Abstract
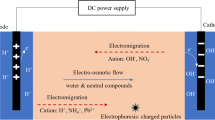
Electrokinetic process is a potential in situ soil remediation process which transports the contaminants via electromigration and electroosmosis. For organic compounds contaminated soil, Fenton’s reagent is utilized as a flushing agent in electrokinetic process (Electrokinetic-Fenton) so that removal of organic contaminants could be achieved by in situ oxidation/destruction. However, this process is not applied widely in industries as the stability issue for Fenton’s reagent is the main drawback. The aim of this mini review is to summarize the developments of Electrokinetic-Fenton process on enhancing the stability of Fenton’s reagent and process efficiency in past decades. Generally, the enhancements are conducted via four paths: (1) chemical stabilization to delay H2O2 decomposition, (2) increase of oxidant availability by monitoring injection method for Fenton’s reagent, (3) electrodes operation and iron catalysts and (4) operating conditions such as voltage gradient, electrolytes and H2O2 concentration. In addition, the types of soils and contaminants are also showing significant effect as the soil with low acid buffering capacity, adequate iron concentration, low organic matter content and low aromatic ring organic contaminants generally gives better efficiency.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaron JJ, Oturan MA (2001) New photochemical and electrochemical methods for the degradation of pesticides in aqueous media. Environmental applications. Turk J Chem 25:509–520
Acar YB, Alshawabkeh AN (1993) Principles of electrokinetic remediation. Environ Sci Technol 27(13):2638–2647
Acar YB, Gale RJ, Alshawabkeh AN, Marks RE, Puppala S, Bricka M, Parker R (1995) Electrokinetic remediation: basics and technology status. J Hazard Mater 40(2):117–137
Alcántara T, Pazos M, Gouveia S, Cameselle C, Sanromán MA, Aaron JJ (2008) Remediation of phenanthrene from contaminated kaolinite by electroremediation-Fenton technology. J Environ Sci Health A 43(8):901–906
Anotai J, Su C-C, Tsai Y-C, Lu M-C (2010) Effect of hydrogen peroxide on aniline oxidation by electro-Fenton and fluidized-bed Fenton processes. J Hazard Mater 183(1–3):888–893
Babuponnusami A, Muthukumar K (2012) Advanced oxidation of phenol: a comparison between Fenton, electro-Fenton, sono-electro-Fenton and photo-electro-Fenton processes. Chem Eng J 183:1–9
Baek K, Kim D-H, Park S-W, Ryu B-G, Bajargal T, Yang J-S (2009) Electrolyte conditioning-enhanced electrokinetic remediation of arsenic-contaminated mine tailing. J Hazard Mater 161(1):457–462
Chung HI, Kang BH (1999) Lead removal from contaminated marine clay by electrokinetic soil decontamination. Eng Geol 53(2):139–150
Doering F, Doering N, Iovenitti JL, Hill DG (2001) Electrochemical remediation technologies for soil, sediment and ground water. In: Paper presented at the innovative strategies for the remediation of chlorinated solvents and DNAPLs in the subsurface, San Diego, CA
Flotron V, Delteil C, Padellec Y, Camel V (2005) Removal of sorbed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from soil, sludge and sediment samples using the Fenton’s reagent process. Chemosphere 59(10):1427–1437
Garrido-Ramírez EG, Theng BKG, Mora ML (2010) Clays and oxide minerals as catalysts and nanocatalysts in Fenton-like reactions—a review. Appl Clay Sci 47(3–4):182–192
Gioannis GD, Muntoni A, Polettini A, Pomi R (2008) Enhanced electrokinetic treatment of different marine sediments contaminated by heavy metals. J Environ Sci Health A 43(8):852
Isosaari P, Piskonen R, Ojala P, Voipio S, Eilola K, Lehmus E, Itävaara M (2007) Integration of electrokinetics and chemical oxidation for the remediation of creosote-contaminated clay. J Hazard Mater 144(1–2):538–548
Khamaruddin PF, Bustam MA, Omar AA (2011) Using Fenton’s reagents for the degradation of diisopropanolamine: effect of temperature and pH. In: Paper presented at the international conference on environment and industrial innovation, Singapore
Kim J, Lee K (1999) Effect of electric field directions on surfactant enhanced electrokinetic remediation of diesel-contaminated sand column. J Environ Sci Health A 34(4):863–877
Kim S-S, Kim J-H, Han S-J (2005) Application of the electrokinetic-Fenton process for the remediation of kaolinite contaminated with phenanthrene. J Hazard Mater 118(1–3):121–131
Kim JH, Han SJ, Kim SS, Yang JW (2006) Effect of soil chemical properties on the remediation of phenanthrene-contaminated soil by electrokinetic-Fenton process. Chemosphere 63(10):1667–1676
Kim JH, Kim SS, Yang JW (2007) Role of stabilizers for treatment of clayey soil contaminated with phenanthrene through electrokinetic-Fenton process—some experimental evidences. Electrochim Acta 53(4):1663–1670
Kim JH, Kim JY, Kim SS (2009) Effect of H2SO4 and HCl in the anode purging solution for the electrokinetic-Fenton remediation of soil contaminated with phenanthrene. J Environ Sci Health A 44(11):1111–1119
Kim B-K, Baek K, Ko S-H, Yang J-W (2011a) Research and field experiences on electrokinetic remediation in South Korea. Sep Purif Technol 79(2):116–123
