2002)
N. Olsen, Ørsted, in Encyclopedia of Geomagnetism and Paleomagnetism, ed. by D. Gubbins, E. Herrero-Bervera (Springer, Heidelberg, 2007)
N. Olsen, M. Mandea, Investigation of a secular variation impulse using satellite data: the 2003 geomagnetic jerk. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 255, 94–105 (2007)
N. Olsen, M. Mandea, Rapidly changing flows in the Earth’s core. Nature Geosci. 1, 390–394 (2008)
N. Olsen, T. Sabaka, F. Lowes, New parameterisation of external and induced fields in geomagnetic field modeling, and a candidate model for IGRF 2005. Earth Planets Space 57, 1141–1149 (2005)
N. Olsen, H. Luhr, T.J. Sabaka, M. Mandea, CHAOS—a model of Earth’s magnetic field derived from CHAMP, Oersted, and SAC-C magnetic satellite data. Geophys. J. Int. 166, 67–75 (2006)
N. Olsen, M. Mandea, T.J. Sabaka, L. Tøffner-Clausen, CHAOS-2—a geomagnetic field model derived from one decade of continuous satellite data. Geophys. J. Int. 179, 1477–1487 (2009)
P.H. Roberts, Yu. Russel, On the 60-year signal from the core. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 101(1), 11–35 (2007)
T.J. Sabaka, R.T. Baldwin, Modelling the Sq magnetic field from POGO and Magsat satellite and contemporaneous hourly observatory data (HSTX/G&G-9302, Hughes STX Corp., 7701 Greenbelt Road, Greenbelt, MD, 1993)
T.J. Sabaka, N. Olsen, R.A. Langel, A comprehensive model of the quiet-time, near-Earth magnetic field: phase 3. Geophys. J. Int. 151, 32–68 (2002)
T.J. Sabaka, N. Olsen, M.E. Purucker, Extending comprehensive models of the Earth’s magnetic field with Oersted and CHAMP data. Geophys. J. Int. 159, 521–547 (2004)
Z. Sun, A. Tangborn, W. Kuang, Data assimilation in a sparsely observed one-dimensional modeled MHD system. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 14, 181–192 (2007)
A.W. Thomson, V. Lesur, An improved geomagnetic data selection algorithm for global geomagnetic field modeling. Geophys. J. Int. 169, 951–963 (2007)
A.W. Thomson, B. Hamilton, S. Macmillan, S. Reay, A global magnetic field model derived from weighted satellite data. Geophys. J. Int. (2009, under review)
G.M. Turner, J.L. Rasson, C.V. Reeves, Observation and measurement techniques, in Treatise in Geophysics, Geomagnetism, vol. 5, ed. by M. Kono, G. Schubert (2007), pp. 93–146
R. Waddington, D. Gubbins, N. Barber, Geomagnetic field analysis—V. Determining steady core surface flows directly from geomagnetic observations. Geophys. J. Int. 122, 326–350 (1995)
I. Wardinski, R. Holme, A time-dependent model of the Earth’s magnetic field and its secular variation for the period 1980–2000. J. Geophys. Res. 111 (2006). doi:10.1029/2006JB004401
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gillet, N., Lesur, V. & Olsen, N. Geomagnetic Core Field Secular Variation Models. Space Sci Rev 155, 129–145 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-009-9586-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-009-9586-6