Kim K-J, Kim D-H, Yoo J-C, Baek K (2011b) Electrokinetic extraction of heavy metals from dredged marine sediment. Sep Purif Technol 79(2):164–169
Korolev VA (2006) Electrokinetic remediation of a contaminated land in cities. The Geological Society of London. http://iaeg2006.geolsoc.org.uk/cd/PAPERS/IAEG_134.PDF. Accessed 14 Jan 2012
Lee Y-J, Han H, Kim S-H, Yang J-W, Aaron JJ (2009) Combination of electrokinetic separation and electrochemical oxidation for acid dye removal from soil. Sep Sci Technol 44(10):2455–2469
Li T, Yuan S, Wan J, Lu X (2010) Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin enhanced electrokinetic remediation of sediment contaminated with HCB and heavy metals. J Hazard Mater 176(1–3):306–312
Lima AT, Kleingeld PJ, Heister K, Loch JPG (2011) Removal of PAHs from contaminated clayey soil by means of electro-osmosis. Sep Purif Technol 79(2):221–229
Ma JW, Wang FY, Huang ZH, Wang H (2010) Simultaneous removal of 2,4-dichlorophenol and Cd from soils by electrokinetic remediation combined with activated bamboo charcoal. J Hazard Mater 176(1–3):715–720
Oonnittan A, Shrestha RA, Sillanpää M (2008) Remediation of hexachlorobenzene in soil by enhanced electrokinetic fenton process. J Environ Sci Health A 43(8):894–900
Oonnittan A, Shrestha RA, Sillanpää M (2009) Effect of cyclodextrin on the remediation of hexachlorobenzene in soil by electrokinetic Fenton process. Sep Purif Technol 64(3):314–320
Oonnittan A, Isosaari P, Sillanpää M (2010) Oxidant availability in soil and its effect on HCB removal during electrokinetic Fenton process. Sep Purif Technol 76(2):146–150
Park J-Y, Kim J-H (2011) Switching effects of electrode polarity and introduction direction of reagents in electrokinetic-Fenton process with anionic surfactant for remediating iron-rich soil contaminated with phenanthrene. Electrochim Acta 56(24):8094–8100
Park J-Y, Kim S-J, Lee Y-J, Baek K, Yang J-W (2005) EK-Fenton process for removal of phenanthrene in a two-dimensional soil system. Eng Geol 77(3–4):217–224
Park J-Y, Lee H-H, Kim S-J, Lee Y-J, Yang J-W (2007) Surfactant-enhanced electrokinetic removal of phenanthrene from kaolinite. J Hazard Mater 140(1–2):230–236
Park S-W, Lee J-Y, Yang J-S, Kim K-J, Baek K (2009) Electrokinetic remediation of contaminated soil with waste-lubricant oils and zinc. J Hazard Mater 169(1–3):1168–1172
Pham TD, Shrestha RA, Sillanpää M (2010) Removal of hexachlorobenzene and phenanthrene from clayey soil by surfactant- and ultrasound-assisted electrokinetics. J Environ Eng 136(7):739–742
Rao NN, Khare P, Kaul SN (2006) Fenton and electro-Fenton methods for oxidation of H-acid and reactive black 5. J Environ Eng 132(3):367–376
Reddy KR, Karri RM (2006) Effect of voltage gradient on integrated electrochemical remediation of contaminant mixtures. Land Contam Reclam 14(3):685–698
Reddy KR, Saichek RE (2003) Effect of soil type on electrokinetic removal of phenanthrene using surfactants and cosolvents. J Environ Eng 129(4):336–346
Reddy KR, Ala PR, Sharma S, Kumar SN (2006) Enhanced electrokinetic remediation of contaminated manufactured gas plant soil. Eng Geol 85(1–2):132–146
Reddy KR, Cameselle C, Ala P (2010) Integrated electrokinetic-soil flushing to remove mixed organic and metal contaminants. J Appl Electrochem 40(6):1269–1279
Shenbagavalli S, Mahimairaja S (2010) Electro kinetic remediation of contaminated habitats. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 4(13):930–935
Tsai T-T, Sah J, Kao C-M (2010) Application of iron electrode corrosion enhanced electrokinetic-Fenton oxidation to remediate diesel contaminated soils: a laboratory feasibility study. J Hydrol 380(1–2):4–13
Valderrama C, Alessandri R, Aunola T, Cortina JL, Gamisans X, Tuhkanen T (2009) Oxidation by Fenton’s reagent combined with biological treatment applied to a creosote-comtaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 166(2–3):594–602
Watts RJ, Haller DR, Jones AP, Teel AL (2000) A foundation for the risk-based treatment of gasoline-contaminated soils using modified Fenton’s reactions. J Hazard Mater 76(1):73–89
Yang GCC, Liu C-Y (2001) Remediation of TCE contaminated soils by in situ EK-Fenton process. J Hazard Mater 85(3):317–331
Yang GCC, Long Y-W (1999) Removal and degradation of phenol in a saturated flow by in situ electrokinetic remediation and Fenton-like process. J Hazard Mater 69(3):259–271
Yuan S, Tian M, Lu X (2006) Electrokinetic movement of hexachlorobenzene in clayed soils enhanced by Tween 80 and β-cyclodextrin. J Hazard Mater 137(2):1218–1225
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by Grant UMQUB6A-2011 and PPP Grant PG143-2012B, University of Malaya.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, Y.S., Sen Gupta, B. & Hashim, M.A. Stability and performance enhancements of Electrokinetic-Fenton soil remediation. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 13, 251–263 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-014-9335-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-014-9335-5